Abstract
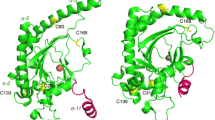
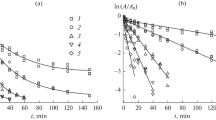
During the catalytic reaction, ACC oxidase (ACO) self inactivates and displays a very short half-life [1]. Functional alterations occurring through metal-catalysed oxidations are considered to be responsible for this inactivation [2]. Hypothesising that chemical modifications could yield changes on the protein surface charge, we have used isoelectric focusing to study the inactivation process. This work has been performed with the apple fruit native protein and with recombinant ACO produced in S. cerevisiae. A more precise investigation has been undertaken using a pure recombinant ACO overproduced in E. coli. Peptides generated from Lys C endoprotease digestion of the active and inactive protein have been separated by HPLC and their molecular mass determined by MALDI-TOF analysis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith, J.J., Zhang, Z.H., Schofield, C.J., John, P. and Baldwin, J.E. (1994) Inactivation of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) oxidase, J. Exp. Bot. 45, 1521–1527.
Barlow, J.N., Zhang, Z., John, P., Baldwin, J.E. and Schofield, C.J. (1997) Inactivation of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) oxidase involves oxidative modifications, Biochemistry 36, 3563–3569.
Lay, V.J., Prescott, A.G., Thomas, P.G. and John, P. (1996) Heterologous expression and sitedirected mutagenesis of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase from kiwi fruit, Eur. J. Biochem. 242, 228–234.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1999 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ramassamy, S., Bidonde, S., Stella, L., Pech, J.C., Latche, A. (1999). Structural Modifications of ACC Oxidase during Catalytic Inactivation. In: Kanellis, A.K., Chang, C., Klee, H., Bleecker, A.B., Pech, J.C., Grierson, D. (eds) Biology and Biotechnology of the Plant Hormone Ethylene II. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-4453-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-4453-7_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-5910-7
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-4453-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive