Abstract
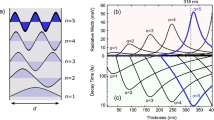
Time resolved photoluminescence in semiconductor microcavities in the strong coupling regime both for non-resonant and resonant excitation is modeled by considering scattering of exciton polaritons by acoustic phonons. Rise time and decay time of the luminescence signal are studied as a function of temperature. The polariton bottleneck effect is put into evidence in model structures which are free of leaky modes. In realistic strucures these modes are instead expected to play a dominant role in the relaxation of non-resonant photoluminescence.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
See e.g. Confined Electrons and Photons: new Physics and Devices i edited by E. Burstein and C. Weisbuch (Plenum, 1994).
Yokoyama, H. et al. (1990), Enhanced Sonpaneous Emission from GaAs Quantum Wells in monolithic microcavities, Appi. Phys. Lett.57, pp. 2814 - 2816.
Weisbuch, C. et al. (1992), Observation of the coupled exciton photon mode splitting in a semiconductor microcavity, Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, pp. 3314-3317;
T. A. Fisher et al., (1995), Electric Field and Temperature tuning of exciton photon coupling in quantum microcavity structures, Phys. Rev. B 51, pp. 2600;
Houdré, R. et al., (1994), Measurement of cavity polariton dispersion curve from anglew resolved photlumi- nescence experiments, Phys. Rev. Lett.73, pp. 2043 - 2046.
see Abram, I. in this volume; see also Hegarty, J. ibid.
McLeod, H. A. Thin-Film Optical Filters, second ed. (Hilger, 1986 ).
Andreani, L. C., Ph. D. Thesis, Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa 1989, unpublished.
Savona, V. and Tassone, F., (1995), Exact quantum calculation of polariton dispersion in semiconductor microcavities, Solid State Comm. 95, pp. 673 - 678
Wolfe, C. M. et al., (1970), Electron Mobilty in High Purity GaAs, Journ. Appi Phys. 41, pp. 3088-3091;
Lee, S. et al., (1985), Theoretical investigation of the Passive Dependences of Energy Gaps in Semiconductors, Phys. Rev. B32, pp. 1152 - 1155.
Piermarocchi, C. et al., (1995), Effect of the scattering by phonons on the temperature dependence of the free QW exciton radiative lifetimes, in “Optics of Confined Excitons and Reduced Dimensional Systems”, Cortona, Italy, to be published in Nuovo Ctm. D.
Toyozawa, Y. (1959), On the dynamical behavior of an exciton,Progr. Theor. Phys. Suppl 12, pp. 111-139;
Sumi, H., (1975), On the exciton luminescence at low temperatures: importance of the polariton viewpoint, J. Phys, Soc. Jpn. 21, pp. 1936-1945;
Weisbuch, C. and Ulbrich, R. (1979) Spatial and spectral features of polariton fluorescence, J. Lum n 18/19, pp. 27-29;
Rappel, W. J. et al., (1988), Exciton-polariton picture of the free-exciton lifetime in GaAs,, Phys. Rev. B38, pp. 7874 - 7876.
Feldmann, J. et al., (1987), Linewidth Dependence of Radiative Exciton Lifetimes in Quantum Wells, Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, pp. 2337-2340;
Martinez-Pastor, J. et al., (1993), Temperature Dependence of Exciton Lifetimes in GaAs/AlGaAs Single Quantum Wells, Phys. Rev. B 47, pp. 10456-10460;
Damen, T. C. et al., (1990), Dynamics of Exciton Formation and Relaxation in GaAs Quantum Wells, Phys. Rev. B42, pp. 7434 - 7438.
Andreani, L. C. et al., (1991), Free Exciton Radiative Lifetimes in Quantum Wells, Solid State Commun. 77, pp. 641 - 644.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1996 Kluwer Academic Publishers
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Tassone, F., Piermarocchi, C., Savona, V., Quattropani, A., Schwendimann, P. (1996). Time Resolved Photoluminescence From A Semiconductor Microcavity. In: Rarity, J., Weisbuch, C. (eds) Microcavities and Photonic Bandgaps: Physics and Applications. NATO ASI Series, vol 324. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-0313-5_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-0313-5_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-6626-6
Online ISBN: 978-94-009-0313-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive