Abstract
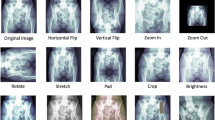
This paper presents a proof-of-concept study on AI-based pre-surgery planning in plastic surgery. The study addresses the challenge of technique selection by developing an AI-driven system that utilises machine learning algorithms to analyse patient-specific data and historical outcomes. By comparing and evaluating diverse inputs, the system generates detailed results for each technique, providing surgeons with valuable insights into expected outcomes. This enhances decision-making during pre-surgery planning and improves surgical precision. The system’s development involved addressing challenges related to data availability, algorithm selection, and interpretability. Preoperative images will be processed using advanced computer vision algorithms to extract relevant features. A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture predicted technique-specific outcomes based on the extracted features. The validation included comparing predictions against ground truth data and expert evaluations. Feedback from plastic surgery practitioners will be collected to assess usability and practicality. Ethical guidelines will be strictly followed to ensure patient data protection and address potential biases. The successful implementation of the proof of concept demonstrates the potential of AI integration in pre-surgery planning for plastic surgery. By empowering surgeons with technique-specific insights, the system enhances decision-making, ultimately improving patient care and treatment outcomes. Future work involves expanding the dataset, considering additional variables, and conducting prospective clinical trials to validate the system’s real-world impact.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamanaka, J., Saito, S., Fujimoto, J.: Impact of preoperative planning using virtual segmental volumetry on liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Surg. 31, 1251–1257 (2007)
Gunes, H., Piccardi, M., Jan, T.: Comparative beauty classification for pre-surgery planning. In: 2004 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37583), vol. 3, pp. 2168–2174. IEEE (2004)
Jarvis, T., Thornburg, D., Rebecca, A.M., Teven, C.M.: Artificial intelligence in plastic surgery: current applications, future directions, and ethical implications. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Global Open 8(10), e3200 (2020)
Lin, X., Chen, Y.: Artificial intelligence and machine learning in plastic and aesthetic surgery. Chin. J. Plastic Surg. 157–160 (2018)
Ma, L., Fei, B.: Comprehensive review of surgical microscopes: technology development and medical applications. J. Biomed. Opt. 26(1), 010901 (2021)
Tokgöz, E., Carro, M.A.: Applications of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning on facial plastic surgeries. In: Cosmetic and Reconstructive Facial Plastic Surgery: A Review of Medical and Biomedical Engineering and Science Concepts, pp. 281–306. Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-31168-0_9
Atiyeh, B., Emsieh, S., Hakim, C., Chalhoub, R.: A narrative review of artificial intelligence (AI) for objective assessment of aesthetic endpoints in plastic surgery. Aesth. Plastic Surg. 1–12 (2023)
Xie, Y., Seth, I., Hunter-Smith, D.J., Rozen, W.M., Ross, R., Lee, M.: Aesthetic surgery advice and counseling from artificial intelligence: a rhinoplasty consultation with ChatGPT. Aesthetic Plast. Sur. 47(5), 1985–1993 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03338-7
Mantelakis, A., Assael, Y., Sorooshian, P., Khajuria, A.: Machine learning demonstrates high accuracy for disease diagnosis and prognosis in plastic surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. – Global Open 9(6), e3638 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000003638
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kolivand, M., Al-jumeily, D. (2024). Pre-planning for Plastic Surgery Using Machine Learning: A Proof of Concept. In: Miraz, M.H., Southall, G., Ali, M., Ware, A. (eds) Emerging Technologies in Computing. iCETiC 2023. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 538. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50215-6_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50215-6_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-50214-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-50215-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)