Abstract
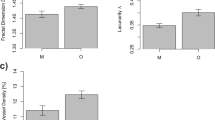
Several studies have found that in people with cancer, the incidence of Alzheimer’s dementia (AD) is very low, while in people with AD the incidence of cancer is very low. These findings imply that both diseases develop through deregulation of a common pathophysiological process, which in each disease occurs in the opposite direction. In this study, we aimed to see if these differences are reflected by changes in retinal microvascular network complexity. Remodeling of retinal microvasculature has already been explored as a potential biomarker for AD. Although some hereditary forms of colon cancer (CC) are associated with retinal microvascular abnormalities, these changes have not been extensively studied. Three groups of retinal fundus images from the UK Biobank were selected, age and gender-matched: group with AD (n = 20), group with CC (n = 20), and a control group (CG, n = 20, participants without either of these two diagnoses). Blood vessels were segmented using a prediction model based on convolutional neural network. Thirty-eight (67.3%) images were successfully segmented. Box-counting dimension (Db) - a measure of microvascular complexity, and lacunarity (Λ) - a measure of microvascular gap distribution, were calculated. Db was lower in AD compared to CC and CG combined (mean Db, AD vs. CC+CG = 1.42 vs. 1.44, p = 0.048). Mean Λ was not different among the groups. More research is needed to improve automatic segmentation. Analysis of a larger sample that accounts for other known factors affecting microvascular complexity such as diabetes mellitus and hypertension should be done in future.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzheimer’s Association: 2022 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 18(4), 700–789 (2022)
Morgan, E., et al.: Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut 72(2), 338–344 (2023)
Roe, C.M., Behrens, M.I., Xiong, C., Miller, J.P., Morris, J.C.: Alzheimer disease and cancer. Neurology 64(5), 895–898 (2005)
Roe, C.M., et al.: Cancer linked to Alzheimer disease but not vascular dementia. Neurology 74(2), 106–112 (2010)
Driver, J.A., Beiser, A., Au, R., Kreger, B.E., Splansky, G.L., Kurth, T., Kiel, D.P., Lu, K.P., Seshadri, S., Wolf, P.A.: Inverse association between cancer and Alzheimer's disease: results from the Framingham Heart Study. BMJ 344 (2012)
Realmuto, S., et al.: Tumor diagnosis preceding Alzheimer’s disease onset: is there a link between cancer and Alzheimer’s disease? J. Alzheimers Dis. 31(1), 177–182 (2012)
Musicco, M., Adorni, F., Di Santo, S., Prinelli, F., Pettenati, C., Caltagirone, C., Palmer, K., Russo A.: Inverse occurrence of cancer and Alzheimer disease: a population-based incidence study. Neurology 81(4), 322–328 (2013)
Zabłocka, A., et al.: Inverse correlation between Alzheimer’s disease and cancer: short overview. Mol. Neurobiol. 58(12), 6335–6349 (2021)
Lanni, C., Masi, M., Racchi, M., Govoni, S.: Cancer and Alzheimer’s disease inverse relationship: an age-associated diverging derailment of shared pathways. Mol. Psychiatry 26(1), 280–295 (2021)
Cheung, C.Y., et al.: Microvascular network alterations in the retina of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 10(2), 135–142 (2014)
Cabrera DeBuc, D., Feuer, W.J., Persad, P.J., Somfai, G.M., Kostic, M., Oropesa, S., Mendoza Santiesteban, C.: Investigating vascular complexity and neurogenic alterations in sectoral regions of the retina in patients with cognitive impairment. Front. Physiol. 11 (2020)
Chen, C.S., et al.: Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE) in familial colorectal cancer. Fam. Cancer 5(4), 397–404 (2006)
Traboulsi, E.I., et al.: Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium predicts colorectal polyposis in Gardner’s syndrome. Arch. Ophthalmol. 108(4), 525–526 (1990)
Munden, P.M., Sobol, W.M., Weingeist, T.A.: Ocular findings in Turcot syndrome (glioma-polyposis). Ophthalmology 98(1), 111–114 (1991)
Touriño, R., Rodríguez-Ares, M.T., López-Valladares, M.J., Gómez-Ulla, F., Gómez-Torreiro, M., Capeans, C.: Fluorescein angiographic features of the congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium in the familial adenomatous polyposis. Int. Ophthalmol. 26(1–2), 59–65 (2005)
Popovic, N., Radunovic, M., Badnjar, J., Popovic, T.: Fractal dimension and lacunarity analysis of retinal microvascular morphology in hypertension and diabetes. Microvasc. Res. 118, 36–43 (2018)
UK Biobank Eye and Vision Consortium homepage, UK Biobank homepage, https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/. Accessed 25 Feb. 2023
UK Biobank homepage, https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/. Accessed 25 Feb. 2023
UK Biobank research ethics approval, https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/learn-more-about-uk-biobank/about-us/ethics. Accessed 25 Feb. 2023
Li, M., et al.: Retinal microvascular network and microcirculation assessments in high myopia. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 174, 56–67 (2017)
Structured analyses of the retina homepage, https://cecas.clemson.edu/~ahoover/stare/. Accessed 25 Feb. 2023
Popovic, N., Radunovic, M., Badnjar, J., Popovic, T.: Manually segmented vascular networks from images of retina with proliferative diabetic and hypertensive retinopathy. Data Brief 18, 470–473 (2018)
ImageJ, National Institutes of Health, http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/. Accessed 25 Feb. 2023
Popovic, N., Vujosevic, S., Radunović, M., Radunović, M., Popovic, T.: TREND database: retinal images of healthy young subjects visualized by a portable digital non-mydriatic fundus camera. PLoS One 16(7) (2021)
Poplin, R., et al.: Prediction of cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs via deep learning. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2, 158–164 (2018)
Acknowledgements
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rubežić, I., Radunović, M., Babić, D., Popović, T., Popović, N. (2024). Fractal Characteristics of Retinal Microvascular Network in Alzheimer's Disease and Colon Cancer in Automatically Segmented Fundus Images from the UK Biobank Database. In: Badnjević, A., Gurbeta Pokvić, L. (eds) MEDICON’23 and CMBEBIH’23. MEDICON CMBEBIH 2023 2023. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 93. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49062-0_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49062-0_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-49061-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-49062-0
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)