Abstract
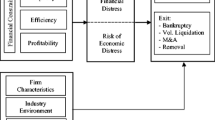
A meta-analysis is a strategic tool to be used in developing new models based on existing ones found in the literature. The implementation of the meta-analysis on the current models of subsidiary exit among 51 academic papers, revealed that there are six important constructs, i.e., parent firm factors, environmental factors at target country, type of experience, organizational characteristics, experience, investment strategy, and subsidiary exit. At least 21 independent variables should be considered in future attempts of measuring or assessing subsidiary exit. US firms compared to Japanese and Korean firms have stronger relationships of the antecedent factors with subsidiary exit indicating their higher sensitivity to changes to factors influencing divestments. Finally, the study reveals 11 significant relationships which are formulated to a relational model which can be exploited in future studies on subsidiary exit/divestitures.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharoni, Y. (1966). The foreign investment decision process. USA: Harvard.
Anand, J., Mesquita, L. F., & Vassolo, R. S. (2009). The dynamics of multimarket competition in exploration and exploitation activities. Academy of Management Journal, 52(4), 802–821.
Baden-Fuller, C. W. F. (1989). Exit from declining industries and the case of steel castings. The Economic Journal, 99, 949–961.
Belderbos, R., & Zou, J. (2006). Divestment of foreign manufacturing affiliates: Country platforms, multinational plant networks, and foreign investor agglomeration. Working Paper, MSI 0601, Department of Managerial Economics, Strategy and Innovation, Catholic University of Leuven, file:///C:/Users/dcoudoun/Downloads/SSRN-id944741.pdf.
Belderbos, R., & Zou, J. (2007). On the growth of foreign affiliates: Multinational plant networks, joint ventures, and flexibility. Journal of International Business Studies, 38, 1095–1112.
Belderbos, R., & Zou, J. (2009). Real options and foreign affiliate divestments: A portfolio perspective. Journal of International Business Studies, 40, 600–620.
Benito, G. R. G. (1997). Divestment of foreign production operations. Applied Economics, 29, 1365–1377.
Bergh, D. D. (1997). Predicting divestiture of unrelated acquisitions: An integrative model of ex ante conditions. Strategic Management Journal, 18(9), 715–731.
Berry, H. (2004). Corporate divestment: The influence of foreign investment strategies. Working paper at The Warton School, Department of Management, University of Pennsylvania.
Berry, H. (2010). Why do firms divest? Organization Science, 21(2), 380–396.
Bloomberg. (2013). http://www.bloomberg.com/bw/articles/2013-09-12/europes-countries-ranked-by-debt-per-capita
Boddewyn, J. J., & Torneden, R. (1973). US foreign divestment: A preliminary survey. Journal of World Business, Summer, 25–29.
Boddewyn, J. J. (1979). Foreign divestment: Magnitute and factors. Journal of International Business Studies, Spring, 21–27.
Boddewyn, J. J. (1983). Foreign direct divestment theory: Is it the reverse of FDI theory? Review of World Economics, 119(2), 345–355.
Brauer, M., & Schimmer, M. (2010). Performance effects of corporate divestiture programs. Journal of Strategy and Management, 3(2), 84–109.
Brauer, M. F., & Wiersema, M. F. (2012). Industry divestiture waves: How a firm’s position influences investor returns. Academy of Management Journal, 55(6), 1472–1492.
Brooke, M. Z., & Remmers, H. L. (1977). The international firm. London, UK: Pitman Publishing Ltd.
Chan, C. M., Makino, S., & Isobe, T. (2006). Interdependent behavior in foreign direct investment: The multi-level effects of prior entry and prior exit on foreign market entry. Journal of International Business Studies, 37, 612–665.
Chung, C. C., Lee, S.-H., & Lee, J.-Y. (2013). Dual-option subsidiaries and exit decisions during times of economic crisis. Management International Review, 53, 555–577.
Chung, C. C., Lee, S.-H., Beamish, P. W., Southam, C., & Nam, D. (2013). Pitting real options theory against risk diversification theory: International diversification and joint ownership control in economic crisis. Journal of World Business, 48, 122–136.
Cui, A. S., & Kumar, M. V. S. (2012). Termination of related and unrelated joint ventures: A contingency approach. Journal of Business Research, 65, 1202–1208.
Dai, L., Eden, L., & Beamish, P. W. (2013). Place, space, and geographical exposure: Foreign subsidiary survival in conflict zones. Journal of International Business Studies, 44, 554–578.
Damaraju, N. L., Barney, J. B., & Makhija, A. K. (2015). Real options in divestment alternatives. Strategic Management Journal, 36, 728–744.
Decker, C., & Mellewigt, T. (2012). Business exit and strategic change: Sticking to the knitting or striking a new path? British Journal of Management, 23, 165–178.
Delios, A., & Beamish, P. W. (2001). Survival and profitability: The roles of experience and intangible assets in foreign subsidiary performance. Academy of Management Journal, 44(5), 1028–1038.
Delios, A., Xu, D., & Beamish, P. W. (2008). Within-country product diversification and foreign subsidiary performance. Journal of International Business Studies, 39, 706–724.
Demirbag, M., Apaydin, M., & Tatoglu, E. (2011). Survival of Japanese subsidiaries in the Middle East and North Africa. Journal of World Business, 46, 411–425.
Dunning, J. H. (1981). International production and the multinational enterprise. London, UK: George Allen & Unwin Ltd.
Durand, R., & Vergne, J-P. (2014). Asset divestment as a response to media attacks in stigmatized industries. Strategic Management Journal, online early view in Wiley Online Library. doi:10.1002/smj.2280.
Engel, D., Procher, V., & Schmidt, C. R. (2013). Does firm heterogeneity affect foreign market entry and exit symmetrically? Empirical evidence for French firms. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 85, 35–47.
Elfenbein, D. W., & Knott, A. M. (2014). Time to exit: Rational, behavioural, and organizational delays. Strategic Management Journal, http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1641242.
Farah, B. E. (2014). Multinational enterprise parent-foreign subsidiary governance. Western University. Unpublished PhD supervised by Professor P.W. Beamish.
Gaur, A. S., & Lu, J. W. (2007). Ownership strategies and survival of foreign subsidiaries: Impacts of institutional distance and experience. Journal of Management, 33(1), 84–110.
Geyskens, I., Steenkamp, J.-B. E. M., & Kumar, N. (1999). A meta-analysis of satisfaction in marketing channel relationships. Journal of Marketing Research, 36, 223–238.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Harrigan, K. R. (1980). Strategies for declining industries. Journal of Business Strategy, 1(2), 20–34.
Hayward, M. L. A., & Shimizu, K. (2006). De-commitment to losing strategic action: Evidence from the divestiture of poorly performing acquisitions. Strategic Management Journal, 27, 541–557.
Hennart, J.-F., Kim, D.-J., & Zeng, M. (1998). The impact of joint venture status on the longevity of Japanese stakes in US manufacturing affiliates. Organization Science, 9(3), 382–395.
Hoskisson, R. E., Johnson, R. A., & Moesel, D. D. (1994). Corporate divestiture intensity in restructuring firms: effects of governance, strategy, and performance. Academy of Management Journal, 37(5), 1207–1251.
Huedo-Medina, T., Sanchez-Meca, J., Marin-Martinez, F., & Botella, J. (2006). Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I2 index? CHIP Documents. Paper 19. http://digitalcommons.uconn.edu/chip_docs/19.
Hultman, M., Katsikeas, C. S., & Robson, M. J. (2011). Export promotion strategy and performance: The role of international experience. Journal of International Marketing, 19(4), 17–39.
Kim, T.-Y., Delios, A., & Xu, D. (2010). Organizational geography, experiential learning and subsidiary exit: Japanese foreign expansions in China, 1979–2001. Journal of Economic Geography, 10, 579–597.
Kindleberger, C. F. (1969). American business abroad. USA: Yale.
Van Kranenburg, H., Cloodt, M., & Hagedoorn, J. (2001). An exploratory study of recent trends in the diversification of Dutch publishing companies in the multimedia + information industries. International Studies of Management & Organization, 31(1), 64–86.
Larimo, J. (2007). International joint venture performance: Impact of performance measures and foreign parent, target country and investment specific variables on performance. In G. Cliquet, G. Hendriks, M. Tuunanen, & J. Windsperger (Eds.), Economics and management of networks: Franchising, strategic alliances and co-operatives (pp. 393–418). New York: Springer.
Lee, D., & Madhavan, R. (2010). Divestiture and firm performance: A meta-analysis. Journal of Management, 36(6), 1345–1371.
Lee, G., Folta, T. B., & Lieberman, M. (2010). Relatedness and market exit. Working Paper, INSEAD.
Li, J. (1995). Foreign entry and survival: Effects of strategic choices on performance in international markets. Strategic Management Journal, 16(5), 333–351.
Li, R., & Liu, Z. (2015). What causes the divestment of multinational companies in China? A subsidiary perspective. Journal of Business Theory and Practice, 3(1), 81–89.
Lu, J. W., & Hébert, L. (2005). Equity control and the survival of international joint ventures: A contingency approach. Journal of Business Research, 58, 736–745.
Lu, J. W., & Xu, D. (2006). Growth and survival of international joint ventures: An external-internal legitimacy perspective. Journal of Management, 32(3), 426–448.
Makino, S., Chan, C. M., Isobe, T., & Beamish, P. W. (2007). Intended and unintended termination of international joint venture. Strategic Management Journal, 28, 1113–1132.
Markides, C. C. (1995). Diversification, restructuring and economic performance. Strategic Management Journal, 16, 101–118.
Mariotti, S., & Piscitello, L. (1999). Is divestment a failure or part of a restructuring strategy? The case of Italian transnational corporations. Transnational Corporations, 8(3), 25–51.
Park, S. H., & Ungson, G. R. (1997). The effect of national culture, organizational, complementarity, and economic motivation on joint venture dissolution. Academy of Management Journal, 40(2), 279–307.
Pathak, S., Hoskisson, R. E., & Johnson, R. A. (2014). Settling up in CEO compensation: The impact of divestiture intensity and contextual factors in refocusing firms. Strategic Management Journal, 35, 1124–1143.
Pattnaik, C., & Lee, J. Y. (2014). Distance and divestment of Korean MNC affiliates: The moderating role of entry mode and experience. Asia Pacific Business Review, 20(1), 174–196.
Peng, G. Z., & Beamish, P. W. (2014). The effect of host country long term orientation on subsidiary ownership and survival. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 31, 423–453.
Reuer, J. J., & Tong, T. W. (2005). Real options in international joint ventures. Journal of Management, 31(3), 403–423.
Rosenthal, R., & DiMatteo, M. R. (2001). Meta-analysis: Recent developments in quantitative methods for literature reviews. Annual Review Psychology, 52, 59–82.
Sachdev, J. C. (1976). A framework for the planning of disinvestment policies for multinational companies. Ph.D. Thesis, International Business Unit, University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology.
Sarkar, M. B., Echambadi, R., Agarwal, R., & Sen, B. (2006). The effect of the innovative environment on exit of entrepreneurial firms. Strategic Management Journal, 27, 519–539.
Shaver, J. M., Mitchell, W., & Yeung, B. (1997). The effect of own-firm and other-firm experience on foreign direct investment survival in the United States, 1987–92. Strategic Management Journal, 18(10), 811–824.
Shimizu, K., & Hitt, M. A. (2005). What constrains or facilitates divestitures of formerly acquired firms? The effects of organizational inertia. Journal of Management, 31(1), 50–72.
Shoham, A., Rose, G. M., & Kropp, F. (2005). Market orientation and performance: A meta-analysis. Marketing Intelligence and Planning, 23(5), 435–454.
Shoham, A., Ruvio, A., Vigola-Gadot, E., & Schwabsky, N. (2006). Market orientations in the non-profit and voluntary sector: A meta-analysis of their relationships with organizational performance. Nonprofit and Voluntary Sector Quarterly, 35(3), 453–476.
Song, S. (2014a). Subsidiary divestment: The role of multinational flexibility. Management International Review, 54, 47–70.
Song, S. (2014b). Entry mode irreversibility, host market uncertainty, and foreign subsidiary exits. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 31, 455–471.
Song, S. (2014c). Unfavorable market conditions, institutional and financial development, and exits of foreign subsidiaries. Journal of International Management, 20, 279–289.
Song, S. (2015). Exchange rate challenges, flexible intra-firm adjustments and subsidiary longevity. Journal of World Business, 50, 36–45.
Steensma, H. K., & Lyles, M. A. (2000). Explaining IJV survival in a transitional economy through social exchange and knowledge-based perspectives. Strategic Management Journal, 21, 831–851.
Tan, Q., & Sousa, C. M. P. (2015). A framework for understanding firms’ foreign exit behavior. In S. Zou, H. Xu, L. H. Shi (Eds.), Entrepreneurship in international marketing. Advances in International Marketing (Vol. 25, pp. 223–238).
Wang, Y., & Larimo, J. (2015). Impact of ownership level on subsidiary survival in foreign acquisitions, In 13th IB Vaasa Conference.
Wu, J., Xu, D., & Phan, P. H. (2011). The effects of ownership concentration and corporate debt on corporate divestitures in Chinese listed firms. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 28, 95–114.
Xia, J., & Li, S. (2013). The divestiture of acquired subunits: A resource dependence approach. Strategic Management Journal, 3, 131–148.
Xu, D., & Lu, J. W. (2007). Technological knowledge, product relatedness, and parent control: The effect on IJV survival. Journal of Business Research, 60, 1166–1176.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Appendix
Appendix
See Table 3.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Academy of Marketing Science
About this paper
Cite this paper
Coudounaris, D.N. (2017). A Meta-analysis on Subsidiary Exit. In: Stieler, M. (eds) Creating Marketing Magic and Innovative Future Marketing Trends. Developments in Marketing Science: Proceedings of the Academy of Marketing Science. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45596-9_155
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45596-9_155
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-45595-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-45596-9
eBook Packages: Business and ManagementBusiness and Management (R0)