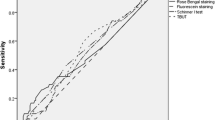
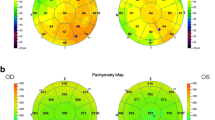
Abstract
A standardized approach to dry eye testing is crucial to diagnose the presence and severity of dry eye and monitor the success or failure of treatment. This is especially important as the severity of dry eye guides the appropriate course of management. Current international guidelines recommend use of standardized and validated questionnaire to record symptoms of dry eye. Routine testing should include a Schirmer test, noninvasive tear film break-up time, and assessment of corneal staining with fluorescein. Assessment of the lid margin, meibomian glands, and the cornea should also be performed. A number of additional diagnostic instruments such as tear interferometry, meibography, and tear osmolarity may be useful adjuncts to standardized testing.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arita R (2013) Validity of noninvasive meibography systems: noncontact meibography equipped with a slit-lamp and a mobile pen-shaped meibograph. Cornea 32(Suppl 1):S65–S70. doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e3182a2c7c6
Ban Y, Shimazaki-Den S, Tsubota K, Shimazaki J (2013) Morphological evaluation of meibomian glands using noncontact infrared meibography. Ocul Surf 11(1):47–53. doi:10.1016/j.jtos.2012.09.005, Epub 2012 Oct 16
Diagnostic Methodology Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop (DEWS) (2007) Methodologies to diagnose and monitor dry eye disease: report of the Diagnostic Methodology Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop (2007). Ocul Surf 5(2):108–152
Downie LE, Keller PR, Vingrys AJ (2013) An evidence-based analysis of Australian optometrists’ dry eye practices. Optom Vis Sci 90(12):1385–1395. doi:10.1097/OPX.0000000000000087
Eom Y, Lee JS, Kang SY, Kim HM, Song JS (2013) Correlation between quantitative measurements of tear film lipid layer thickness and meibomian gland loss in patients with obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction and normal controls. Am J Ophthalmol 155(6):1104–1110.e2. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2013.01.008, Epub 2013 Mar 7
García N, Tesón M, Enríquez-de-Salamanca A, Mena L, Sacristán A, Fernández I, Calonge M, González-García MJ (2014) Basal values, intra-day and inter-day variations in tear film osmolarity and tear fluorescein clearance. Curr Eye Res 8
Gayton J (2009) Etiology, prevalence, and treatment of dry eye disease. Clin Ophthalmol 3:405–412
Hosaka E, Kawamorita T, Ogasawara Y, Nakayama N, Uozato H, Shimizu K, Dogru M, Tsubota K, Goto E (2011) Interferometry in the evaluation of precorneal tear film thickness in dry eye. Am J Ophthalmol 151(1):18–23.e1. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2010.07.019
Kaštelan S, Tomic M, Salopek-Rabatic J, Novak B (2013) Diagnostic procedures and management of dry eye. Biomed Res Int 2013:309723. doi:10.1155/2013/309723, Epub 2013 Aug 19
Korb DR, Blackie CA (2008) Meibomian gland diagnostic expressibility: correlation with dry eye symptoms and gland location. Cornea 27(10):1142–1147. doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e3181814cff
Lemp MA, Bron AJ, Baudouin C, Benítez Del Castillo JM, Geffen D, Tauber J, Foulks GN, Pepose JS, Sullivan BD (2011) Tear osmolarity in the diagnosis and management of dry eye disease. Am J Ophthalmol 151(5):792–798.e1. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2010.10.032, Epub 2011 Feb 18
Levinson BA, Rapuano CJ, Cohen EJ, Hammersmith KM, Ayres BD, Laibson PR (2008) Referrals to the Wills Eye Institute Cornea Service after laser in situ keratomileusis: reasons for patient dissatisfaction. J Cataract Refract Surg 34(1):32–39. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2007.08.028
Management and therapy of dry eye disease: report of the Management and Therapy Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye Workshop (2007) Ocul Surf 5(2):163–178
Meadows JF, Ramamoorthy P, Nichols JJ, Nichols KK (2012) Development of the 4-3-2-1 meibum expressibility scale. Eye Contact Lens 38(2):86–92. doi:10.1097/ICL.0b013e318242b494
Nettune GR, Pflugfelder SC (2010) Post-LASIK tear dysfunction and dysesthesia. Ocul Surf 8(3):135–145, Review
Nichols KK, Mitchell GL, Zadnik K (2004) The repeatability of clinical measurements of dry eye. Cornea 23(3):272–285
Nichols KK, Foulks GN, Bron AJ, Glasgow BJ, Dogru M, Tsubota K, Lemp MA, Sullivan DA (2011) The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: executive summary. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(4):1922–1929. doi:10.1167/iovs.10-6997a
Pult H, Riede-Pult B (2013) Comparison of subjective grading and objective assessment in meibography. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 36(1):22–27. doi:10.1016/j.clae.2012.10.074, Epub 2012 Oct 27
Qin Q, Wang H, Wang HZ, Huang YL, Li H, Zhang WW, Zhang JR, He LL, Xia R, Zhao DB, Deng AM (2014) Diagnostic accuracy of anti-alpha-fodrin antibodies for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Mod Rheumatol 24(5):793–797
Reddy P, Grad O, Rajagopalan K (2004) The economic burden of dry eye: a conceptual framework and preliminary assessment. Cornea 23(8):751–761
Schiffman RM, Christianson MD, Jacobsen G, Hirsch JD, Reis BL (2000) Reliability and validity of the Ocular Surface Disease Index. Arch Ophthalmol 118(5):615–621
Solomon KD, Fernández de Castro LE, Sandoval HP, Biber JM, Groat B, Neff KD, Ying MS, French JW, Donnenfeld ED, Lindstrom RL, Joint LASIK Study Task Force (2009) LASIK world literature review: quality of life and patient satisfaction. Ophthalmology 116(4):691–701. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.12.037, Review
The Epidemiology of Dry Eye Disease. Report of the Epidemiology Subcommittee of the International Dry eye Workshop (2007) (2007) Ocul Surf 5(2):93–107
Tomlinson A, Bron AJ, Korb DR, Amano S, Paugh JR, Pearce EI, Yee R, Yokoi N, Arita R, Dogru M (2011) The International Workshop on Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: report of the Diagnosis Subcommittee. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:2006–2049. doi:10.1167/iovs.10-6997f
Tong L, Waduthantri S, Wong TY, Saw SM, Wang JJ, Rosman M, Lamoreux E (2010) Impact of symptomatic dry eye on vision-related daily activities: the Singapore Malay Eye Study. Eye (Lond) 24(9):1486–1491. doi:10.1038/eye.2010.67, Epub 2010 May 21
Woodward MA, Randleman JB, Stulting RD (2009) Dissatisfaction after multifocal intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg 35(6):992–997. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2009.01.031
Yu J, Asche CV, Fairchild CJ (2011) The economic burden of dry eye disease in the United States: a decision tree analysis. Cornea 30(4):379–387. doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e3181f7f36310.1097/ICO.0b013e3181f7f363
Compliance with Ethical Requirements
Colin Chan declares that he has no conflict of interest.
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000 (5). Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
No animal studies were carried out by the authors for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Chan, C. (2015). Practical Office-Based Screening and Diagnostics. In: Chan, C. (eds) Dry Eye. Essentials in Ophthalmology. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44106-0_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44106-0_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-44105-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-44106-0
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)