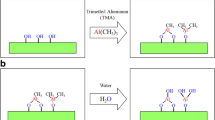
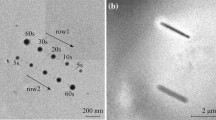
Abstract
Nanoparticles and nanoparticle aggregates are produced as colloids and related nanocrystals by sol–gel and wet chemical synthesis as well as a variety of vapor, spray, and plasma processes, including flames. Vapor-phase material can be condensed or deposited on variously heated or cooled substrates, even crystalline substrates where films, islands, and quantum dots can be grown. The role of catalysts in promoting reactions is described. Sputter deposition and other physical vapor deposition (PVD) processes are discussed, including arc evaporation. Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), including reaction product production and collection, is presented. Molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) and atomic layer deposition are described. Collected nanopowders can be statically or dynamically consolidated to form bulk billets. Mechanical alloying and mechanochemical synthesis of nanomaterials are discussed along with electrodeposition, friction-stir processing (FSP), and equal-channel angular processing (ECAP) or extrusion as these apply to severe plastic deformation (SPD) processes to produce nanocrystalline bulk solids.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad P, Mukherjee S, Senapati D, Mandal MI, Khan RK, Sastry M (2003) Extra cellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 28:313–318
Anastas PT, Warner JC (2000) Green chemistry: theory and practice. Oxford University Press, New York
Brinker CJ, Scherer GW (1990) Sol–gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol–gel processing. Academic, New York
Cao G (2004) Nanostructures and nanomaterials: synthesis properties and applications. Imperial college Press, London
Das SK, Marsili E (2010) A green chemical approach for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles: Characterization and mechanistic aspect. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. Published online 4 Feb 2010. doi:10.1007/S11157-010-9188-5
Kumar M, Ando Y (2010) Chemical vapor deposition of carbon nanotubes: a review on growth mechanisms and mass production. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10:3739–3758
Lu K (1996) Nanocrystalline metals crystallized from amorphous solids: nanocrystallization, structure and properties. Mater Sci Eng R16:161–221
Lu L, Shen Y, Chen X, Qian L, Lu K (2004) Ultrahigh strength and high electrical conductivity in copper. Science 304:422–426
Marchiol L (2012) Synthesis of metal nanoparticles in living plants. Ital J Agron 7(e37):274–282
Murr LE (ed) (1988) Shock waves for industrial applications. Noyes, Park Ridge
Nagasekhar AV, Tick-Hon Y, Seow HP (2007) Deformation behavior and strain homogeneity in equal channel angular extrusion/pressing. J Mater Process Technol 192–193:449–452
Robertson A, Erb U, Palumbo G (1999) Practical applications for electrodeposited nanocrystalline materials. Nanostruct Mater 12:1035–1040
Scott SL, Crudden CM, Jones CW (eds) (2003) Nanostructured catalysts, Nanostructure science and technology series. Springer, New York
Tjong SC, Chen H (2004) Nanocrystalline materials and coatings. Mater Sci Eng R 45:1–88
Valiev RZ, Longdon TG (2006) Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement. Progress in Materials Science, vol 51. Issue 7, Elsevier, New York
Zehetbauer MJ, Zhu YT (eds) (2009) Bulk nanostructured materials. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Zhao P, Li N, Astroe D (2013) State of the art in gold nanoparticle synthesis. Coordin Chem Rev 257:638–665
Zhou Z-Y, Tian N, Li J-T, Broadwell I, Sun S-G (2011) Nanomaterials of high surface energy with exceptional properties in catalysis and energy storage. Chem Soc Rev 40:4167–4185
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this entry
Cite this entry
Murr, L.E. (2015). Synthesis and Processing of Nanomaterials. In: Handbook of Materials Structures, Properties, Processing and Performance. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01815-7_46
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01815-7_46
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-01814-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-01815-7
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics