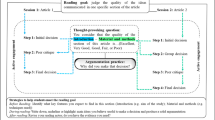
Abstract
In attempting to read a scholarly article, learners (students) often struggle with problems of comprehension. It is likely that when a scholar writes a paper and discusses a new idea or a method within a particular discipline, they assume that readers have a scholarly background enabling them to understand the paper content in detail. Such an assumption is not justified, and there is evidence that students who are learning to carry out research for the first time find that understanding scholars’ papers is not always an easy task. Deciding which RE (Requirement Elicitation) technique and tool to apply to issues can become complicated for educators constructing a learning approach which emphasises that group learners should read scholarly articles in a short time and be able to summarise the content from the article, while at the same time allowing learners to devise solutions that will, enhance their creativity and innovation, allowing them to explore how an idea in a paper could be integrated into an industry application. A case study in this paper introduces a university framework, which can be applied to aid students in their decision-making on selecting a presentation technique; that is, choosing role-playing as the appropriate technique for an effective learning outcome.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous. What is a scholarly article or book? http://instructional1.calstaela.edu/tclim/definition-boxes/scholarly_article.htm (accessed on November 25, 2010)
California State University, Chico Meriam Library http://www.csuchico.edu/lins/handouts/scholarly.pdf (accessed on November 25, 2010)
Hussein, R., Goodman, J.: Leading with Knowledge: The Nature of Competition in the 21st Century. Sage, Thousand Oaks (1998)
Sommerville, I.: Software Engineering. Addison Wesley, Wokingham (1983)
Ambler, S.W.: Agile Modelling: Extreme Practices for eXtreme Programming and the Unified Process. John Wiley and Sons, New York (2002)
Cockburn, A., Highsmith, J.: Agile software development: The people factor. IEEE Computer 34(11), 131–133 (2001)
Kotonya, G., Sommerville, I.: Requirements Engineering Processes and Techniques. John Wiley and Sons, New York (1998)
Kotonya, G., Sommerville, I.: Requirements engineering with viewpoints. Software Engineering 1(11), 5–18 (1996)
Vonk, R.: Prototyping: The Effective Use of CASE Technology. Prentice Hall, New York (1990)
Young, R.R.: Effective Requirements Practices. Addison-Wesley, Boston (2001)
Tyson, R.H., LaFrance, J.: Integrating Role-Play into Software Engineering Courses. Journal of Computing Sciences in Colleges 22(2), 32–38 (2006)
Berstein, L., Klappholz, D., Kelley, C.: Eliminating adversion to software process in computer science students and measuring the results. In: Proceedings of the 15th Conference on Software Engineering Education and Training (2002)
Sullivan, S.A.: A software project management course role play team project approach emphasizing written and oral communication skills. In: Proceedings of the 24th SIGCSE Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education (1993)
Skehan, P.: A Cognitive Approach To Language Learning. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1998)
Henry, T.R., LaFrance, J.: Integrating role-play into software engineering courses. Journal of Computing Science in Colleges 22(2), 32–88 (2006)
Ludi, S., Natarajan, S., Reichlmayr, T.: An introductory software engineering course that facilitates active learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th SIGCSE Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education, pp. 302–306 (2005)
Jones, J.: Participatory teaching methods in computer science. In: Proceedings of the 18th SIGCSE Technical Symposium On Computer Science Education (1987)
Andrianoff, S., Levine, D.: Role playing in an object-oriented world. In: Proceedings of the 33rd SIGCSE Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education (2002)
McGuffee, J.: Drama in the computer science classroom. Journal of Computing Sciences in Colleges 19(4), 292–298 (2004)
Kane, L.: Learners and active learning methodologies. International Journal of Lifelong Education 23(3), 275–286 (2004)
Buchanan, D., Huczynski, A.: Organizational Behaviour. Prentice Hall, London (1995)
Kheong, L.S.: Framework for structuring learning in problem-based learning, http://pbl.tp.edu.sg/Understanding%20PBL/Articles/lyejayarartna.pdf (accessed December 6, 2009)
Clarke, S., Thomas, R., Adams, M.: Developing case studies to enhance student learning, http://crpit.com/confpapers/CRPITV42Clarke.pdf (accessed December 6, 2009)
Aha, D.W.: Case-based learning algorithms. In: Proceedings of DARPA Workshop on Case-Based Reasoning, pp. 147–157. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo (1991)
Cardie, C.: Using decision trees to improve case-based learning, fMJ: http://www.cs.cornell.edu/home/cardie/papers/ml-93.ps+8.+C.+Cardie,+1991.+%E2%80%9CUsing+Decision+Trees+to+Improve+Case-Based+Learning&cd=1&hl=en&ct=clnk&gl=sg (accessed December 6, 2009)
Drummond, C.: Using a case base of surfaces to speed-up reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Case-Based Reasoning Research and Development, pp. 435–444. Springer, London (1997)
Kolodner, J.L.: Case-Based Learning. Morgan-Kaufmann, San Mateo (1993)
Drucker, P.F.: The coming of the new organization. Harvard Business Review on Knowledge Management, 1–19 (1998)
Hussein, R., Goodman, J.: Leading with Knowledge: The Nature of Competition in the 21st Century. Sage, Thousand Oaks (1998)
Davenport, T., Prusak, L.: Working Knowledge: How Organizations Manage What They Know. Harvard Business School Press, Boston (1998)
Chua, B.B., Dyson, L.E.: Applying the ISO 9126 model to the evaluation of an e-learning System. In: Proceedings of the 21st ASCILITE Conference, pp. 184–190 (2004)
Chua, B.B., Bernardo, D.V.: Introducing scholarly articles: A way for attaining educational sustainability. In: 2nd International IEEE Conference on Mobile, Hybrid, and On-Line Learning (2010)
Kotter, J.P., Schlesinger, L.A.: Choosing strategies for change. Harvard Business Review, 1–13 (2008)
Kaplan, M.A.: Learning to converse in a foreign language: the Reception Game. Simulation and Gaming, 149–163 (2008)
University of Technology, Sydney, Think. Change. Do, http://www.uts.edu.au/ (accessed November 26, 2010)
Chua, B.B., Bernardo, D.V.: Integrating scholarly articles within e-learning courses: a framework. In: Proceedings of the 16th Annual SIGCSE Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education, ITiCSE 2011, Darmstadt, Germany, June 27-29. ACM (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chua, B.B. (2011). Role Playing for Scholarly Articles. In: Kim, Th., et al. Software Engineering, Business Continuity, and Education. ASEA 2011. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 257. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27207-3_72
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27207-3_72
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-27206-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-27207-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)