Zusammenfassung
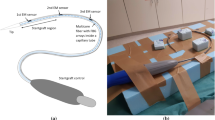
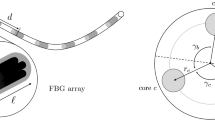
In endovascular aortic repair (EVAR) procedures fluoroscopy and conventional digital subtraction angiography are currently used to guide the medical instruments inside the patient. Drawbacks of these methods are X-ray exposure and the usage of contrast agents. Moreover, the fluoroscopy provides only a 2D view, which makes the guidance more difficult. For this reason, a catheter prototype including an optical fiber for shape sensing and three electromagnetic (EM) sensors, which provide the position and orientation information, was built to enable a 3D catheter guidance.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Jäckle S, García-Vázquez V, von Haxthausen F, et al. 3D catheter guidance including shape sensing for endovascular navigation. Proc SPIE. 2020;.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, ein Teil von Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jäckle, S. et al. (2020). Abstract: 3D Catheter Guidance Including Shape Sensing for Endovascular Navigation. In: Tolxdorff, T., Deserno, T., Handels, H., Maier, A., Maier-Hein, K., Palm, C. (eds) Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2020. Informatik aktuell. Springer Vieweg, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-29267-6_58
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-29267-6_58
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer Vieweg, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN: 978-3-658-29266-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-658-29267-6
eBook Packages: Computer Science and Engineering (German Language)