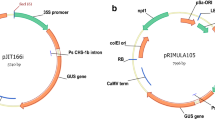
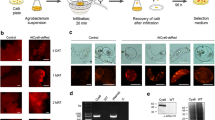
Abstract
Plant transformation is a key methodology that has allowed transfer and expression of novel genes for the improvement of economically important plant species as well as enquiry into deeper questions about the function of plant genes. For many plant species, stable transformation remains difficult or impossible. Where it is possible, there is usually a need for expensive resources such as laminar flow hoods, controlled environment growth rooms and highly skilled practitioners. In addition, there are often problems related to combining efficient plant regeneration with gene transfer as transfer techniques are carried out in undifferentiated cell cultures. Low transformation efficiency, instability of transgene expression, somaclonal variation and inability to regenerate whole plants are common problems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bechtold N, Ellis J, Pelletier G (1993) In planta Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants. CR Acad Sci Paris Life Sci 316:1194–1199
Booy G, Krens FA, Huizing HJ (1989) Attempted pollen-mediated transformation of maize. J Plant Physiol 135: 319–324
Chang SS, Park SK, Kim BC, Kang BJ, Kim DU, Nam HG (1994) Stable genetic transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana by Agrobacterium inoculation in planta. Plant J 5: 551–558
Christou P (1996) Transformation technology. Trend Plant Sci 1: 423–431
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16: 735–743
Dellaporta S, Wood J, Hick J (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation; version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1: 19–21
Desfeux C, Clough SJ, Bent AF (2000) Female reproductive tissues are the primary target of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation by the Arabidopsis floral-dip method. Plant Physiol 123: 895–904
Feldmann KA (1991) T-DNA insertion mutagenesis in Arabidopsis: mutational spectrum. Plant J 1: 71–83
Feldmann K (1992) T-DNA insertion mutagenesis in Arabidopsis: seed infection transformation. In: Koncz C, Chua N-H, Schell J (eds) Methods in Arabidopsis research. World Scientific, Singapore, pp 274–289
Feldmann K, Marks M (1987) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of germinating seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana: a non-tissue culture approach. Mol Gen Genet 208: 1–9
Fernando DD, Owens JN, Misra S (2000) Transient gene expression in pine pollen tubes following particle bombardment. Plant Cell Rep 19: 224–228
Hess D, Dressler K, Nimmrichter R (1990) Transformation experiments by pipetting Agrobacterium into the spikelets of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Sci 72: 233–244
Hobbs SLA, Warkentin TD, Delong CMO (1993) Transgene copy number can be positively or negatively associated with transgene expression. Plant Mol Biol 21: 17–26
Hoekema A, Hirsch PR, Hooykaas PJJ, Schilperoort RA (1983) A binary plant vector strategy based on separation of vir-and T-region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti-plasmid. Nature 303: 179–180
Hooykaas PJJ, Schilperoort RA (1992) Agrobacterium and plant genetic engineering. Plant Mol Biol 13: 327–336
Hu CY, Wang LZ (1999) In planta soybean transformation technologies developed in China: procedure, confirmation and field performance. In Vitro Cell Devel Biol-Plant 35:417–420
Janssen BJ, Gardner RC (1989) Localized transient expression of GUS in leaf disks following cocultivation with Agrobacterium. Plant Mol Biol 14: 61–72
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the gus gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5: 387–405
Joersbo M, Okkels FT (1996) A novel principle for selection of transgenic plant cells–positive selection. Plant Cell Rep 16: 219–221
Katavic V, Haughn GW, Reed D, Martin M, Kunst L (1994) In planta transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 245:363–370
Kilby NJ, Leyser HMO, Fumer IJ (1992) Promoter methylation and progressive transgene inactivation in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 20: 103–112
Langridge P, Brettschneider R, Lazzeri P, Lorz H (1992) Transformation of cereals via Agrobacterium and the pollen pathway: a critical assessment. Plant J 2: 631–638
Lazo GR, Pascal AS, Ludwig RA (1991) A DNA transformation-competent Arabidopsis genomic library in Agrobacterium. Bio/tech 9: 963–967
Luo Z-X, Wu R (1989) A simple method for the transformation of rice via the pollen-tube pathway. Plant Mol Biol Rep 7: 69–77
Martin T, Wohner RV, Hummel S, Willmitzer L, Frommer WB (1992). The GUS reporter gene system as a tool to study plant gene expression. In: Gallagher SR (ed) GUS protocols: the GUS gene as a reporter of gene expression. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 23–43
Mentewab A. Letellier V, Marque C. Sarrafi A (1999) Use of anthocyanin biosynthesis stimulatory genes as markers for the genetic transformation of haploid embryos and isolated microspores in wheat. Cereal Res Commun 27: 17–24
Meyer P (1995) Understanding and controlling transgene expression. Trends Biol Technol 13: 332–337
Meyer P, Niedenhof I, ten Lohuis M (1994) Evidence for cytosine methylation of non-symmetrical sequences in transgenic Petunia hybrida. EMBO J 13: 2084–2088
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15: 473–479
Ohta (1986) High-efficiency genetic transformation of maize by a mixture of pollen and exogenous DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 715–719
Ottaviani MP, Smits T, Hanisch ten Cate HH (1993) Differential methylation and expression of the 3-glucuronidase and neomycin phosphotransferase genes in transgenic plants of potato cv. Bintje. Plant Sci 88: 73–81
Prols F, Meyer P (1992) The methylation patterns of chromosomal integration regions influence gene activity of transferred DNA in Petunia hybrida. Plant J 2: 465–475
Qing CM, Fan L, Lei Y, Bouchez D, Tourneur C, Yan L, Robaglia C (2000) Transformation of Pakchoi (Brassica rapa L. ssp. chinensis) by Agrobacterium infiltration. Mol Breed 6: 67–72
Ramaiah SM, Skinner DZ (1997) Particle bombardment–a simple and efficient method of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) pollen transformation. Curr Sci 73: 674–682
Sanford JC, Skubik KA (1986) Attempted pollen-mediated transformation using Ti plasmids. In: Mulcahy DL, Bergamini-Mulcahy H, Ottaviano E (eds) Biotechnology and ecology of pollen. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–82
Senior IJ, Dale PJ (1996) Plant transgene silencing–gremlin or gift ? Chem Indus 19:604–608 Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98: 503–517
Tjokrokusumo D, Heinrich T, Wylie S, Potter R, McComb J (2000) Vacuum infiltration of Petunia hybrida pollen with Agrobacterium tumefaciens to achieve plant transformation. Plant Cell Rep 19: 792–797
Trieu AT, Burleigh SH, Kardailsky IV, Maldonado-Mendoza IE, Versaw WK, Blaylock LA, Shin HS, Chiou TJ, Katagi H, Dewbre GR, Weigel D, Harrison MJ (2000) Transformation of Medicago truncatula via infiltration of seedlings or flowering plants with Agrobacterium. Plant J 22: 531–541
Zheng J-Z, Wang D-J, Wu T.-Q, Zhang J, Zhou W-J, Zhu X-P, Xu N-Z (1994) Transgenic wheat plants obtained with pollen-tube pathway method. Sci China 37: 319–325
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wylie, S.J., Tjokrokusumo, D., McComb, J.A. (2003). Transformation of Petunia hybrida by the Agrobacterium Suspension Drop Method. In: Jackson, J.F., Linskens, H.F. (eds) Genetic Transformation of Plants. Molecular Methods of Plant Analysis, vol 23. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-07424-4_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-07424-4_3
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-05553-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-07424-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive