Abstract
The content of this chapter is mainly based on the publication “Quantum entanglement of high angular momenta” (Fickler et al., Science 338:640, 2012, [1]). The chapter will describe a novel way of entangling two photons in the transverse spatial degree of freedom (DOF) in a very efficient, clean and flexible way. Moreover, it allows the entanglement of very higher-order modes, which carry a large amount of orbital angular momentum (OAM) quanta. To verify the generated entanglement of high OAM, a novel technique was developed to test the non-classicality of the state only by looking at its intensity structure. Both, the novel way to entangle two photons in the transverse spatial DOF and the new method for verifying entanglement, led to the demonstration of entanglement of the highest quantum number that has been experimentally shown till date.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution.
Buying options
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Learn about institutional subscriptionsNotes
- 1.
As it was shown earlier, the photon state can be considered to be a vector polarization state with transverse spatially varying polarization. See Sect. 2.2.5 for more information.
- 2.
A measurement of the actual pump and down conversion wavelength identified both values to be 405.5 nm and 811 nm (at 30 \(^\circ \)C crystal temperature). However, in all later descriptions the wavelengths will be labeled with “405 nm” for the pump and “810 nm” for the down converted photon pairs.
- 3.
One should be careful with the term “macroscopic”. There is no generally accepted definition about when an object or a property connected to it, can be considered macroscopic. A possible and loose definition can be found in the paper of Leggett [10].
- 4.
The scope of the experiment in [17] is a different one. There, the focus was to increase the dimensionality of entanglement.
- 5.
In an earlier investigation [1] an erroneous witness was introduced and used to show entanglement. Here, we show that only for the highest OAM quanta, namely the state
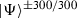 , a direct evaluation of an entanglement witness is not tenable anymore. However, it is still possible to demonstrate that the measurements cannot be described by a separable state, hence the claims from [1] remain the same.
, a direct evaluation of an entanglement witness is not tenable anymore. However, it is still possible to demonstrate that the measurements cannot be described by a separable state, hence the claims from [1] remain the same. - 6.
The accidental coincidences are calculated according to \(\textit{accs}=S_1*S_2*\tau \), where \(S_i\) labels the singles behind both slit-wheels \(i=1,2\) and \(\tau \) stands for the coincidence window.
References
Fickler, R., et al. (2012). Quantum entanglement of high angular momenta. Science, 338, 640.
Jesacher, A. (2009). Applications of spatial light modulators for optical trapping and image processing. Ph.D. thesis, Leopold-Franzens University.
Fedrizzi, A. (2008). Fundamental experiments with a high brightness source of entangled photons. Ph.D. thesis, University of Vienna.
Kim, T., Fiorentino, M., & Wong, F. N. C. (2006). Phase-stable source of polarization-entangled photons using a polarization Sagnac interferometer. Physical Review A, 73, 012316.
Fedrizzi, A., Herbst, T., Poppe, A., Jennewein, T., & Zeilinger, A. (2007). A wavelength-tunable fiber-coupled source of narrowband entangled photons. Optics Express, 15, 15377.
Żukowski, M., & Pykacz, J. (1988). Bell’s theorem: Proposition of realizable experiment using linear momenta. Physics Letters A, 127, 1.
Ramelow, S., Ratschbacher, L., Fedrizzi, A., Langford, N. K., & Zeilinger, A. (2009). Discrete tunable color entanglement. Physical Review Letters, 103, 253601.
Nagali, E., et al. (2009). Quantum information transfer from spin to orbital angular momentum of photons. Physical Review Letters, 103, 013601.
Galvez, E.J., Nomoto, S., Schubert, W. & Novenstern, M. (2011). Polarization-spatial-mode entanglement of photon pairs. In International Conference on Quantum Information, Washington, Optical Society of America.
Leggett, A. J. (2002). Testing the limits of quantum mechanics: Motivation, state of play, prospects. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 14, R415.
Aspelmeyer, M., Meystre, P., & Schwab, K. (2012). Quantum optomechanics. Physics Today, 65, 29.
Mair, A., Vaziri, A., Weihs, G., & Zeilinger, A. (2001). Entanglement of the orbital angular momentum states of photons. Nature, 412, 313.
Miatto, F. M., Yao, A. M., & Barnett, S. M. (2011). Full characterization of the quantum spiral bandwidth of entangled biphotons. Physical Review A, 83, 033816.
Jack, B., et al. (2009). Precise quantum tomography of photon pairs with entangled orbital angular momentum. New Journal of Physics, 11, 103024.
Pires, H. D. L., Florijn, H. C. B., & van Exter, M. P. (2010). Measurement of the spiral spectrum of entangled two-photon states. Physical Review Letters, 104, 020505.
Romero, J., Giovannini, D., Franke-Arnold, S., Barnett, S. M., & Padgett, M. J. (2012). Increasing the dimension in high-dimensional two-photon orbital angular momentum entanglement. Physical Review A, 86, 012334.
Krenn, M., et al. (2014). Generation and confirmation of a (100 \(\times \) 100)-dimensional entangled quantum system. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 11, 6243.
Svozilík, J., Peřina, J, Jr, & Torres, J. P. (2012). High spatial entanglement via chirped quasi-phase-matched optical parametric down-conversion. Physical Review A, 86, 052318.
Campbell, G., Hage, B., Buchler, B., & Lam, P. K. (2012). Generation of high-order optical vortices using directly machined spiral phase mirrors. Applied Optics, 51, 873.
Shen, Y., et al. (2013). Generation and interferometric analysis of high charge optical vortices. Journal of Optics, 15, 044005.
Jesacher, A., Fürhapter, S., Maurer, C., Bernet, S., & Ritsch-Marte, M. (2006). Holographic optical tweezers for object manipulations at an air-liquid surface. Optics Express, 14, 6342.
Nielsen, M. A., & Chuang, I. L. (2010). Quantum computation and quantum information. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Audretsch, J. (2008). Entangled systems. New York: Wiley.
Jha, A. K., Agarwal, G. S., & Boyd, R. W. (2011). Supersensitive measurement of angular displacements using entangled photons. Physical Review A, 83, 053829.
D’Ambrosio, V., et al. (2013). Photonic polarization gears for ultra-sensitive angular measurements. Nature Communications, 4, 2432.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Fickler, R. (2016). Entanglement of High Angular Momenta. In: Quantum Entanglement of Complex Structures of Photons. Springer Theses. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-22231-8_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-22231-8_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-22230-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-22231-8
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)


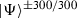 , a direct evaluation of an entanglement witness is not tenable anymore. However, it is still possible to demonstrate that the measurements cannot be described by a separable state, hence the claims from [
, a direct evaluation of an entanglement witness is not tenable anymore. However, it is still possible to demonstrate that the measurements cannot be described by a separable state, hence the claims from [