Abstract
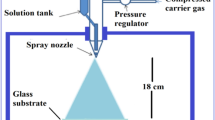
Tin oxide is a transparent conductive oxide with potential use in heterojunction thin film solar cells such as CdS/CdTe solar cell as a fore contact, and in optoelectronic devices. These applications require a deep understanding of the optical properties of the material and optimization of its optical parameters. Fluorine doping of the films increases their conductivity, which is important for high cell performance. In this work fluorine doped tin oxide (SnO2:F) thin films were prepared by the spray pyrolysis (SP) technique on glass substrates. The films were found to be polycrystalline as seen in the scanning electron microscope (SEM) images. The transmittance spectra of the films were measured at room temperature and used to deduce the optical parameters such as the direct and indirect optical bandgap energies, Urbuch tail width, extinction coefficient, and refractive index. The dependence of these parameters on film thickness was investigated.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khudheir A. Mishjil et al., “Influence of Copper Doping on the Structural and Optical Properties of Sprayed SnO2 Thin Film,” Journal of Electron Devices, 14 (2012), 1170–1177.
Songqing Zhao et al., “Effect of Ambient Oxygen Pressure on Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of SnO Thin Films,” Rare Metals, 25 (6) (2006), 1–4.2
H.A. Mohamed, “Properties of Pure and Light Antimony-Doped Tin Oxide Thin Films Prepared by e-Beam Technique,” Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, 3(9) (2009), 936– 941.
Sung Uk Lee, Jin-Hyo Boo, and Byungyou Hong, “Structural, Electrical, and Optical Properties of SnO2:Sb Films Prepared on Flexible Substrate at Room Temperature,” Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50 (2011), 01AB10.
R.G. Dhere et al., Characterization of SnO2 Films Prepared Using Tin Tetrachloride and Tetra Methyl Tin Precursors,” (Paper Presented at the National Center for Photovoltaics Program Review Meeting, Denver, Colorado, September 8–11, 1998).
M.A. Batal, G. Nashed, and Fares Haj Jneed, “Electrical Properties of Nanostructure Tin Oxide Thin Film Doped with Copper Prepared by Sol-Gel Method,” Lat. Am. J. Phys. Educ., 6 (2) (2012), 311–316.
Shadia J. Ikhmayies and Riyad N. Ahmad-Bitar, “An Investigation of the Bandgap and Urbach Tail of Vacuum-Evaporated SnO2 Thin Films,” Renewable Energy, 49 (2013), 143–146.
Shadia J. Ikhmayies, “Properties of Amorphous SnO2 Thin Films Prepared by Thermal Evaporation,” International Journal of Materials and Chemistry, 2(4) (2012), 173–177.
T.R. Giraldi et al., “Effect of Thickness on the Electrical and Optical Properties of Sb Doped SnO2 (ATO) Thin Films,” Journal of Electroceramics, 13 (2004), 159–165.
F.de Moure-Flores et al., “SnO2:F Thin Films Deposited by RF Magnetron Sputtering: Effect of the SnF2 Amount in the Target on the Physical Properties,” Revista Mexicana de Física, 59 (2013), 335–338.
A.A. Yadava et al., “Electrical, Structural and Optical Properties of SnO2:F Thin Films: Effect of the Substrate Temperature,” Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 488 (2009), 350–355.
E. Elangovan, and K. Ramamurthi, “Optoelectronic Properties of Spray Deposited SnO2:F Thin Films for Window Materials in Solar Cells,” Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, 5(1) (2003), 45 – 54.
Shadia J. Ikhmayies and Riyad N. Ahmad-Bitar, “An investigation of the Bandgap and Urbach Tail of Spray-Deposited SnO2:F Thin Films,” Phys. Scr., 84 (2011), 055801.
V. Bilgin et al., “The Effect of Substrate Temperature on the Structural and Some Physical Pproperties of Ultrasonically Sprayed CdS Films,” Materials Chemistry and Physics, 94 (2005), 103–108.
Y. Natsume, H. Sakata, and T. Hirayama, “Low Temperature Electrical Conductivity and Optical Absorption Edge of ZnO Films Prepared by Chemical Vapor Deposition,” Phys. Stat. Sol. (A), 148 (1995), 485–495.
Saeed Salem Babkair, Najat Mohammad Al-Twarqi, and Azhar Ahmad Ansari, Optical characterization of CdTe films for solar cell applications, Karachi University Journal of Science 39 (2011) 1–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society)
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ikhmayies, S.J. (2015). Thickness Dependence of the Optical Parameters of Spray-Deposited SnO2:F Thin Films. In: TMS 2015 144th Annual Meeting & Exhibition. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48127-2_74
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48127-2_74
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-48608-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-48127-2
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)