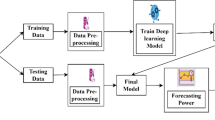
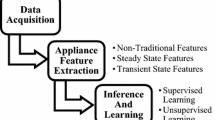
Abstract
This review article investigates the methods proposed for disaggregating the space heating units’ load from the aggregate electricity load of commercial and residential buildings. It explores conventional approaches together with those that employ traditional machine learning, deep supervised learning and reinforcement learning. The review also outlines corresponding data requirements and examines the suitability of a commonly utilised toolkit for disaggregating heating loads from low-frequency aggregate power measurements. It is shown that most of the proposed approaches have been applied to high-resolution measurements and that few studies have been dedicated to low-resolution aggregate loads (e.g. provided by smart meters). Furthermore, only a few methods have taken account of special considerations for heating technologies, given the corresponding governing physical phenomena. Accordingly, the recommendations for future works include adding a rigorous pre-processing step, in which features inspired by the building physics (e.g. lagged values for the ambient conditions and values that represent the correlation between heating consumption and outdoor temperature) are added to the available input feature pool. Such a pipeline may benefit from deep supervised learning or reinforcement learning methods, as these methods are shown to offer higher performance compared to traditional machine learning algorithms for load disaggregation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
IEA (2022). https://www.iea.org/reports/buildings
Energy Transitions Commission, ‘Making Mission Possible’, Health Prog. 76(6), 45–7, 60 (2020)
SSB, 11561: Energibalanse. Tilgang og forbruk, etter energiprodukt 1990 - 2018 (2020). https://www.ssb.no/statbank/table/11561. Accessed 02 Jun 2023
Ødegården, L., Bhantana, S.: Status og prognoser for kraftsystemet 2018 rapportnr. 103–2018. NVE (2018). http://publikasjoner.nve.no/rapport/2018/rapport2018_103.pdf. Accessed 31 May 2023
NVE, NVE.no: Smarte strømmålere (AMS) (2022). https://www.nve.no/reguleringsmyndigheten/kunde/strom/stromkunde/smarte-stroemmaalere-ams/
Lindberg, K.B.: Doctoral thesis Impact of Zero Energy Buildings on the Power System A study of load profiles, flexibility and Impact of Zero Energy Buildings on the Power System A study of load profiles , flexibility and system, vol. 6 (2017)
Carrie Armel, K., Gupta, A., Shrimali, G., Albert, A.: Is disaggregation the holy grail of energy efficiency? The case of electricity. Energy Policy 52, 213–234 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.08.062
Hart, G.W.: Nonintrusive appliance load monitoring. Proc. IEEE 80(12), 1870–1891, (1992). https://doi.org/10.1109/5.192069
Huber, P., Calatroni, A., Rumsch, A., Paice, A.: Review on deep neural networks applied to low-frequency NILM. Energies 14(9), Art. no. 9, Jan. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14092390
Zeifman, M., Roth, K.: Nonintrusive appliance load monitoring: Review and outlook. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 57(1), 76–84 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2011.5735484
Makonin, S.: Approaches to Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM) in the Home APPROACHES TO NON-INTRUSIVE LOAD MONITORING (NILM) by Doctor of Philosophy School of Computing Science, no. October 2012, 2014
Kong, W., Dong, Z.Y., Hill, D.J., Luo, F., Xu, Y.: Improving nonintrusive load monitoring efficiency via a hybrid programing method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 12(6), 2148–2157 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2016.2590359
Farinaccio, L., Zmeureanu, R.: Using a pattern recognition approach to disaggregate the total electricity consumption in a house into the major end-uses. Energy Build. 30(3), 245–259 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7788(99)00007-9
Figueiredo, M.B., De Almeida, A., Ribeiro, B.: An experimental study on electrical signature identification of non-intrusive load monitoring (NILM) systems. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinforma., vol. 6594 LNCS, no. PART 2, pp. 31–40 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20267-4_4
Nguyen, K.T., et al.: Event detection and disaggregation algorithms for NIALM system. In: NILM Workshop, June 2014, pp. 2–5 (2014)
Gonçalves, H., Ocneanu, A., Bergés, M.: Unsupervised disaggregation of appliances using aggregated consumption data. Environ (2011)
Wang, L., Luo, X., Zhang, W.: Unsupervised energy disaggregation with factorial hidden Markov models based on generalized backfitting algorithm. In: EEE International Conference of IEEE Region 10 (TENCON 2013) (2013)
Egarter, D., Bhuvana, V.P., Elmenreich, W.: PALDi: online load disaggregation via particle filtering. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 64(2), 467–477 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2014.2344373
Wu, Q., Wang, F.: Concatenate convolutional neural networks for non-intrusive load monitoring across complex background. Energies 12(8) (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/en12081572
Kelly, J., et al.: NILMTK v0.2: a non-intrusive load monitoring toolkit for large scale datasets: demo abstract. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, in BuildSys ’14. Nov. 2014, pp. 182–183, Association for Computing Machinery, New York. https://doi.org/10.1145/2674061.2675024
Batra, N., et al. Towards reproducible state-of-the-art energy disaggregation. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM International Conference on Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, Cities, and Transportation, Nov. 2019, pp. 193–202. ACM, New York. https://doi.org/10.1145/3360322.3360844
Virtsionis, N., Gkalinikis, C., Nalmpantis, Vrakas, D.: Torch-NILM: an effective deep learning toolkit for non-intrusive load monitoring in pytorch. Energies 15(7), Art. no. 7, Jan. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072647
Lindberg, K.B.: Impact of zero energy buildings on the power system, p. 192
Abbasi, A.R.: Fault detection and diagnosis in power transformers: a comprehensive review and classification of publications and methods. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 209, 107990 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2022.107990
Makonin, S., Ellert, B., Bajić, I.V., Popowich, F.: Electricity, water, and natural gas consumption of a residential house in Canada from 2012 to 2014. Sci. Data 3(1), Art. no. 1, Jun. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.37
Himeur, Y., Ghanem, K., Alsalemi, A., Bensaali, F., Amira, A.: Artificial intelligence based anomaly detection of energy consumption in buildings: a review, current trends and new perspectives. Appl. Energy 287, 116601 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.116601
Himeur, Y., Alsalemi, A., Bensaali, F., Amira, A., Al-Kababji, A.: Recent trends of smart nonintrusive load monitoring in buildings: a review, open challenges, and future directions. Int. J. Intell. Syst.Intell. Syst. 37(10), 7124–7179 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/int.22876
Angelis, G.-F., Timplalexis, C., Krinidis, S., Ioannidis, D., Tzovaras, D.: NILM applications: Literature review of learning approaches, recent developments and challenges. Energy Build. 261, 111951 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2022.111951
Ruano, A., Hernandez, A., Ureña, J., Ruano, M., Garcia, J.: NILM techniques for intelligent home energy management and ambient assisted living: a review. Energies 12(11), Art. no. 11, January 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112203
Batra, N., Gulati, M., Singh, A., Srivastava, M.B.: It’s Different: insights into home energy consumption in India. In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM Workshop on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, in BuildSys’13. November 2013, pp. 1–8. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, November 2013. https://doi.org/10.1145/2528282.2528293
Kelly, J., Knottenbelt, W.: The UK-DALE dataset, domestic appliance-level electricity demand and whole-house demand from five UK homes. Sci. Data 2(1), Art. no. 1, March 2015. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2015.7
‘NILMTK: Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Toolkit’. nilmtk, Feb. 27, 2023 . https://github.com/nilmtk/nilmtk. Accessed 28 Feb 2023
Murray, D., Stankovic, L., Stankovic, V.: An electrical load measurements dataset of United Kingdom households from a two-year longitudinal study. Sci. Data 4(1), Art. no. 1, January 2017. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.122
Kolter, J.Z., Johnson, M.J.: REDD: A Public Dataset for Energy Disaggregation Research’
Beckel, C., Kleiminger, W., Cicchetti, R., Staake, T., Santini, S.: The ECO dataset and the performance of non-intrusive load monitoring algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, Memphis Tennessee: ACM, pp. 80–89, November 2014. https://doi.org/10.1145/2674061.2674064
Klemenjak, C., Kovatsch, C., Herold, M., Elmenreich, W.: A synthetic energy dataset for non-intrusive load monitoring in households. Sci. Data 7(1), Art. no. 1, April 2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-020-0434-6
