Abstract
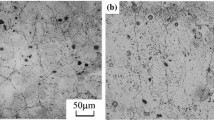
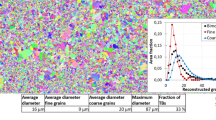
Recent results show that fatigue crack initiation in very high cycle fatigue regime can occur at a non-defect origin in the matrix. The mechanism is not well understood. This paper provides a study on the influence of cyclic loading on the damage behavior at grain and twin boundaries in Alloy 690 material. The results show that the strains in the fatigue-tested specimen were highly localized, which were mainly caused by the dislocation accumulation in the grains with high Schmid factors during each small cyclic loading. This has led to the formation of local fine grain area consisting of numbers of new twins. The study also shows that the impingement between slip bands and grain or twin boundary is one of the main fatigue damage mechanisms. The results in this paper indicate that the role of a twin or grain boundary to block dislocation slip transmission depends on crystal orientation, Schmid factor and boundary orientations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. A. Meyers, Acta Metallurgical, 26 (1978), p. 951.
J. W. Christina, S. Mahajan, Prog. Mater. Sci. 39 (1995), p. 1.
[3] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crystal_twinning
K. Lu, L. Lu and S. Suresh, Science 324 (2009), p. 349.
N. Thompson, N. Wadsworth, N. Louat, Philos. Mag. 1 (1956), p. 113.
Z. Wang, H. Margolin, Metall. Trans. 16A (1985), p. 873.
A. Heniz, P. Neumann, Acta Metall. Mater. 38 (1990), p. 1933.
M.D. Sangid, T. Ezaz, H. Sehitoglu, I.M. Robertson, Acta Mater. 59 (2011), p. 283.
D. Michael, H.J. Sangid, H. Sehitoglu, Acta Mater. 59 (2011), p. 328.
L. L. Li, Z. J. Zhang, O. Zhang and Z. F. Zhang, Scripta Mater, 65 (2011), p. 505.
S. E. Stanzl-Tschegg and B. Schönbauer, Inter. J. of Fatigue 32 (2010), p. 886.
H Knobbe, P Köster, U Krupp, H-J Christ1, C-P Fritzen, Journal of Physics: Conference Series 240 (2010) 012–061.
C. Wang, D. Wagner and C. Bathias, Proc. of ICF 13, (2013).
L. Kunz, P. Lukas and M. Svoboda, Mater. Sci. and Eng. A 424 (2006), p. 97.
A. Weidner, D. Amberger, F. Pyczak, B. Schönbauer, S. Stanzl-Tschegg, H. Mughrabi, International Journal of Fatigue 32 (2010), p. 872.
G. Chai, N. Zhou, S. Ciurea, M. Andersson, and R. Lin Peng, Scripta Materialia 66 (2012), p. 769.
Q. Yu, J. Zhang, and Y. Jiang, Philosophical Magazine Letters, vol. 91(2011), p. 757.
B. M. Morrow, R. J. McCabe, E. K. Cerreta, C. N. Tomé, Metall. and Mater. Transactions A, 574 (2013), p. 157.
U. Essmann, U. Gösele, H. Mughrabi, Philos. Mag. 44 (1981), p. 405.
Y.H. Kim, C. Laird, Acta Metall. 26 (1976), p. 789.
G Chai, Inter. J. of Fatigue, 28 (2006), p. 1533.
R. Lillbacka, G. Chai, M. Ekh, P. Liu, E. Johnson, K. Runesson, Acta Materialia 55 (2007), p. 5359.
U. Krupp, H. Knobbe, H-J. Christ, P. Köster, C-P. Fritzen, Inter. J. of Fatigue 32 (2010), p. 914.
P. Zhang, Z.J. Zhang, L.L. Li and Z.F. Zhang, Scripta Materialia 66 (2012), p. 854.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society)
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chai, G. (2015). Damage Behaviors at Twin and Grain Boundary in Alloy 690 Material in Very High Cycle Fatigue Regime. In: TMS 2015 144th Annual Meeting & Exhibition. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48127-2_120
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48127-2_120
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-48608-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-48127-2
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)