Abstract
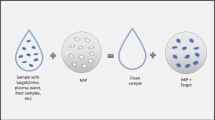
A highly effective purification process combined with molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) was developed to selectively isolate Epothilones (Epos) from a complex milieu. The MIPs of Epos were successfully synthesized by precipitation polymerization, and the optimal ratio of the template molecule to functional monomer and cross-linker was 1:4:20 (with the molar ratio). Under the optimized condition, the resulted products were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The binding properties of the MIPs were evaluated by the adsorption kinetics and static adsorption. From the correlation coefficients (R 2) of the fitting models, the equilibrium data fitted well to Freundlich model (R 2 = 0.9987), indicating multilayer adsorption. Finally, we successfully applied the MIPs in the solid-phase extraction (SPE) process of Epos, and its purity was improved more than 40 % than the origin. It achieved an effectively selective Epos cleanup procedure, sequentially established a favorable foundation for later research on Epos.
R. Sun and L. Zhao have contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Höfle G, Bedorf N, Steinmetz H, Schomburg D, Gerth K, Reichenbach H (1996) Epothilone A and B—Novel 16-membered macrolides with cytotoxic activity: isolation, crystal structure, and conformation in solution. Angew Chem Int Edit 35:1567–1569
Gerth K, Bedorf N, Höfle G, Irschik H, Reichenbach H (1996) Epothilones A and B: antifungal and cytotoxic compounds from Sorangium cellulosum (myxobacteria) production, physico-chemical and biological properties. J Antibiot 49:560–563
Gerth K, Steinmetz H, Höfle G, Reichenbach H (2000) Studies on the biosynthesis of epothilones: the biosynthetic origin of the carbon skeleton. J Antibiot 53:1373–1377
Gerth K, Steinmetz H, Höfle G, Reichenbach H (2001) Studies on the biosynthesis of epothilones: the PKS and epothilone C/D monooxygenase. J Antibiot 54:144–148
Domling A, Richter W (2005) Myxobacterial epothilones and tubulysins as promising anticancer agents. Mol. Divers. 9:141–147
Julien B, Shah S, Ziermann R, Goldman R, Katz L, Khosla C (2000) Isolation and characterization of the epothilone biosynthetic gene cluster from Sorangium cellulosum. Gene 249:153–160
Alexander C, Smith CR, Whitcombe MJ, Vulfson EN (1999) Imprinted polymers as protecting groups for regioselective modification of polyfunctional substrates. J Am Chem Soc 121:6640–6651
Haupt K, Mosbach K (2000) Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors. Chem Rev 100:2495–2504
Ge Y, Turner APF (2009) Molecularly imprinted sorbent assays: recent developments and applications. J Chem Eur 15:8100–8107
Haginaka J (2009) Molecularly imprinted polymers as affinity-based separation media for sample preparation. J Sep Sci 32:1548–1565
Sumaoka J, Komiyama M (2009) Molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of biomolecules in water. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 66:191–201
Wulff G (2002) Enzyme-like catalysis by molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem Rev 102:1–27
Ye L, Mosbach K (2008) Molecular imprinting: synthetic materials as substitutes for biological antibodies and receptors. Chem Mater 20:859–868
Vieira AC, Zampieri RA, Siqueira ME, Martins I, Figueiredo EC (2012) Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection for the determination of urinary trans, trans-muconic acid: a comparison with ionic exchange extraction. Analyst 137:2462–2469
Yang W, Zhou W, Xu W, Li H, Huang W, Jiang B, Zhou ZP, Yan YS (2012) Synthesis and characterization of a surface molecular imprinted polymer as a new adsorbent for the removal of dibenzothiophene. J Chem Eng Data 57:1713–1720
Dai J, Pan J, Xu L, Li X, Zhou Z, Zhang R, Yan Y (2012) Preparation of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles with superparamagnetic susceptibility through atom transfer radical emulsion polymerization for the selective recognition of tetracycline from aqueous medium. J Hazard Mater 205(206):179–188
Ren Y, Ma W, Ma J, Wen Q, Wang J, Zhao F (2012) Synthesis and properties of bisphenol A molecular imprinted particle for selective recognition of BPA from water. J Colloid Interface Sci 367:355–361
Acknowledgments
The work was financially supported by Research Projects of Science and Technology Division, Shandong (2012GSF12107), and Provincial Post-Doctoral Innovation Foundation (201203006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sun, R., Zhao, L., Yang, J., Wang, N., Liu, X. (2015). Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Purification and Separation for Epothilones. In: Zhang, TC., Nakajima, M. (eds) Advances in Applied Biotechnology. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 333. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46318-5_59
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46318-5_59
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-46317-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-46318-5
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)