Summary
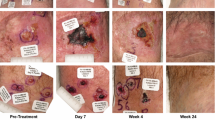
Subcutane adjuvant Viscum treatment is given to tumor patients to achieve immunomodulation with stimulation of NK cells, IL-2 activating T lymphocytes (CD25+) and cytokine-associated cytotoxicity. Intralesional Viscum therapy can at present only be used in exceptional cases: for patients who refuse other treatment and for those who no longer respond to treatment. High concentrations of cytotoxic Viscum preparations are injected directly into the tumor in such situations. The case of a patient is reported where intralesional treatment with ABNOBAviscum Betulae and ABNOBAviscum Quercus (dilution level) 2 injected into a melanoma skin secondary caused brain-metastases to regress twice. Treatment with subcutaneous injections and lower concentrations did not prevent the development of new brain and skin metastases. The immunological background to such a remission of brain metastases is not yet known. The patient has been symptom-free since Viscum treatment started in 4/92; at present (1/97) there is no sign of new brain-metastases (CT).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berg PA (1996) Rolle des Immunsystems bei der Tumorabwehr. In: Scheer R, Becker H, Berg PA (Hrsg) Grundlagen der Misteltherapie - Aktueller Stand der Forschung und klinische Anwendung, Hippokrates Verlag, Stuttgart
Beuth J, Ko HL, Gabius HJ, Burrichter H, Pulverer G (1992) Behavior of lymphocyte subsets and expression of activation markers in respons to immunotherapy with galactosid-specific lectin from mistletoe in breast cancer patients. Clinical Investigator 70: 658–661
Drees M, Berger DP, Dengler WA, Fiebig HH (1996) Direct Cytotoxic Effects of Preparations Used as Unconventional Methods in Cancer Therapy in Human Tumor Xenografts in the Clonogenic Assay and in Nude Mice. In: Huber H, Queißer W (eds) Contributions to Oncology, vol. 51. In: Arnold W, Köpf-Maier P, Micheel B (eds) Immunodeficient Animals: Models for Cancer Research. Karger, Freiburg, S 115–122
Fischer S (1996) T-Zellreaktivität mistelbehandelter Tumorpatienten und unbehandelter Gesundspender auf Mistelinhaltsstoffe. Dissertation Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg. Hippokrates Verlag, Stuttgart
Röcken M et al. (1996) IL-4-induced immune deviation as antigen-specific therapy for inflammatory autoimmune disease. Immunol today vol 17,5, pp 225–231
Scheer R, Fiebig HH, Scheffler A (1995a) Synergisms between Lectins and Vesicles of Viscum Album L., 2) Direct Cytotoxic Effects, Short Lecture, APGI 7th International Conference on Pharmaceutical Technology, 41st Annual Congress of APV, Budapest 9 to 11 May 1995, Abstract im Kongreßband, pp 873–874
Scheer R, Errenst M, Scheffler A (1995b) Wirtsbaumbedingte Unterschiede von Mistelpräparaten. Dtsch Zschr Onkol 27: 143–149
Schlodder D (1996) 75 Jahre Misteltherapie bei Krebspatienten - Kritische Zusammenfassung der ärztlichen Erfahrungen. In: Scheer R, Becker H, Berg PA (Hrsg) Grundlagen der Misteltherapie - Aktueller Stand der Forschung und klinische Anwendung. Hippokrates Verlag, Stuttgart
Silberstein DS (1995) Eosiniphil function in health and disease. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 19:47–77
Stettin A, Schultze JL, Stechemesser E, Berg PA (1990) Anti-mistletoe antibodies are produced in patients during therapy with an aqueous mistletoe extract derived from Viscum album L. and neutralize lectin-induced cytotoxicity in vitro. Klinische Wochenschrift 68: 896–90
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1997 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
von Laue, HB. (1997). Mistletoe Treatment for Melanoma Brain Metastases: A Single Case. In: Altmeyer, P., Hoffmann, K., Stücker, M. (eds) Skin Cancer and UV Radiation. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-60771-4_154
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-60771-4_154
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-64547-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-60771-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive