Abstract
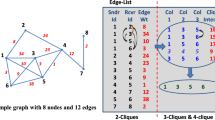
The study of complete sub-graphs belongs to the classical problems of graph theory. Thanks to sociology, the term clique has come to be used for structures representing a small group of people or other entities who share common characteristics and know each other. Clique detection algorithms can be applied in all domains where networks are used to describe relationships among entities. That is not only in social, information, or communication networks but also in biology, chemistry, medicine, etc. In large-scale, e.g., social networks, cliques can have hundreds or more nodes. On the other hand, e.g., in co-authorship networks representing publishing activities of groups of authors, cliques contain, at most, low dozens of nodes. Our paper describes experiments on detecting strong cliques in two weighted co-authorship networks. These experiments are motivated by the assumption that not every clique detected by traditional algorithms truly satisfies the sociological assumption above. Informally speaking, the approach presented in this paper assumes that each pair of clique nodes must be closer to each other and other clique nodes than to non-clique nodes. Using experiments with weighted co-authorship networks, we show how clique detection results differ from the traditional approach when both the strength of the edge (weight) and the structural neighborhood of the clique are considered simultaneously in the analysis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batagelj, V., Zaveršnik, M.: Fast algorithms for determining (generalized) core groups in social networks. Adv. Data Anal. Classif. 5(2), 129–145 (2011)
Bron, C., Kerbosch, J.: Algorithm 457: finding all cliques of an undirected graph. Commun. ACM 16(9), 575–577 (1973)
Chuan, P.M., Son, L.H., Ali, M., Khang, T.D., Huong, L.T., Dey, N.: Link prediction in co-authorship networks based on hybrid content similarity metric. Appl. Intell. 48, 2470–2486 (2018)
Csermely, P., London, A., Wu, L.Y., Uzzi, B.: Structure and dynamics of core/periphery networks. J. Complex Netw. 1(2), 93–123 (2013)
Gansner, E.R., Hu, Y., Kobourov, S.: GMap: visualizing graphs and clusters as maps. In: 2010 IEEE Pacific Visualization Symposium (PacificVis), pp. 201–208. IEEE (2010)
Grodzinski, N., Grodzinski, B., Davies, B.M.: Can co-authorship networks be used to predict author research impact? a machine-learning based analysis within the field of degenerative cervical myelopathy research. Plos one 16(9), e0256, 997 (2021)
Halim, Z., Waqas, M., Baig, A.R., Rashid, A.: Efficient clustering of large uncertain graphs using neighborhood information. Int. J. Approximate Reason. 90, 274–291 (2017)
Halim, Z., Waqas, M., Hussain, S.F.: Clustering large probabilistic graphs using multi-population evolutionary algorithm. Inf. Sci. 317, 78–95 (2015)
Jain, B., Obermayer, K.: Extending bron kerbosch for solving the maximum weight clique problem. arXiv preprint arXiv:1101.1266 (2011)
Kudelka, M., Ochodkova, E., Zehnalova, S., Plesnik, J.: Ego-zones: non-symmetric dependencies reveal network groups with large and dense overlaps. Appl. Netw. Sci. 4(1), 1–49 (2019)
Kumar, S.: Co-authorship networks: a review of the literature. Aslib J. Inf. Manag. 67(1), 55–73 (2015)
Lambiotte, R., Panzarasa, P.: Communities, knowledge creation, and information diffusion. J. Inform. 3(3), 180–190 (2009)
Lü, L., Zhou, T.: Role of weak ties in link prediction of complex networks. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Workshop on Complex Networks Meet Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 55–58 (2009)
Luo, F., Li, B., Wan, X.F., Scheuermann, R.H.: Core and periphery structures in protein interaction networks. In: BMC Bioinformatics, vol. 10, pp. 1–11. BioMed Central (2009)
Newman, M.: Networks. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2018)
Newman, M.E.: Coauthorship networks and patterns of scientific collaboration. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 101(suppl_1), pp. 5200–5205 (2004)
Newman, M.E.: Who is the best connected scientist? a study of scientific coauthorship networks. In: Complex networks, pp. 337–370. Springer (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-44485-5_16
Uddin, S., Hossain, L., Abbasi, A., Rasmussen, K.: Trend and efficiency analysis of co-authorship network. Scientometrics 90(2), 687–699 (2012)
Wasserman, S., Faust, K.: Social network analysis: methods and applications (1994)
Funding
This work is supported by SGS, VSB-Technical University of Ostrava, under the grant no. SP2023/076, and by Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic under grants no. NU20-06-00269 and NU21-06-00370.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Papik, L., Ochodkova, E., Kudelka, M. (2024). Detecting Strong Cliques in Co-authorship Networks. In: Cherifi, H., Rocha, L.M., Cherifi, C., Donduran, M. (eds) Complex Networks & Their Applications XII. COMPLEX NETWORKS 2023. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 1142. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53499-7_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53499-7_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-53498-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-53499-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)