Abstract
Complex network research literatures have increased rapidly over last decade, most remarkable in the past four years. This paper attempted to visualise the research outputs of complex network research in a global context for the purpose in knowledge discovery on the world research progress and quantitative analysing on current research publication trends. The scientometric methods and knowledge visualization technologies are employed with a focus on global production, main subject categories, core journals, the most productive countries, leading research institutes, publications’ most used keywords as well as the most cited papers, and the knowledge basement. The keywords cluster analysis is used to trace the hot topics from the research literatures in this field. Research outputs descriptors suggested that the research in this domain has mainly focused on the dynamics, model and systems for complex networks. All the publications have been concentrated in two journals such asPhysical Review E andPhysica A. The USA is the leading country in complex network research field since it has both the world research centres and most of the top scientists worldwide. The research trend in complex network research are involved in complex routing strategy, models complex networks social as well as scale free percolation efficiency. Complex networks, dynamics, model and small-world networks are highly used keywords in the literatures from the main scientific database.
Fei-cheng Ma is a senior professor and doctoral supervisor, and currently the director of Centre for the Studies of Information Resources (CSIR) at Wuhan University. He is both the Editor-in-Chief of an information journal and international editor for several journals of information science. His major research lies in information resource management and planning, theory and methodologies of information science, and information economics. He can be touched at fchma@whu.edu.cn.
Peng-hui Lyu, as the corresponding author of this contributuoin, is an assistant researcher in Research and Development Centre for Smart City and also a Ph. D candidate in CSIR at Wuhan University. He is one of academic committees for the journal of Advanced Management Science, and the international reviewer for the journals of PLoS One and Water Resources Management. His academic interest involves in knowledge management, knowledge networks and knowledge city, especially in quantitative research for science information. He can be touched through lvph@whu.edu.cn.
Xiao-guang Wang is a professor of the School of Information Management, Wuhan University. He has published in many international journals such as Journal of Information Science, Journal of Knowledge Management and Scientometrics. His research interests are in the areas of knowledge network analysis, digital assets management and semantic publishing. He can be contacted at wxguang@whu.edu.cn.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
- Complex Networks
- Knowledge Discovery
- Publication Trend
- Citation Analysis
- Knowledge Base
- Subjects Category
- Keywords Plus
- Co-Citation
Introduction
Complex networks, attracting the attention of computer scientists, biologists, mathematicians and physicists et.al, are thoroughly studied in more and more evolved research fields now. As an effective reflection contacting the real world and theoretical exploration, it was initially come from the domain of chaos theory and fractal studies. Two pioneering works, small world network and scale-free network, encouraged an instantly wave of international research concerning complex networks by the end of the twentieth century. Small-world networks explored by Watts and Strogatz, which can be highly clustered and have small characteristic path lengths (Watts and Strogatz 1998), can portray biological, technological and social networks better than the networks completely regular or completely random. In many large networks it was found that the property that the vertex connectivity followed a scale-free power-law distribution (Barabasi and Albert 1999) by Barabási A.L and Albert R. Counting from this emergence, complex networks have gone through its first research decade.
In the early twenty-first century, the discovery of small world effect and scale-free property in the real network largely provoked the publications boom of complex networks. Initial research on complex networks focused on the analysis and modelling of network structure at large, such as degree exponents (Dorogovtsev and Goltsev 2002), dynamical processes (Yang et al. 2008), network growth (Gagen and Mattick 2005), link prediction (Zhou et al. 2009) and so on. Then Strogatz S.H tried to unravel the structure and dynamics of complex networks from the perspective of nonlinear dynamics (Strogatz 2001). The statistical mechanics of network as topology and dynamics of the main models as well as analytical tools were discussed (Albert and Barabasi 2002), the theory of evolving networks was introduced in Albert R and Barabasi A.L’s work.
The developments of complex networks, including several major concepts, models of network growth, as well as dynamical processes (Newman 2003) were discussed in Newman MEJ’s paper. The basic concepts as well as the results achieved in the study of the structure and dynamics of complex networks (Boccaletti et al. 2006) were summarized. The error tolerance was displayed only in scale-free networks, and it showed an unexpected degree of robustness (Albert et al. 2000). Network motifs and patterns of interconnections to uncover the structural design principles of complex networks was defined (Milo et al. 2002). The way in which self-organized networks grows into scale-free structures, and the role of the mechanism of preferential linking were investigated (Dorogovtsev and Mendes 2002). A number of models demonstrating the main features of evolving networks were also presented. Mixing patterns in a variety of networks were measured (Newman 2003) and technological as well as biological networks were found disproportionally mixed, while social networks tend to be assorted. It was pointed out that scale-free networks catalysed the emergence of network science (Barabasi and Oltvai 2004). The number of driver nodes is determined primarily by the network’s degree distribution was also found, and the driver nodes tend to avoid the high-degree nodes (Liu et al. 2011). The control of degrees on complex networks was carefully studied later (Egerstedt 2011). The fragility of interdependency on complex networks was also studied hence (Vespignani 2010).
With the continuous development of complex networks, in addition to the theoretical and technical research on the complex network itself, scholars have also focused on the network function. Barabasi A.L and Oltvai Z.N indicated that cellular networks offer a new conceptual framework for biology and disease pathologies (Barabasi 2009), which could potentially revolutionize the traditional view. An approach which not only stresses the systemic complexity of economic networks was pointed out (Schweitzer et al. 2009), it can be used to revise and extend traditional paradigms in economic theory which is urgently needed. A biologically complex multistring network model was designed to observe the evolution and transmission dynamics of ARV resistance (Smith et al. 2010).
The current situation is that the complex network research was not only limited to the study of the theory and methods, but has become a new research direction of multi-disciplinary and a powerful tool in multi-disciplinary research. Nowadays complex network have been applied in many different areas including spread (Yang et al. 2008), network synchronization (Motter et al. 2005), transports (Wang et al. 2006), game theory (Perc and Szolnoki 2010), physics (Newman 2002), computer science (Guimera and Amaral 2005), biochemistry or molecular biology (Jeong et al. 2000), mathematics (Guimera and Amaral 2005), engineering (Olfati-Saber et al. 2007), cell biology (Rosen and MacDougald 2006). These research directions took us more and more productions and publications in recent years.
Most important it was known to all that the methods of complex networks are used more and more for scientomtrics and informetrics research in information science. For example the complex networks analysis was employed for co-citation or co-occurrence network to get the knowledge structure as well as scientific cooperation performance for a specific filed. While in these studies, the metric data is the base of all complex networks analysis. Traditional bibliometrics research was widely applied to acquaint information from the scientific or technical literatures, and for further study the complex networks method could also help.
In this study the records of literature were analysed with scientometric methods via several aspects. This effort will provide a current view of the mainstream research on complex networks as well as clues to the impact of this hot topic. In addition, this study also attempted to analyse the significance of the complex networks production patterns, especially in the way of co-authors and authors’ keywords study originally acted from WoS database. The main body of this article includes scientometric analyses in production, subject category, and geographical distribution of WoS data. Moreover, appropriate statistical tests were used in the authors’ keyword yearly to predict the developing trend of complex networks research.
Data and Method
This study is based on the metadata analysis of the articles from the authoritative scientific and technical literature indexing databases such as SCI-E, SSCI and CPCI. The impact factor of SCI & SSCI journals with the latest data available in 2012 was determined by Journal Citation Reports (JCR) of Thomson Reuters, which was operated by Thomson Scientific, Philadelphia, PA now (Proudfoot, McAuley et al. 2011). The statistical analysis tool is Thomson Data Analyser (TDA) and the drawing tool is Aureka and MS Office Excel 2010.
Date Source
The data source was come from WoS database offered by Thomson Reuters, and the publishing time span was last updated in Dec 28th, 2013. Data in this study was acquired on December 30th, 2013 using the topic= “complex* network*” selecting “all the years” within the metadata including publication’s title, keywords and abstract. In total, 10,832 articles were retrieved from the database of Web of Science (WoS). Precision retrieval strategy used in this paper make the ability of the search term to minimize the number of irrelevant records retrieved. As an abstract database, WoS offered only the metadata, certainly if given the chance to extract information from the full text of all paper the results may be more accurate.
Methodology
In this scientometrics study, the annual publications, subjects’ category, core journals, productive countries, fruitful institutes, main authors and keywords of the papers was deeply studied using the quantitative analysis methods. In this study comparative analysis was also used to analyse the data by putting the SCI and SSCI data into the same figure so that a direct and vivid result can be gotten from the figures and as much as possible information obtained.
Results Analysis
In this section, figures and tables are employed to describe the production and the development trends of complex networks research in both science and social science fields. Publications (as indicator for scientific performance) are commonly accepted indicators for quantitative analysis on innovation research performance (Garfield 1970). Papers from SCI as well as SSCI were studied together in this paper with scientometric analysis to explore the knowledge discovery.
Production Trend
As seen in Fig. 1 the complex networks publications increased dramatically in the last two decades. From 1990 to 2001, the complex networks’ research were just begun and its publications were relatively low and there were not more than 200 papers in the WoS database. After 2001, the research outputs increased rapidly from less than 200 in 2001 to more than 2000 in 2009 and then stabilized changed in recent. The complex networks research came into its fast growth stage in twenty-first century and may enter the mature period of its publish life cycle in the next decade.
Subjects Category
The complex networks related research was distributed in the subjects of physics, computer science, biochemistry & molecular biology, mathematics and engineering. Most complex networks outputs were produced under the subject of physics due to it is a branch of theoretical physics originally. As time went by, this approach was used in bioscience or engineering to solve many problems as a migrating concept, which proved its superiority for many disciplines from the metadata of SCI & SSCI papers. Through the subject co-occurrence networks it can be known that the complex network is based on the mathematics and computer science, and be successfully used in engineering and related sciences, which is shown in Fig. 2. Bio-related sciences such as biochemistry, biophysics, biotechnology, and cell biology are the best domains in which complex networks being well developed. In future, there will be more and more bio-scientists put their attention into complex networks research.
Journals Analysis
The complex networks research was published mainly in physics related journals such asPhysical Review E andPhysica A, which published most complex networks papers in all journals from the SCI&SSCI database.PLoS Oneproduced 217 papers and ranked third,European physical journal B with 205 papers in forth andChaos with 205 papers in fifth for publications in the complex networks research. The American journalsPNAS andPhysical Review Letters were two journals with the highest impact factor in 2011. The annual publications distribution about complex networks papers are shown in Fig. 3. The research in this field attracted the most attentions from scientists far in the year 2001.Physical Review E was the main publisher of complex networks in the last decade, whilePhysica A reached the publication level ofPhysical Review E in 2007 once. Other journals kept a stable publication state in the past decade with about 30 papers per year in SCI&SSCI database;PLoS One (Full name ofPublic Library of Science One) was the only exception with a dramatically increasing rate in recent three years.
Countries Analysis
In all complex networks publications, the United States of America and the People’s Republic of China contributed the most parts as shown in Fig. 4. Hence the research centre was located in these two countries at present. However, the USA started complex networks research as early in 1997 but dropped behind P.R. China in productions after 2007. Other countries such as Germany, Italy, England and Spain produced less outputs with a stable increasing rate in complex networks related publications. While in total these European countries published more papers than former other countries.
Active degree is defined as the outputs number in recent three years to all years’ publication number in general bibliometric research. P.R. China had the highest active degree of 52.3 % in all countries in the world, indicating that the research of complex networks was treasured much and in fact such activity as the Conference for Chinese Complex Networks (short for CCCN) was held for eight times already in recent years in P.R. China (Fig. 5).
The SCI&SSCI papers’ citations results were shown in Fig. 4. From this figure it can be found that the USA obtained the most citations, which attested its high level in the field of complex network research. The highest citation per paper was from European countries such as England and Germany. P.R. China’s average citation was relatively lower than most European countries and Brazil or Japan, but not far behind the USA with less total citations.
In the international collaboration of papers of complex networks, the USA, Germany and P.R. China are located in the central positions which can be seen in Fig. 6. It is also clear that USA is in the centre of collaborating activities. Other countries such as England, France, Italy, Spain and Switzerland had less cooperation in complex networks research in SCI&SSCI publications. The cooperation network between top productive countries reflected the knowledge transmission in the field of complex networks research in the world.
Institutes Analysis
The top productive institutes with an accumulative paper quantity of more than 40 are ranked in Fig. 6. The Harvard University published 70 papers in total, ranking first, followed by University of Science and Technology of China (USTC, 69) and CNR from France with an output of 63 papers. Other institutes produced many papers as the former ones did in complex networks, which reflecting their overall strength like these American and Chinese agencies.
For most productive institutes, the time span during 2005 to 2007 was the best years with most publications. The Harvard University from USA as well as University of Science and Technology of China produced the most complex networks research papers accumulatively before, far more than all the institutes in world organizations. After 2008, all top productive institutes published less paper for about five years while Boston University not. The production came into a former maturity stage in its publish cycle then (Fig. 8).
It can be seen from as shown in Fig. 7 that the Northwestern University has the most total citations as well as citations per paper in the world, which proved their priority in complex networks research. The Harvard University had the second most total citations and citations per paper. Compared with the University of Science and Technology of China, North western University and Harvard University has the highest citations per paper and most total citations. US agencies have the best research in complex networks research in the world.
Keywords Analysis
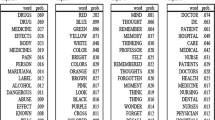
All the high frequency keywords plus more than 200 are listed in Table 1. The complex networks related hotspots were mainly distributed in the dynamics, model and systems research as we can see from Table 1. What’s more, the research of Small World networks, the internet and evolution were also the high frequency key words that emerged in research papers. Scale-Free Networks as well as organizations became the hot words only less than words plus listed above.
The annual keywords plus distribution was drawn in Fig. 9. The main retrieval word of complex networks was turned up in 2001 and with a fast increasing trend in the past decade. Scholars paid little attentions in the dynamics research before 2000, while they were interested in it during 2001 to 2007 so that the number of this word increased sharply from then. In the year 2006, almost all the research of systems, internet and Small-World Networks maintained a fast increase in papers production.
The complex networks research co-words map was drawn for the hotspot analysis in this paper as Fig. 10. All the words were extracted from the title, author keywords and abstracts of the publications automatically by the Aureka software and then clustered in the knowledge map to trace the research trends. The complex routing strategy is the most popular research domain in all outputs for complex networks research. And such fields as models complex networks social as well as scale free percolation efficiency were less popular than the complex routing strategy research in recent years.
Citation Analysis
The most frequently cited papers are key literatures link the research of complex networks for years so the top SCI&SSCI papers with most citations are listed in Table 2. In the top 10 high influence research papers, six of which came from the USA and the remainders were produced by European countries. The paper “Statistical mechanics of complex networks” written by Albert R and Barabasi A.L from Notre Dame University was the most frequently cited paper in the world. These two famous scientists also wrote other three most cited papers under the topics of error and attack tolerance, network biology and metabolic networks before.
Figure 11 shows all the reference year of the complex networks related publications. Most complex networks outputs cited the papers published after 1998, the citation account before and after 1998 were at a huge difference. One reason was that the complex network research started at this time span, and the other was that the published papers attracted more and more attentions from this time point. In fact, the most important works published in 2000–2002 gained so much citation as can be seen from Table 3. While the new published papers, especially after 2010, were cited not much as the papers before due to their values not known by most scholars. The citation time window is of the normal distribution, with little citation in the former and later years and much citation in the middle location of the figure.
The reference account reflected the influence in the local domain, which is listed in Table 3. In the top 10 high influence research papers, most of them came from the USA and the remainders were produced by European countries. Those papers published in famous journals such as Science, Nature, and PNAS (Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences in USA). The paper wrote by Albert R in Review Modern Physics also attracted lots of attentions in the domain of complex networks’ research. The results are accordance with the citation rank in Table 3.
Co-citation Analysis
Figure 12 give a vividly picture of the journals co-cited by the complex networks domain. Those journals co-cited by one given research topic are usually considered as the knowledge base, and they provided the original citations. In complex network domain, those journals such as Science, Nature, PNAS, Cell, Physica A, and Review Modern Physics, Physics Review E, New England Journal Medicine, Physics Review Letter, PLoS One are in the center location of the ci-citation network. Naturally, many other journals including Social Networks, Nature Physics, Physica D, Chaos, New Journal of Physics et.al also provided lots of knowledge base for complex networks’ research development.
Conclusion
As a strictly selected academic thesis abstract database, Web of Science (WoS, including SCI and SSCI) has been long recognized as the useful tool that can cover the most important science & technology, social science research productivities. SCI & SSCI citation search systems are unique and significant, not only from the perspective of literature cited but also from the academic assessment of the value in articles or from cooperation networks to research references. So all the papers published in this database were carefully studied to get the publication pattern and production orderliness.
The methods of complex networks are used more and more in other research such as in information science. The complex networks analysis was employed for co-citation or co-occurrence network to get the knowledge structure as well as scientific cooperation performance for a specific scientific filed often. Hence traditional scientometrics research was widely applied to acquaint information from the scientific or technical literatures, this will lead us a new direction for complex networks method in future as this research do.
Hence in this study, the impact of global complex networks literature has been studied with scientometric methods and the research history has been recalled firstly according to the complex networks research literatures. The publications history started from 1990 and boosted in recent four or five years. From 1990 to about 2001, the complex networks research stepped into its infancy stage and then began a fast increasing stage in growth, and now in the former stage of maturity in its life cycle. In near future the publications in this field will still keep going larger and larger for quite a long time as can be predicted.
Complex networks research are mainly in the subjects of physics. All the output concentrated in two journals such asPhysical Review E andPhysica A in SCI&SSCI database. The research papers were mainly completed by several authors according to network theory aggregation nodes in a power law correlation, and the multiple-authors made up an increasingly larger ratio to form a group size measured using papers. So the co-authored papers in the complex networks research were the mainstream of complex networks research and it formed a complex collaboration networks about complex networks research.
Complex networks related papers were distributed unevenly over all countries. The USA, China and Germany were the top productive countries of SCI&SSCI papers. Some Europe countries such as Italy and Germany published top influence paper than those productive countries. The complex networks research centre was located in the USA in the last few decades according to the metadata from countries and institutes analysis. Harvard University and USTC produced most SCI papers and some USA institutes such as University of Michigan and University of Notre Dame contributed most influence SCI articles.
Research on the fields of complex networks research focused on complex routing strategy, models complex networks social as well as scale free percolation efficiency. From the analysis of author keywords, except “complex networks”, “dynamics”, “model” and “small-world networks” were highly used key words plus in the scientific database. It is clear that complex networks research will be a hot spot in the complexity science field in the future. With scientometric and informetric method, the findings of this study can help scientific researchers understand the performance and central trends of complex networks research in the world, and therefore suggest directions for further research.
References
Albert R, Barabasi AL (2002) Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev Mod Phys 74(1):47–97
Albert R, Jeong H et al (2000) Error and attack tolerance of complex networks. Nature 406(6794):378–382
Barabasi AL (2009) Scale-free networks: a decade and beyond. Science 325(5939):412–413
Barabasi AL, Albert R (1999) Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 286(5439):509–512
Barabasi AL, Oltvai ZN (2004) Network biology: understanding the cell’s functional organization. Nat Rev Genet 5(2):101–U115
Boccaletti S, Latora V et al (2006). Complex networks: structure and dynamics. Phys Rep-Rev Sect Phys Lett 424(4–5):175–308
Dorogovtsev SN, Goltsev AV et al (2002) Pseudofractal scale-free web. Phys Rev E 65(6)
Dorogovtsev SN, Mendes JFF (2002) Evolution of networks. Adv Phys 51(4):1079–1187
Egerstedt M (2011) Complex networks degrees of control. Nature 473(7346):158–159
Gagen MJ, Mattick JS (2005) Accelerating, hyperaccelerating, and decelerating networks. Phys Rev E 72(1)
Garfield E (1970) Citation indexing for studying science. Nature 227(5259):669–671
Guimera R, Amaral LAN (2005) Functional cartography of complex metabolic networks. Nature 433(7028):895–900
Jeong H, Tombor B et al (2000) The large-scale organization of metabolic networks. Nature 407(6804):651–654
Liu YY, Slotine JJ et al (2011) Controllability of complex networks. Nature 473(7346):167–173
Milo R, Shen-Orr S et al (2002) Network motifs: simple building blocks of complex networks. Science 298(5594):824–827
Motter AE, Zhou CS et al (2005) Network synchronization, diffusion, and the paradox of heterogeneity. Phys Rev E 71(1)
Newman MEJ (2002) Assortative mixing in networks. Phys Rev Lett 89(20)
Newman MEJ (2003) The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev 45(2):167–256
Olfati-Saber R, Fax JA et al (2007) Consensus and cooperation in networked multi-agent systems. Proc IEEE 95(1):215–233
Perc M, Szolnoki A (2010) Coevolutionary games-A mini review. Biosystems 99(2):109–125
Proudfoot AG, McAuley DF et al (2011) Translational research: what does it mean, what has it delivered and what might it deliver? Curr Opin Crit Care 17(5):495–503
Rosen ED, MacDougald OA (2006) Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7(12):885–896
Schweitzer F, Fagiolo G et al (2009) Economic Networks: the new challenges. Science 325(5939):422–425
Smith RJ, Okano JT et al (2010). Evolutionary dynamics of complex networks of HIV drug-resistant strains: the case of San Francisco. Science 327(5966):697–701
Strogatz SH (2001) Exploring complex networks. Nature 410(6825):268–276
Vespignani A (2010) Complex networks the fragility of interdependency. Nature 464(7291):984–985
Wang WX, Wang BH et al (2006) Traffic dynamics based on local routing protocol on a scale-free network. Phys Rev E 73(2)
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 393(6684):440–442
Yang R, Zhou T et al (2008) Optimal contact process on complex networks. Phys Rev E 78(6)
Zhou T, Lu L et al (2009) Predicting missing links via local information. Eur Phys J B 71(4):623–630
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Open Access
Open Access
This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License, which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Rights and permissions
This chapter is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
Copyright information
© 2014 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and the Author(s)
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ma, FC., Lyu, PH., Wang, XG. (2014). Knowledge Discovery of Complex Networks Research Literatures. In: Chen, C., Larsen, R. (eds) Library and Information Sciences. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-54812-3_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-54812-3_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-54811-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-54812-3
eBook Packages: Business and EconomicsBusiness and Management (R0)