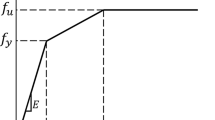
In this article, we utilized the lumped damage mechanics method to implement the damage analysis to the 3D frame structure under impulsive load. First, take the damage parameters as the interior variable of the system, and based on the finite unit, combine continuum mechanics, fracture mechanics and plastic hinge to analyze the mechanical behaviors of the structure, and finally implement numerical simulation analysis to the frame structure with two layers, and compare the result with the computation result of ABAQUS to validate the feasibility.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolzon G. (1996). An approximate method for fatigue-life prediction of framed structures. Fatigue Fract. Engng Mater. Struct., 19(12):1481–1491.
Chopra A.K. (2000). Dynamics of Structures: Theory and Applications to Earthquake Engineering. Prentice Hall.
Cipollina A., López-Inojosa A. and Flórez-López J. (1995). A simplified damage mechanics approach to nonlinear analysis of frames. Comput. Struct., 54(6):1113–1126.
Marante M.E. and Flórez-López J. (2002). Model of damage for RC elements subjected to biaxial bending. Engng Struct., 24(9):1141–1152.
Marante M.E. and Flórez-López J. (2003). Three-dimensional analysis of reinforced concrete frames based on lumped damage mechanics. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 40:5109–5123.
Mazza, F. (1998). Modelli di danneggiamento nell'analisi sismica non lineare di strutture inte-laiate in C.A. Tesis. Universita degli Studi della Calabria Cosenza, Italy [in Italian].
Perera A., Carnicero, Alarcón E. and Gómez S. (2000). A fatigue damage model for seismic response of RC structures. Comput. Struct., 78:293–302.
Taucer F., Enrico F. and Spacone (1991). A fiber beam-column element for seismic response analysis of reinforced concrete structures. Earthquake Engineering Research Center.
Xue W.C. and Zhang Z.T. (1999). Nonlinear full range analysis methods of steel concrete structures and its application. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 16(3):334–342.
Zhu Bolong and Yu Andong (1991). Nonlinear full-range analysis of R.C. frames. Journal of Tongji University, 83(3):21–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, J., Yang, T. (2009). Damage Analysis of 3D Frame Structure under Impulsive Load. In: Yuan, Y., Cui, J., Mang, H.A. (eds) Computational Structural Engineering. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2822-8_81
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2822-8_81
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-90-481-2821-1
Online ISBN: 978-90-481-2822-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)