Summary
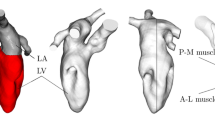
We studied the blood flow in the left ventricle of the human heart using a realistic Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) model. The CFD model was constructed from two-dimensional ultrasound echocardiogram data. An ultrasound image was sampled and smoothed by our own software system, which smoothes the obtained contour of the ventricular cavity using a cubic spline function. The time course of the contraction and dilatation of the left ventricle was also smoothed using the cubic spline function. Thus a time series of ventricular CFD models was established and CFD computation was performed using these models. With the simulated ventricular wall motion, we were able to visualize the diffusion of the blood inflow jet, which is reported to be important in the diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujimoto S, Parker KH, Xiao HB, and Gibson DG (1995) Detection and localization of early diastolic forces whithin the left ventricle from inflow jet dynamics. A comparison between normal subjects and patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Heart and Vessels, 10: 204 - 210
Fujimoto S, Parker KH, Xiao HB, Inge KS, and Gibson DG (1995) Early diastolic left ventricular inflow pressures in normal subjects and patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Reconstruction from pulsed Doppler echocardiography. Br Heart J 74: 419 - 425
Nakanishi Y, Kusaka Y, Mizuno R, Fujimoto S, Nakano H, Dohi N, and Yamaguchi T (1997) Intraventricular blood flow analysis using ultrasound image based CFD models (in Japanese). Proceedings of Japanese Society of Mechanical Engineers 97–1: 258 - 259
Taylor TW, Okino H, and Yamaguchi T (1994) Three dimensional analysis of left ventricular ejection using computational fluid dynamics. J Biomech Engng 116: 127 - 130
Taylor TW, Yamaguchi T (1995) Realistic three-dimensional left ventricular ejection determined from computational fluid dynamics. Med Engng Phys 17: 602 - 608
Liu H, Yamaguchi T (1999) Validation in modeling of biological and physiological flows. Proc. ASME/FED summer Meeting, No. 6787 (CD-ROM)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer Japan
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kusaka, Y. et al. (2000). Intraventricular blood flow analysis using robust CFD models. In: Yamaguchi, T. (eds) Clinical Application of Computational Mechanics to the Cardiovascular System. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-67921-9_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-67921-9_11
Publisher Name: Springer, Tokyo
Print ISBN: 978-4-431-67989-9
Online ISBN: 978-4-431-67921-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive