Abstract
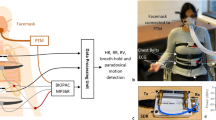
A technique for heart and respiratory rate detection using a common electronic weighing scale is proposed. For heart rate detection, the system senses force variations related to the blood accelerations in the aorta. Because respiration modulates that force signal, we can extract the respiratory rate from it. We have applied our method on three different weighing scales whose static and dynamic characteristics were first estimated by a mechanical pulse test. Their sensitivities were from 4 μV/N to 15 μV/N, and their frequency response was broad enough for heart and respiratory rate estimation. For sensing the low force variations (about 240 mN), we designed an amplifier with an overall gain about 75 × 103. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the main peaks of the pulse signal detected was up to 60 dB, which is large enough for heart rate estimation by simple signal processing methods. Respiratory rate was estimated using frequency domain analysis. The technique was tested on 16 volunteers, wearing footwear and without any additional electrodes/sensors attached to their bodies. The error was ± 0.58 beats/minute for heart rate and ± 1.40 breaths/minute for respiratory rate.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Referencias
S. Rhee, B.-H. Yang, and H. H. Asada (2001) Artifact-resistant power-efficient design of finger-ring plethysmographic sensors. IEEE Tran Biomed Eng 48: 795–805
Y.-Y. Chen, “Wireless heart rate monitor with infrared detecting module”, US20050075577A1, Apr. 7, 2005.
S. Okada, Y. Fujiwara, M. Yasuda, et al. (2006) Non-restrictive Heart Rate Monitoring Using an Acceleration Sensor, Proc. 28th International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, New York, USA, 2006, pp 5093–5096
L. E. Baker (1989) Applications of the impedance technique to the respiratory system. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag, 8: 50–52
T. Reinvuo, M. Hannula, H. Sorvoja, et al. (2006) Measurement of respiratory rate with high-resolution accelerometer and emfit pressure sensor, Proc. IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium, Houston, Texas, 2006, pp 192–195
M. Folke, L. Cernerud, M. Ekstrom, et al. (2003) Critical review of non-invasive respiratory monitoring in medical care. Med Biol Eng Comp 41: 377–383
J. Siivola (1989) New noninvasive piezoelectric transducer for recording of respiration, heart rate and body movements. Med Biol Eng Comp 27: 423–424
W. S. Johnston and Y. Mendelson (2004) Extracting breathing rate information from a wearable reflectance pulse oximeter sensor, Proc. 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, vol. 2, San Francisco, CA, 2004, pp 5388–5391
K. Watanabe, T. Watanabe, H. Watanabe, et al. (2005) Noninvasive measurement of heartbeat, respiration, snoring and body movements of a subject in bed via a pneumatic method. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52: 2100–2107
T. Koivistoinen, S. Junnila, A. Varri, et al. (2004) A new method for measuring the ballistocardiogram using EMFi sensors in a normal chair, Proc. 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, vol. 1, San Francisco, CA, 2004, pp 2026–2029
A. Matsubara and S. Tanaka (2002) Unconstrained and noninvasive measurement of heartbeat and respiration for drivers using a strain gauge, Proc. 41st. SICE Annual Conference vol. 2, 2002, pp 1067–1068
K. Hoffmann, (1989) An Introduction to Measurements using Strain Gages. Hottinger Baldwin Messtecnik, Darmstadt
A. Cuadras and O. Casas (2006) Determination of heart rate using a high-resolution temperature measurement. IEEE Sens J 6: 836–843
J. G. Webster, (1998) Medical Instrumentation: Application and Design. John Wiley and Sons, New York
M. Nagurka and S. Huang (2006) A Mass-Spring-Damper Model of a Bouncing Ball. Int J Eng Educ 22: 393–401
E. M. Spinelli, R. Pallas-Areny, and M. A. Mayosky (2003) AC-coupled front-end for biopotential measurements. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 50: 391–395
A. M. Weissler (1974) Noninvasive Cardiology. Grune & Stratton, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
González Landaeta, R., Casas, O., Pallàs Areny, R. (2007). Detección de las frecuencias cardiaca y respiratoria mediante una báscula electrónica. In: Müller-Karger, C., Wong, S., La Cruz, A. (eds) IV Latin American Congress on Biomedical Engineering 2007, Bioengineering Solutions for Latin America Health. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 18. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74471-9_104
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74471-9_104
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-74470-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-74471-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)