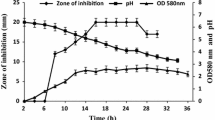
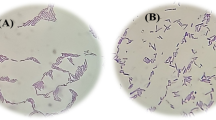
Abstract
Gardnerella vaginalis is a common component of the normal vaginal flora. However, it has been reported to cause postpartum bacteremia and neonatal sepsis (1), and a high concentration of Gardnerella vaginalis is significantly associated with nonspecific vaginitis (2).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Venkataramani, T. K., Räthburn, H. K.: Coryne- bacterium vaginale (Hemophilus vaginalis) bacteremia: clinical study of 29 cases. Johns Hopkins Medical Journal 1976, 139: 93–97.
Amsel, R., Totten, P. A., Spiegel, C. A., Chen, K. C. S., Eschenbach, D., Holmes, K. K.: Nonspecific vaginitis. The American Journal of Medicine 1983, 74: 14–22.
Mardh, P. A.: Gardnerella vaginalis and non-specific vaginitis. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1982, 1: 285–287.
Balsdon, M. J.: Gardnerella vaginalis and its clinical syndrome. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1982, 1: 288–293.
Shanker, S., Toohey, M., Munro, R.: In vitro activity of seventeen antimicrobial agents against Gardnerella vaginalis. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1982, 1: 298–300.
McCarthy, L. R., Mickelsen, P. A., Grover-Smith, E.: Antibiotic susceptibility of Haemophilus vaginalis (Corynebacterium vaginale) to 21 antibiotics. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1979, 16: 186189.
Durfee, M. A., Forsyth, P. S., Hale, J. A., Holmes, K. K.: Ineffectiveness of erythromycin for treatment of Haemophilus vaginalis associated vaginitis: possible relationship to acidity of vaginal secretions. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1979, 16: 635637.
Balsdon, M. J., Taylor, G. E., Pead, L., Maskell, R.: Corynebacterium vaginale and vaginitis: a controlled trial of treatment. Lancet 1980, is 501–503.
Goldstein, E. J. C., Kwok, Y. Y., Sutter, V. L.: Susceptibility of Gardnerella vaginalis to cephradine. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1983, 24: 418419.
Gardner, H. L.: Haemophilus vaginalis vaginitis after 25 years. American Journal of Obstetics and Gynecology 1980, 137: 385–391.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1986 Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Machka, K. (1986). In Vitro Activity of Ciprofloxacin and Norfloxacin Against Gardnerella vaginalis . In: Neu, H.C., Reeves, D.S. (eds) Ciprofloxacin. Current Topics in Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology, vol 1. Vieweg+Teubner Verlag, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-663-01930-5_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-663-01930-5_13
Publisher Name: Vieweg+Teubner Verlag, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN: 978-3-663-01931-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-663-01930-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive