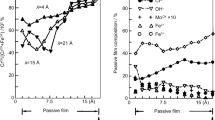
Abstract
For industrial steels, pitting occurs on manganese sulphides, when they are present in the steel. Adding a slight amount of titanium as alloying element prevents the MnS formation, since titanium is a stronger sulphide former than manganese. Titanium sulphides are more stable in chloride-containing aqueous solutions than MnS. For titanium bearing steels, pits initiate either on titanium sulphides (in acidic concentrated chloride media), on other metallurgical defects, or are the result of some local passive film instabilities, irrespectively of the presence or not of non metallic inclusions. One shows that the pitting potential-pH dependence is the signature of the actual pitting sites: as far as sulphides (MnS or Ti2S) act as pitting sites, a strong decrease in pitting potential is observed when the pH becomes smaller than a critical value corresponding to the formation of some sulphur-containing species in the aqueous solution, due to the dissolution of the sulphides inclusions. Otherwise, no pitting potential/pH-dependence is found. When polarising a sample below the pitting potential, some pre-pitting events are observed, resulting in anodic current transients revealing the initiation then the repassivation of unstable pits. The form of these transients (slow anodic current increase followed by a sharp decrease, or sharp current increase followed by a smooth decay) is the signature of the type of pitting site (MnS or other). Moreover, for MnS-containing steel, a strong pre-pitting noise is observed, exhibiting a pH-dependence similar to the pitting potentials one. The intensity of the pre-pitting noise or, when only isolated events are observed, the occurrence frequency of the prepitting events, decreases when the polarisation time increases. Furthermore, potentiostatic aging at constant potential (lower than the pitting potential) decreases the further probability for the occurrence of stable pits, indicating a beneficial effect on the pitting resistance. This effect is believed to be due to the passive film reinforcement and not to a decrease in the available pitting sites density.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Szklarska-Smialowska, Pitting Corrosion of metals, NACE , (1986), Houston, Texas, USA
J. L Crolet et al., Mem. Sci. Rev. Met. (France), Nov. 1977, 647.
A. Szummer and M. Janik-Czachor, Br. Corr. J., Vol. 9, (1974), 216.
B. Baroux, Corr. Sci., Vol. 28, (1988), 969.
G.S. Eklund, J. Electrochem. Soc., Vol. 121, (1974), 467.
J.P. Petit, L. Antoni, B.Baroux: Proceedings of the European symposium on the modification of passive film, Paris, 1993, in press.
D. Lizzarazu: Diplome d’Etudes Approfondies d’Electrochimie, 1992, Institut National Polytechnique de Grenoble.
J. Stewart and D. E. Williams: Advances in Localized Corrosion, NACE, Orlando, June 1987. Proceedings, p131.
G. Gabrielli, F. Huet, M. Keddam, R. Oltra, Corrosion, Vol. 46, (1990), 266.
A. M. Riley, D. B. Wells and D. E. Williams, Corr. Sci., Vol. 32, (1991), 1307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1994 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Baroux, B., Gorse, D. (1994). The Respective Effects of Passive Films and Non Metallic Inclusions on the Pitting Resistance of Stainless Steels — Consequences on the Pre-Pitting Noise and the Anodic Current Transients. In: Trethewey, K.R., Roberge, P.R. (eds) Modelling Aqueous Corrosion. NATO ASI Series, vol 266. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-1176-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-1176-8_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-4513-1
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-1176-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive