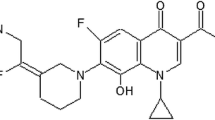
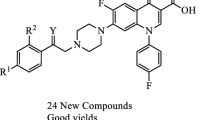
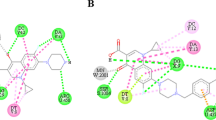
Abstract
Fluoroquinolones such as pefloxacin are antimicrobial agents with an excellent activity against various bacteria. The activity of fluoroquinolones depends on two factors: their uptake by the cell and their specific inhibition of the activity of DNA gyrase, an enzyme involved in the supercoiling of DNA. Some cations such as Mg2+ and Ca2+ cause maladsorption of most fluoroquinolones, what may result in therapeutic failure. Furthermore, conflicting reports have been accumulated in the literature on the mechanism of action of the quinolone, which implicates also magnesium.1-3
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. L. Shen et al. A. G. Pernet, Biochemistry.28, 3886–3894 (1989)
B. Lhorente, F. Lecler, R. Cedergren, Bioorg. Med Chem. 4, 61–71 (1996).
G. Palu et al M. Palumbo, Proc. Nad. Acad. Sci. USA, 89, 9671–9675 (1992).
S. Lecomte, M. T. Chenon, Int. J. Pharm., 139, 105–112 (1996).
S. Lecomte, M. H. Baron, Biospectroscopy, 3, 31–45 (1997).
J. S. Chapman, N. H. Georgopapadakou, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, 32, 438–442 (1988).
Y. X. Furet, J. Deshusses, J. C. Pechere, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, 36, 2506–2511 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1997 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Lecomte, S., Chenon, M.T., Baron, M.H. (1997). Mechanism of Activity of Fluoroquinolones. In: Carmona, P., Navarro, R., Hernanz, A. (eds) Spectroscopy of Biological Molecules: Modern Trends. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-5622-6_185
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-5622-6_185
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-6369-2
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-5622-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive