Abstract
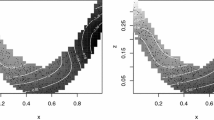
Smoothing techniques are used to reduce the variability of point clouds. There is great interest not only among applied statisticians but also among applied workers in biostatistics, economics and engineering to model the data in a nonparametric fashion. The benefits of this more flexible modeling come at the cost of greater computation, especially in high dimensions. In this paper several possibilities of smoothing in high dimensions are described using additive models. The algorithms for solving the nonparametric smoothing problems are based on WARPing, i.e. Weighted Averaging using Rounded Points. Interactive graphical techniques are a conditio sine qua non for tuning and checking the structure of lower dimensional projections of the data and of smooths produced by the algorithms. Applications of the WARPing technique to a side impact study are shown by smoothing in Projection-Pursuit-type models using Average Derivative Estimation.
This research was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Sonderforschungsbereich 303.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker, R.A. and Chambers, J.M. (1984). S.: An Interactive Environment for Data Analysis and Graphics. Wadsworth, Belmont.
Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Olshen, R. and Stone, C.J. (1984). Classification and Regression Trees. Wadsworth, Belmont.
Breiman, L. and Friedman, J. (1985). Estimating Optimal Transformations for Multiple Regression and Correlation (with discussion). J.Amer.Stat.Assoc. 80, 580–619.
Caussinus, H. (1986). Models and Uses of Principal Component Analysis. Proc. Multidimensional Data Analysis, Cambridge, DSWO Press.
Caussinus, H. (1987). Discussion of “What is Projection Pursuit ?” by Jones, M.C. and Sibson, R. J.Royal Statist. Soc.(A), 150, 26.
Chambers, J.M. (1986). Computing Environments for Quantitative Applications. ATT Bell Labs Stat. Research Reports 17.
Friedman, J. and Stuetzle, W. (1981). Projection Pursuit Regression. J.Amer.Stat.Ass 76, 817–823.
Friedman, J. and Stuetzle, W. (1982). Smoothing of Scatterplots. Tech. Report Orion 8. Dept. Statistics, Stanford University.
Hardie, W. (1988a). Interactive Smoothing Techniques, in: Proceedings of the Interface Conference, 1988, Reston Virginia, E. Wegman, Ed.
Hardie, W. (1988b). Applied Nonparametric Regression. Cambridge University Press, to appear.
Hardie, W. and Bowman A. (1988). Bootstrapping in Nonparametric Regression: Local Adaptive Smoothing and Confidence Bands. J. Amer. Statist. Assoc, 88, 102–110.
Hardie, W.; Hall, P. and Marron, J.S. (1988). How Far are Automatically Chosen Regression Smoothing Parameters from Their Optimum ? (with discussion). J. Amer. Statist. Assoc, 88, 86–101.
Hardie, W. and Scott, D.W. (1988). Smoothing in Low and High Dimensions by Weighted Averaging using Rounded Points. Statistical Science, submitted.
Hardie, W. and Stoker, T. (1988). Investigating Smooth Multiple Regression by the Method of Average Derivatives. J. Amer. Statist. Assoc, submitted.
Hastie, T. and Tibshirani, R. (1986). Generalized Additive Models. Statistical
Heckman, N. (1986). Spline Smoothing in a Partly Linear Model. J.Royal Statist. Soc.(B), 48, 244–248.
Huber, P.J. (1985). Projection Pursuit (with discussion). Ann. Statist., 18, 485–875.
Ibragimov, I.A. and Khasm’insksii, R.Z. (1981). Asymptotic Quality Boundaries of Regression Estimation in L p . Zap. Nauch. Sem. Lomi., 97, 88–101.
Jones, M.C. and Sibson, R. (1987). What is Projection Pursuit ? (with discussion). J.Royal Statist. Soc.(A), 150, 1–89.
Kallieris, D.; Mattern, R. and Hardie, W. (1986). Belastbarkeitsgrenye und Verletzungsmechanik des angegurteten PKW-Insassen beim Seitaufprall. Phase II: Ansätze zur Verletzungsprädiktion. FAT Schriftenreihe 60, Forschungsvereinigung Automobiltechnik e.V. (FAT).
McDonald, J. and Pederson, J. (1986). Computing Environments for Data Analysis, Part 3: Programming Environments. Laboratory for Computational Statistics, Stanford Technical Report 24-
Müller, H.G. (1987). Weighted Local Regression and Kernel Methods for Non-parametric Curve Fitting. J. Amer. Statist. Assoc, 82, 281–288.
Oldford, R.W. and Peters, S.C. (1985). DINDE: Towards more Statistically Sophisticated Software. MIT, Technical Report 55.
Rice, J.A. (1986). Convergence Rates for Partially Splined Models. Statistics and Probability Letters, 4, 203–208.
Scott, D.W. (1986). Data Analysis in 3 and 4 Dimensions with Nonparametric Density Estimation, in: Statistical Image Processing, E. Wegman and D. DePriest, eds., Marcel Dekker, New York, 291–805.
Scott, D.W. and Terrell, G.R. (1987). Biased and Unbiased Crossvalidation in Density Estimation. J. Amer. Statist. Assoc, 82, 1131–1146.
Silverman, B.W. (1984). Spline Smoothing: The equivalent Variable Kernel Method. Ann. Statist, 12, 898–916.
Silverman, B.W. (1986). Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis. Chapman and Hall, London.
Stone, C.J. (1982). Optimal Global Rates of Convergence for Nonparametric Regression. Ann.Statist., 10, 1040–1058.
XploRe (1987). XploRe — a computing environment for eXploratory Regression and density smoothing. Wirtschaftstheorie II, Universität D-5800 Bonn.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1988 Physica-Verlag Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Härdle, W. (1988). Efficient Nonparametric Smoothing in High Dimensions Using Interactive Graphical Techniques. In: Edwards, D., Raun, N.E. (eds) Compstat. Physica-Verlag HD. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-46900-8_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-46900-8_2
Publisher Name: Physica-Verlag HD
Print ISBN: 978-3-7908-0411-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-46900-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive