Abstract
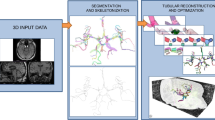
The analysis of vessel morphology and connectivity has an impact on a number of cardiovascular and neurovascular applications by providing patient-specific high-level quantitative features such as spatial location, direction and scale. In this paper we present an end-to-end approach to extract an acyclic vascular tree from angiographic data by solving a connectivity-enforcing anisotropic fast marching over a voxel-wise tensor field representing the orientation of the underlying vascular tree. The method is validated using synthetic and real vascular images. We compare VTrails against classical and state-of-the-art ridge detectors for tubular structures by assessing the connectedness of the vesselness map and inspecting the synthesized tensor field as proof of concept. VTrails performance is evaluated on images with different levels of degradation: we verify that the extracted vascular network is an acyclic graph (i.e. a tree), and we report the extraction accuracy, precision and recall.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annunziata, R., Kheirkhah, A., Hamrah, P., Trucco, E.: Scale and curvature invariant ridge detector for tortuous and fragmented structures. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 588–595. Springer, Cham (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_70
Antiga, L., Piccinelli, M., Botti, L., Ene-Iordache, B., Remuzzi, A., Steinman, D.A.: An image-based modeling framework for patient-specific computational hemodynamics. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 46, 1097 (2008)
Arsigny, V., Fillard, P., Pennec, X., Ayache, N.: Log-euclidean metrics for fast and simple calculus on diffusion tensors. Magn. Reson. Med. 56, 411–421 (2006)
Benmansour, F., Cohen, L.D.: Tubular structure segmentation based on minimal path method and anisotropic enhancement. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 92, 192–210 (2011)
Bergman, R.A., Afifi, A.K., Miyauchi, R.: Illustrated encyclopedia of human anatomic variation: Circle of Willis. www.anatomyatlases.org/AnatomicVariants/
Bullitt, E., Aylward, S., Liu, A., Stone, J., Mukherji, S.K., Coffey, C., Gerig, G., Pizer, S.M.: 3D graph description of the intracerebral vasculature from segmented MRA and tests of accuracy by comparison with x-ray angiograms. In: Kuba, A., Šáamal, M., Todd-Pokropek, A. (eds.) IPMI 1999. LNCS, vol. 1613, pp. 308–321. Springer, Heidelberg (1999). doi:10.1007/3-540-48714-X_23
Cardoso, M.J., Modat, M., Vercauteren, T., Ourselin, S.: Scale factor point spread function matching: beyond aliasing in image resampling. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9350, pp. 675–683. Springer, Cham (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-24571-3_81
Frangi, A.F., Niessen, W.J., Vincken, K.L., Viergever, M.A.: Multiscale vessel enhancement filtering. In: Wells, W.M., Colchester, A., Delp, S. (eds.) MICCAI 1998. LNCS, vol. 1496, pp. 130–137. Springer, Heidelberg (1998). doi:10.1007/BFb0056195
Gülsün, M.A., Funka-Lea, G., Sharma, P., Rapaka, S., Zheng, Y.: Coronary centerline extraction via optimal flow paths and CNN Path pruning. In: Ourselin, S., Joskowicz, L., Sabuncu, M.R., Unal, G., Wells, W. (eds.) MICCAI 2016. LNCS, vol. 9902, pp. 317–325. Springer, Cham (2016). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-46726-9_37
Hamarneh, G., Jassi, P.: VascuSynth: simulating vascular trees for generating volumetric image data with ground-truth segmentation and tree analysis. Comput. Med. Imag. Graph. 34, 605–616 (2010)
Kwitt, R., Pace, D., Niethammer, M., Aylward, S.: Studying cerebral vasculature using structure proximity and graph kernels. In: Mori, K., Sakuma, I., Sato, Y., Barillot, C., Navab, N. (eds.) MICCAI 2013. LNCS, vol. 8150, pp. 534–541. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-40763-5_66
Law, M.W.K., Chung, A.C.S.: Three dimensional curvilinear structure detection using optimally oriented flux. In: Forsyth, D., Torr, P., Zisserman, A. (eds.) ECCV 2008. LNCS, vol. 5305, pp. 368–382. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-88693-8_27
Lesage, D., Angelini, E.D., Bloch, I., Funka-Lea, G.: A review of 3D vessel lumen segmentation techniques: models, features and extraction schemes. Med. Image Anal. 13, 819–845 (2009)
Lin, Q.: Enhancement, extraction, and visualization of 3D volume data (2003)
Oppenheim, A.V., Schafer, R.W.: Discrete-Time Signal Processing. Pearson Higher Education, New York (2010)
Schaap, M., Manniesing, R., Smal, I., Walsum, T., Lugt, A., Niessen, W.: Bayesian tracking of tubular structures and its application to carotid arteries in CTA. In: Ayache, N., Ourselin, S., Maeder, A. (eds.) MICCAI 2007. LNCS, vol. 4792, pp. 562–570. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-75759-7_68
Wang, C., Oda, M., Hayashi, Y., Yoshino, Y., Yamamoto, T., Frangi, A.F., Mori, K.: Tensor-based graph-cut in riemannian metric space and its application to renal artery segmentation. In: Ourselin, S., Joskowicz, L., Sabuncu, M.R., Unal, G., Wells, W. (eds.) MICCAI 2016. LNCS, vol. 9902, pp. 353–361. Springer, Cham (2016). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-46726-9_41
Zuluaga, M.A., Rodionov, R., Nowell, M., Achhala, S., Zombori, G., Mendelson, A.F., Cardoso, M.J., Miserocchi, A., McEvoy, A.W., Duncan, J.S., Ourselin, S.: Stability, structure and scale: improvements in multi-modal vessel extraction for SEEG trajectory planning. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 10, 1227–1237 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The study is co-funded from the EPSRC grant (EP/H046410/1), the Wellcome Trust and the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) University College London Hospitals (UCLH) Biomedical Research Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Moriconi, S., Zuluaga, M.A., Jäger, H.R., Nachev, P., Ourselin, S., Cardoso, M.J. (2017). VTrails: Inferring Vessels with Geodesic Connectivity Trees. In: Niethammer, M., et al. Information Processing in Medical Imaging. IPMI 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10265. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59050-9_53
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59050-9_53
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-59049-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-59050-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)