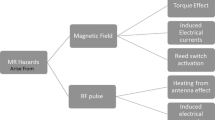
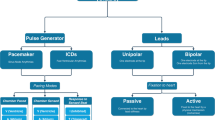
Abstract
Implantable cardiac device technology plays an ever increasing role in modern medicine and the probability of a cardiac device patient to benefit from MRI has been estimated to be 50–75 % over the lifetime of the device. Consequently the issue of MRI in patients with cardiac devices will be encountered with increasing frequency. However, in clinical practise scanning cardiac device patients is associated with logistic challenges and requires both an understanding of device indication and technology to facilitate safe scanning. This chapter will equip the interested reader with the required knowledge to set out in this interesting and expanding field.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach S, Moshage W, Diem B, Bieberle T, Schibgilla V, Bachmann K. Effects of magnetic resonance imaging on cardiac pacemakers and electrodes. Am Heart J. 1997;134(3):467–73. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9327704.
Ahmed FZ, Morris GM, Allen S, Khattar R, Mamas M, Zaidi A. Not all pacemakers are created equal: MRI conditional pacemaker and lead technology. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2013;24(9):1059–65. doi:10.1111/jce.12238.
Ainslie M, Miller C, Brown B, Schmitt M. Cardiac MRI of patients with implanted electrical cardiac devices. Heart (Br Cardiac Soc). 2013;1–7. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2013-304324.
Bottomley PA, Edelstein WA. Power deposition in whole body NMR imaging. Med Phys. 1981.
Bottomley PA, Redington RW, Edelstein WA, Schenck JF. Estimating radiofrequency power deposition in body NMR imaging. Magn Reson Med: Off J Soc Magn Reson Med Soc Magn Reson Med, 1985;2(4): 336–49. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4094551.
Bovenschulte H, Schlüter-Brust K, Liebig T, Erdmann E, Eysel P, Zobel C. MRI in patients with pacemakers: overview and procedural management. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2012;109(15):270–5. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2012.0270.
Chou CK, Bassen H, Osepchuk J, Balzano Q, Petersen R, Meltz M, Cleveland R, Lin JC, Heynick L. Radio frequency electromagnetic exposure: tutorial review on experimental dosimetry. Bioelectromagnetics. 1996;17:195–208.
Cline H, Mallozzi R, Li Z, McKinnon G, Barber W. Radiofrequency power deposition utilizing thermal imaging. Magn Reson Med Off J Soc Magn Reson Med Soc Magn Reson Med. 2004;51(6):1129–37. doi:10.1002/mrm.20064.
Cohen JD, Costa HS, Russo RJ. Determining the risks of magnetic resonance imaging at 1.5 tesla for patients with pacemakers and implantable cardioverter defibrillators. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110(11):1631–6. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.07.030.
Cunningham D, Whittaker T. Cardiac Rhythm Management UK National Clinical Audit Report. 2011. http://www.hqip.org.uk/assets/NCAPOP-Library/CRM-2011-National-Clinical-Audit-Report-2010.pdf
Erlebacher JA, Cahill PT, Pannizzo F, Knowles RJ. Effect of magnetic resonance imaging on DDD pacemakers. Am J Cardiol. 1986;57(6):437–40.
Ferreira PF, Gatehouse PD, Mohiaddin RH, Firmin DN. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance artefacts. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2013;15(1):41. doi:10.1186/1532-429X-15-41.
Fetter J, Aram G, Holmes Jr DR, Gray JE, Hayes DL. The effects of nuclear magnetic resonance imagers on external and implantable pulse generators. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1984;7(4):720–7.
Gimbel JR. Unexpected asystole during 3 T magnetic resonance imaging of a pacemaker-dependent patient with a “modern” pacemaker. Europace. 2009;11(9):1241–2. doi:10.1093/europace/eup162.
Gimbel JR, Bailey SM, Tchou PJ, Ruggieri PM, Wilkoff BL. Strategies for the safe magnetic resonance imaging of pacemaker-dependent patients. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2005;28(10):1041–6. PACE230 [pii] 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2005.00230.x.
Irnich W, Irnich B, Bartsch C, Stertmann WA, Gufler H, Weiler G. Do we need pacemakers resistant to magnetic resonance imaging? Europace. 2005;7(4):353–65. doi:10.1016/j.eupc.2005.02.120.
Jones M, Rajappan K. Implantable devices and cardiac MRI scans-no longer an absolute contraindication. Cardiol News. 2011;14(2):14–7.
Jung W, Zvereva V, Hajredini B, Jäckle S. Initial experience with magnetic resonance imaging-safe pacemakers: a review. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2011;32(3):213–9. doi:10.1007/s10840-011-9610-0.
Jung W, Zvereva V, Hajredini B, Jäckle S. Safe magnetic resonance image scanning of the pacemaker patient: current technologies and future directions. Europace. 2012;14(5):631–7. doi:10.1093/europace/eur391.
Junttila MJ, Fishman JE, Lopera G, Pattany PM, Velazquez DL, Williams AR, Trachtenberg BH, Sanina C, Mather J, Hare JM. Safety of serial MRI in patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators. Heart (Br Cardiac Soc). 2011;97(22):1852–6. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2011-300153.
Kalin R, Stanton MS. Current Clinical issues for MRI scanning of pacemaker and defibrillator patients. PACE. 2005;28:2878–91.
Lauck G, von Smekal A, Wolke S, Seelos KC, Jung W, Manz M, Luderitz B. Effects of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging on cardiac pacemakers. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1995;18(8):1549–55.
Levine GN, Gomes AS, Arai AE, Bluemke DA, Flamm SD, Kanal E, Manning WJ, Martin ET, Smith JM, Wilke N, Shellock FS; American Heart Association Committee on Diagnostic and Interventional Cardiac Catheterization; American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology; American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention. Safety of magnetic resonance imaging in patients with cardiovascular devices: an American Heart Association scientific statement from the Committee on Diagnostic and Interventional Cardiac Catheterization, Council on Clinical Cardiology, and the Council o. Circulation. 2007;116(24):2878–91. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.187256.
Luechinger R, Duru F, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P, Candinas R. Force and torque effects of a 1.5-Tesla MRI scanner on cardiac pacemakers and ICDs. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol PACE. 2001;24(2):199–205. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11270700.
Luechinger R, Duru F, Zeijlemaker VA, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P, Candinas R. Pacemaker reed switch behavior in 0.5, 1.5, and 3.0. Tesla magnetic resonance imaging units: are reed switches always closed in strong magnetic fields? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2002;25(10):1419–23.
Luechinger R, Zeijlemaker VA, Pedersen EM, Mortensen P, Falk E, Duru F, Candinas R, Boesiger P. In vivo heating of pacemaker leads during magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Heart J. 2005;26(4):376–83. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi009; discussion 325–7.
Martin ET, Coman JA, Shellock FG, Pulling CC, Fair R, Jenkins K. Magnetic resonance imaging and cardiac pacemaker safety at 1.5-Tesla. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(7):1315–24.
Mollerus M, Albin G, Lipinski M, Lucca J. Ectopy in patients with permanent pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators undergoing an MRI scan. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2009;32(6):772–8. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.2009.02364.x.
Nazarian S, Halperin HR. How to perform magnetic resonance imaging on patients with implantable cardiac arrhythmia devices. Heart Rhythm. 2009;6(1):138–43. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2008.10.021.
Nazarian S, Hansford R, Roguin A, Goldsher D, Zviman MM. A prospective evaluation of a protocol for magnetic resonance. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155:415–24.
Pavlicek W, Geisinger M, Castle L, Borkowski GP, Meaney TF, Bream BL, Gallagher JH. The effects of nuclear magnetic resonance on patients with cardiac pacemakers. Radiology. 1983;147(1):149–53. Retrieved from http://radiology.rsna.org/content/147/1/149.abstract.
Roguin A, Zviman MM, Meininger GR, Rodrigues ER, Dickfeld TM, Bluemke DA, Lardo A, Berger RD, Calkins H, Halperin HR. Modern pacemaker and implantable cardioverter/defibrillator systems can be magnetic resonance imaging safe: in vitro and in vivo assessment of safety and function at 1.5 T. Circulation. 2004;110(5):475–82. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000137121.28722.33.
