Abstract
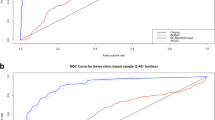
In this work we perform a comparison of machine learning methods in an association study with the goal of finding reliable classifiers that predict the presence or absence of breast cancer based on single nucleotide polymorphisms from the BRCA1, BRCA2 and TP53 genes. We emphasize how misleading some common statistical measures can be when evaluating classifiers whose learning was biased by an unbalanced dataset, as in our case. Then we compare and discuss the format of different solutions from the interpretability point of view, revealing a correlation between size and performance of the solutions, and also identify a small set of preferred features that agree with previously published work. We designate CART regression trees as the best classifiers, both in terms of performance and interpretability, and discuss how to improve the results reported here.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aha, D., Kibler, D., Albert, M.: Instance-based learning algorithms. Machine Learning 6(1), 37–66 (1991)
Anunciação, O., Gomes, B., Vinga, S., Gaspar, J., Oliveira, A., Rueff, J.: A Data Mining Approach for the Detection of High-Risk Breast Cancer Groups. In: Advances in Bioinformatics, pp. 43–51 (2010)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Machine Learning 45(1), 5–32 (2001)
Breiman, L., Friedman, J., Olshen, R., Stone, C.: Classification and Regression Trees. Wadsworth International Group, Belmont (1984)
Broomhead, D., Lowe, D., Signals, R., Malvern, R.: Radial basis functions, multi-variable functional interpolation and adaptive networks (1988)
Cho, Y., Ritchie, M., Moore, J., Park, J., Lee, K., Shin, H., Lee, H., Park, K.: Multifactor-dimensionality reduction shows a two-locus interaction associated with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 47(3), 549–554 (2004)
Farinaccio, A., Vanneschi, L., Giacobini, M., Mauri, G., Provero, P.: On the use of genetic programming for the prediction of survival in cancer. In: GECCO, pp. 163–170 (2010)
Griffiths, A., Wessler, S., Lewontin, R., Gelbart, W., Suzuki, D., Miller, J.: Introduction to Genetic Analysis. W.H. Freeman and Co. Ltd., New York (2008)
Hardy, J., Singleton, A.: Genomewide association studies and human disease. New England Journal of Medicine 360(17), 1759–1768 (2009)
Li, M., Wang, K., Grant, S., Hakonarson, H., Li, C.: ATOM: a powerful gene-based association test by combining optimally weighted markers. Bioinformatics 25(4), 497 (2009)
Listgarten, J., Damaraju, S., Poulin, B., Cook, L., Dufour, J., Driga, A., Mackey, J., Wishart, D., Greiner, R., Zanke, B.: Predictive models for breast cancer susceptibility from multiple single nucleotide polymorphisms. Clinical Cancer Research 10, 2725–2737 (2004)
Lotz, M., Silva, S.: Application of genetic programming classification in an industrial process resulting in greenhouse gas emission reductions. In: Di Chio, C., Brabazon, A., Di Caro, G.A., Ebner, M., Farooq, M., Fink, A., Grahl, J., Greenfield, G., Machado, P., O’Neill, M., Tarantino, E., Urquhart, N. (eds.) EvoApplications 2010. LNCS, vol. 6025, pp. 131–140. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Matthews, B.: Comparison of the predicted and observed secondary structure of T4 phage lysozyme. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Structure 405(2), 442–451 (1975)
Mitchell, T.M.: Machine Learning. McGraw-Hill, New York (1997)
Moore, J., Asselbergs, F., Williams, S.: Bioinformatics Challenges for Genome-Wide Association Studies. Bioinformatics 26(4), 445–455 (2010)
Platt, J.: Fast training of support vector machines using sequential minimal optimization. Advances in Kernel Methods – Support Vector Learning (1998)
Poli, R., Langdon, W.B., McPhee, N.F.: A field guide to genetic programming. Published via http://lulu.com and freely (2008), http://www.gp-field-guide.org.uk (With contributions by J. R. Koza)
Quinlan, J.R.: C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (1993)
Ritchie, M., Hahn, L., Roodi, N., Bailey, L., Dupont, W., Parl, F., Moore, J.: Multifactor-dimensionality reduction reveals high-order interactions among estrogen-metabolism genes in sporadic breast cancer. The American Journal of Human Genetics 69(1), 138–147 (2001)
Vanneschi, L., Farinaccio, A., Giacobini, M., Mauri, G., Antoniotti, M., Provero, P.: Identification of individualized feature combinations for survival prediction in breast cancer: A comparison of machine learning techniques. In: Pizzuti, C., Ritchie, M.D., Giacobini, M. (eds.) EvoBIO 2010. LNCS, vol. 6023, pp. 110–121. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Vapnik, V.: Statistical Learning Theory. Wiley, New York (1998)
Wu, T., Chen, Y., Hastie, T., Sobel, E., Lange, K.: Genome-wide association analysis by lasso penalized logistic regression. Bioinformatics 25(6), 714–721 (2009)
Xiang, W., Can, Y., Qiang, Y., Hong, X., Nelson, T., Weichuan, Y.: MegaSNPHunter: a learning approach to detect disease predisposition SNPs and high level interactions in genome wide association study. BMC Bioinformatics 10(13) (2009)
Yang, C., He, Z., Wan, X., Yang, Q., Xue, H., Yu, W.: SNPHarvester: a filtering-based approach for detecting epistatic interactions in genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 25(4), 504 (2009)
Zhang, Y., Liu, J.: Bayesian inference of epistatic interactions in case-control studies. Nature Genetics 39(9), 1167–1173 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Silva, S., Anunciação, O., Lotz, M. (2011). A Comparison of Machine Learning Methods for the Prediction of Breast Cancer. In: Pizzuti, C., Ritchie, M.D., Giacobini, M. (eds) Evolutionary Computation, Machine Learning and Data Mining in Bioinformatics. EvoBIO 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6623. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20389-3_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20389-3_17
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-20388-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-20389-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)