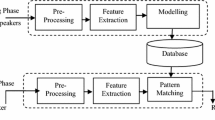
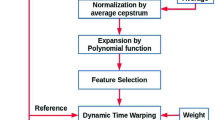
Abstract
Research in automatic speaker recognition has now spanned four decades. This paper surveys the major themes and advances made in the past 40 years of research so as to provide a technological perspective and an appreciation of the fundamental progress that has been accomplished in this important area of speech-based human biometrics. Although many techniques have been developed, many challenges have yet to be overcome before we can achieve the ultimate goal of creating human-like machines. Such a machine needs to be able to deliver satisfactory performance under a broad range of operating conditions. A much greater understanding of the human speech process is still required before automatic speaker recognition systems can approach human performance.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
References
Atal, B.S.: Text-independent speaker recognition: J.A.S.A. 52(181) (A), 83th ASA (1972)
Atal, B.S.: Effectiveness of linear prediction characteristics of the speech wave for automatic speaker identification and verification: J.A.S.A. 55(6), 1304–1312 (1974)
Beek, B., et al.: Automatic speaker recognition system: Rome Air Development Center Report (1971)
Bimbot, F.J., et al.: A tutorial on text-independent speaker verification. EURASIP Journ. on Applied Signal Processing, 430–451 (2004)
Bricker, P.D., et al.: Statistical techniques for talker identification. B.S.T.J. 50, 1427–1454 (1971)
Campbell, W.M., Campbell, J.P., Reynolds, D.A., Jones, D.A., Leek, T.R.: High-level speaker verification with support vector machines. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust., Speech, Signal Processing, pp. I-73–76 (2004)
Campbell, W.M., Campbell, J.P., Reynolds, D.A., Singer, E., Torres-Carrasquillo, P.A.: Support vector machines for speaker and language recognition. Computer Speech and Language 20(2-3), 210–229 (2006)
Cheung, M.-C., Mak, M.-W., Kung, S.-Y.: A two-level fusion approach to multimodal biometric verification. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust., Speech, Signal Processing, pp. V-485-488 (2005)
Doddington, G.R.: A method of speaker verification. J.A.S.A. 49(139) (A) (1971)
Doddington, G.R.: Speaker recognition based on idiolectal differences between speakers. In: Proc. Eurospeech, pp. 2521–2524 (2001)
Endres, W., et al.: Voice spectrograms as a function of age, voice disguise, and voice imitation. J.A.S.A. 49, 6(2), 1842–1848 (1971)
Ferguson, J. (ed.): Hidden Markov models for speech, IDA, Princeton, NJ (1980)
Furui, S.: An analysis of long-term variation of feature parameters of speech and its application to talker recognition. Electronics and Communications in Japan 57-A, 34–41 (1974)
Furui, S., et al.: Talker recognition by long time averaged speech spectrum. Electronics and Communications in Japan 55-A, 54–61 (1972)
Furui, S.: Cepstral analysis technique for automatic speaker verification. IEEE Trans. Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing ASSP-29, 254–272 (1981)
Furui, S.: Speaker-independent and speaker-adaptive recognition techniques. In: Furui, S., Sondhi, M.M. (eds.) Advances in Speech Signal Processing, pp. 597–622. Marcel Dekker (1991)
Furui, S.: Recent advances in speaker recognition. In: Proc. First Int. Conf. Audio- and Video-based Biometric Person Authentication, Crans-Montana, Switzerland, pp. 237–252 (1997)
Furui, S.: Digital Speech Processing, Synthesis, and Recognition, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York (2000)
Furui, S.: Fifty years of progress in speech and speaker recognition. In: Proc. 148th ASA Meeting (2004)
Gales, M.J.F., Young, S.J.: HMM recognition in noise using parallel model combination. In: Proc. Eurospeech, Berlin, pp. II-837-840 (1993)
Gish, H., Siu, M., Rohlicek, R.: Segregation of speakers for speech recognition and speaker identification. In: Proc. ICASSP, S13.11, pp. 873–876 (1991)
Higgins, A., et al.: Speaker verification using randomized phrase prompting. Digital Signal Processing 1, 89–106 (1991)
Juang, B.-H., Soong, F.K.: Speaker recognition based on source coding approaches. In: Proc. ICASSP, vol. 1, pp. 613–616 (1990)
Leggetter, C.J., Woodland, P.C.: Maximum likelihood linear regression for speaker adaptation of continuous density hidden Markov models. Computer Speech and Language 9, 171–185 (1995)
Li, K.P., Hughes, G.W.: Talker differences as they appear in correlation matrices of continuous speech spectra. J.A.S.A. 55, 833–837 (1974)
Li, K.P., et al.: Experimental studies in speaker verification using a adaptive system. J.A.S.A. 40, 966–978 (1966)
Martin, F., Shikano, K., Minami, Y.: Recognition of noisy speech by composition of hidden Markov models. In: Proc. Eurospeech, Berlin, pp. II-1031–1034 (1993)
Matsui, T., Furui, S.: Text-independent speaker recognition using vocal tract and pitch information. In: Proc. Int. Conf. Spoken Language Processing, Kobe, vol. 5.3, pp. 137–140 (1990)
Matsui, T., Furui, S.: Comparison of text-independent speaker recognition methods using VQ-distortion and discrete/continuous HMMs. In: Proc. ICSLP, pp. II-157–160 (1992)
Matsui, T., Furui, S.: Concatenated phoneme models for text-variable speaker recognition. In: Proc. ICASSP, pp. II-391–394 (1993)
Matsui, T., Furui, S.: Similarity normalization method for speaker verification based on a posteriori probability. In: Proc. ESCA Workshop on Automatic Speaker Recognition, Identification and Verification, pp. 59–62 (1994)
Matsui, T., Furui, S.: Speaker recognition using HMM composition in noisy environments. Computer Speech and Language 10, 107–116 (1996)
McLaren, M., Vogt, R., Baker, B., Sridharan, S.: A comparison of session variability compensation techniques for SVM-based speaker recognition. In: Proc. Interspeech, pp. 790–793 (2007)
Naik, J.M., et al.: Speaker verification over long distance telephone lines. In: Proc. ICASSP, pp. 524–527 (1989)
Petri, A., Bonastre, J.-F., Matrouf, D., Capman, F., Ravera, B.: Confidence measure based unsupervised target model adaptation for speaker verification. In: Proc. Interspeech, pp. 754–757 (2007)
Poritz, A.B.: Linear predictive hidden Markov models and the speech signal. In: Proc. ICASSP, vol. 2, pp. 1291–1294 (1982)
Pruzansky, S.: Pattern-matching procedure for automatic talker recognition. J.A.S.A. 35, 354–358 (1963)
Pruzansky, S., Mathews, M.V.: Talker recognition procedure based on analysis of variance. J.A.S.A. 36, 2041–2047 (1964)
Rabiner, L.R., Juang, B.H.: Fundamentals of Speech Recognition. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1993)
Rose, R., Reynolds, R.A.: Text independent speaker identification using automatic acoustic segmentation. In: Proc. ICASSP, pp. 293–296 (1990)
Rose, R.C., Hofstetter, E.M., Reynolds, D.A.: Integrated models of signal and background with application to speaker identification in noise. IEEE Trans. Speech and Audio Processing 2(2), 245–257 (1994)
Rosenberg, A.E., Sambur, M.R.: New techniques for automatic speaker verification. IEEE Trans. Acoustics, Speech, Signal Proc. ASSP-23(2), 169–176 (1975)
Rosenberg, A.E., Soong, F.K.: Evaluation of a vector quantization talker recognition system in text independent and text dependent models. Computer Speech and Language 22, 143–157 (1987)
Sambur, M.R.: Speaker recognition and verification using linear prediction analysis. Ph. D. Dissert., M.I.T (1972)
Siu, M., et al.: An unsupervised, sequential learning algorithm for the segmentation of speech waveforms with multiple speakers. In: Proc. ICASSP, pp. I-189–192 (1992)
Stolcke, A., Ferrer, L., Kajarekar, S., Shriberg, E., Venkataraman, A.: MLLR transforms as features in speaker recognition. In: Proc. Interspeech 2005, pp. 2425–2428 (2005)
Sugiyama, M.: Segment based text independent speaker recognition. In: Proc. Acoust., Spring Meeting of Soc. Japan, pp. 75–76 (1988) (in Japanese)
Tishby, N.: On the application of mixture AR hidden Markov models to text independent speaker recognition. IEEE Trans. Acoust., Speech, Signal Processing ASSP-30(3), 563–570 (1991)
Wilcox, L., et al.: Segmentation of speech using speaker identification. In: Proc. ICASSP, pp. I-161–164 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Furui, S. (2009). 40 Years of Progress in Automatic Speaker Recognition. In: Tistarelli, M., Nixon, M.S. (eds) Advances in Biometrics. ICB 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5558. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01793-3_106
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01793-3_106
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-01792-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-01793-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)