Roguin A, Schwitter J, Vahlhaus C, Lombardi M, Brugada J, Vardas P, Auricchio A, Priori S, Sommer T. Magnetic resonance imaging in individuals with cardiovascular implantable electronic devices. Europace. 2008;10(3):336–46. doi:10.1093/europace/eun021.
Russo RJ. Determining the risks of clinically indicated nonthoracic magnetic resonance imaging at 1.5 T for patients with pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: rationale and design of the MagnaSafe Registry. Am Heart J. 2013;165(3):266–72. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2012.12.004.
Russo RJ, et al. Determining the risks of magnetic resonance imaging at 1.5 Tesla for patients with pacamakers and implantable cardioverter defibrillators (The Magnasafe Registry). Am Heart Assoc Sci Sess, 2012;126:A11726.
Sasaki T, Hansford R, Zviman MM, Kolandaivelu A, Bluemke DA, Berger RD, Calkins H, Halperin HR, Nazarian S. Quantitative assessment of artifacts on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of patients with pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011a;4(6):662–70. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.111.965764.
Schmitt M, Busca R, Davidson NC. Risk of needing an MRI in pacemaker patients based on analysis of English Hospital statistics. ESMRMB Congress. Belek/Antalya; Turkey. 2009;491–2.
Schwitter J, Kanal E, Schmitt M, Anselme F, Albert T, Hayes DL, Bello D, Tóth A, Chang Y, van Osch D, Sommer T. Impact of the Advisa MRITM Pacing System on the diagnostic quality of cardiac MR images and contraction patterns of cardiac muscle during scans: Advisa MRI randomized clinical multicenter study results. Heart Rhythm Off J Heart Rhythm Soc. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2013.02.019.
Shellock FG, Tkach JA, Ruggieri PM, Masaryk TJ. Cardiac pacemakers, Icds, and loop recorder: evaluation of translational attraction using conventional (“long-bore”) and “short-bore” 1.5- and 3.0-Tesla Mr systems. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2003;5(2):387–97. doi:10.1081/JCMR-120019424.
Sommer T, Naehle CP, Yang A, Zeijlemaker V, Hackenbroch M, Schmiedel A, Meyer C, Strach K, Skowasch D, Vahlhaus C, Litt H, Schild H. Strategy for safe performance of extrathoracic magnetic resonance imaging at 1.5 Tesla in the presence of cardiac pacemakers in non-pacemaker-dependent patients: a prospective study with 115 examinations. Circulation. 2006;114(12):1285–92. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.597013.
Suh J, Jeong E, Shin K, Cho J, Na J, Kim D, Han C. Minimizing artifacts caused by metallic implants at MR imaging: experimental and clinical studies. Am J Roentgenol. 1998;171:1207–13.
Tandri H, Zviman MM, Wedan SR, Lloyd T, Berger RD, Halperin H. Determinants of gradient field-induced current in a pacemaker lead system in a magnetic resonance imaging environment. Heart Rhythm. 2008;5(3):462–8. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2007.12.022.
Wilkoff BL, Bello D, Taborsky M, Vymazal J, Kanal E, Heuer H, Hecking K, Johnson WB, Young W, Ramza B, Akhtar N, Kuepper B, Hunold P, Luechinger R, Puererfellner H, Duru F, Gotte MJ, Sutton R, Sommer T, EnRhythm MRI SureScan Pacing System Study Investigators. Magnetic resonance imaging in patients with a pacemaker system designed for the magnetic resonance environment. Heart Rhythm Off J Heart Rhythm Soc. 2011;8(1):65–73. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.10.002.
Zikria JF, Machnicki S, Rhim E, Bhatti T, Graham RE. MRI of patients with cardiac pacemakers: a review of the medical literature. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196(2):390–401. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.4239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Schmitt, M., Ainslie, M. (2015). CMR and Implantable Devices. In: Plein, S., Greenwood, J., Ridgway, J. (eds) Cardiovascular MR Manual. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20940-1_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20940-1_31
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-20939-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-20940-1
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)