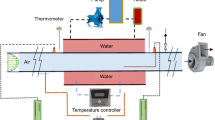
The aim of this study is to test numerically the influence that incompressible flow pulsation has on heat transfer in configurations, such as the backward facing step, that appear in micro-electro mechanical systems (MEMS) and that are not very efficient from the thermal point of view. Two control parameters have been used to increase heat transfer: velocity pulsation frequency and pressure gradient amplitude at the inlet section. The working fluid is water with temperature dependent viscosity and thermal conductivity. The results obtained show that the time averaged Nusselt number grows when using appropriate flow pulsations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. F. Armaly, F. Durst and J. Pereira. Experimental and theoretical investigation of backwards facing step flow. J. Fluid. Mech. 127 (1983), 473-496.
F. Durst and J. C. F. Pereira. Time dependent laminar backward facing step flow in a two dimensional duct. J. Fluids. Eng. 110 (1988). 289-296.
L. Kaiktsis, G. E. Kairnaidakis and S. A. Orszag. Onset of three dimen- sionality, equilibria, and early transition in flow over a backward facing step. J. Fluid. Mech. 231 (1991), 501-558.
D. Barkley, M. G. Gomes, and R. Henderson. Three dimensional insta- bility in flow over a backward facing step. J. Fluid. Mech. 473 (2002) 167-190.
J. C. Yu, Z. X. Li, and T. S. Zhao. An analytical study of pulsating laminar heat convection in a circular tube with constant heat flux. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 47 (2004) 5297-5301.
B. Mendez and A. Velazquez. Finite Point Solver for the simulation of 2-D laminar incompressible unsteady flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 193 (2004) 825-848.
J. C. Tannehill, D. A. Anderson and R. H. Pletcher. Computational fluid mechanics and heat transfer. Taylor and Francis. Philadelphia, 1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Velazquez, A., Arias, J.R., Mendez, B. (2008). Model and Method to Increase the Thermal Efficiency of Micro-Heat Exchangers for Aerospace Applications. In: Bonilla, L.L., Moscoso, M., Platero, G., Vega, J.M. (eds) Progress in Industrial Mathematics at ECMI 2006. Mathematics in Industry, vol 12. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71992-2_129
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71992-2_129
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-71991-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-71992-2
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)