Shin, C., Lee, E., Han, J., Yim, J., Rhee, W., Lee, H.: The ENERTALK dataset, 15 Hz electricity consumption data from 22 houses in Korea. Sci. Data 6(1), 193 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0212-5
Household Electricity Survey - Data Briefing
Medico, R., et al.: A voltage and current measurement dataset for plug load appliance identification in households. Sci. Data 7(1), Art. no. 1, February 2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-020-0389-7
Anderson, K.D., Ocneanu, A.F., Benitez, D., Carlson, D., Rowe, A., Berges, M.: BLUED: a fully labeled public dataset for event-based non-intrusive load monitoring research, August 2023
Reinhardt, A., et al.: On the accuracy of appliance identification based on distributed load metering data, p. 9 (2012)
Maasoumy, M., Sanandaji, B.M., Poolla, K., Vincentelli, A.S.: BERDS-BERkeley EneRgy Disaggregation Dataset. https://tokhub.github.io/dbecd/links/berds.html. Accessed 24 Jan 2023
Monacchi, A., Egarter, D., Elmenreich, W., D’Alessandro, S., Tonello, A.M.: GREEND: an energy consumption dataset of households in Italy and Austria. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), pp. 511–516, November 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/SmartGridComm.2014.7007698
Uttama Nambi, A.S.N., Reyes Lua, A., Prasad, V.R.: LocED: location-aware energy disaggregation framework. In: Proceedings of the 2nd ACM International Conference on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Built Environments, Seoul South Korea: ACM, pp. 45–54, November 2015. https://doi.org/10.1145/2821650.2821659
Parson, O., et al.: Dataport and NILMTK: a building dataset designed for non-intrusive load monitoring. In: 2015 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Orlando, FL, USA: IEEE, pp. 210–214, December 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/GlobalSIP.2015.7418187
Makonin, S., Wang, Z.J., Tumpach, C.: RAE: the rainforest automation energy dataset for smart grid meter data analysis. Data 3(1), 8 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/data3010008
Rashid, H., Singh, P., Singh, A.: I-BLEND, a campus-scale commercial and residential buildings electrical energy dataset. Sci. Data 6(1), Art. no. 1, February 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2019.15
Basu, K., Debusschere, V., Bacha, S.: Residential appliance identification and future usage prediction from smart meter. In: IECON 2013 - 39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, pp. 4994–4999, November 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2013.6699944
Barker, S., Mishra, A., Irwin, D., Cecchet, E., Shenoy, P., Albrecht, J.: Smart*: an open dataset and tools for enabling research in sustainable homes. In: Proceedings of SustKDD, January 2012
Batra, N., Parson, O., Berges, M., Singh, A., Rogers, A.: A comparison of non-intrusive load monitoring methods for commercial and residential buildings (2014)
Sæle, H., Rosenberg, E., Feilberg, N.: State-of-the-art Projects for estimating the electricityu end-use demand (2010). Accessed 20 Mar 2023. https://www.sintef.no/globalassets/project/eldek/publisering/tr-a6999-state-of-the-art-projects-for-estimating-the-electricity-end-use-demand.pdf
Andersen, K.H., Krekling Lien, S., Byskov Lindberg, K., Taxt Walnum, H., Sartori, I.: Further development and validation of the “PROFet” energy demand load profiles estimator. In: presented at the 2021 Building Simulation Conference, September 2021. https://doi.org/10.26868/25222708.2021.30159
Schaffer, M., Tvedebrink, T., Marszal-Pomianowska, A.: Three years of hourly data from 3021 smart heat meters installed in Danish residential buildings. Sci. Data 9(1), Art. no. 1, July 2022. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-022-01502-3
Liu, L., et al.: Non-intrusive load monitoring method considering the time-segmented state probability. IEEE Access 10, 39627–39637 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3167132
Balletti, M., Piccialli, V., Sudoso, A.M.: Mixed-integer nonlinear programming for state-based non-intrusive load monitoring. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 13(4), 3301–3314 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSG.2022.3152147
Morch, A., Sæle, H., Feilberg, N., Lindberg, K.B.: Method for development and segmentation of load profiles for different final customers and appliances. In: ECEEE 2013 Summer Stud. Proc., 2013, Accessed: Mar. 20, 2023. https://www.eceee.org/library/conference_proceedings/eceee_Summer_Studies/2013/7-monitoring-and-evaluation/method-for-development-and-segmentation-of-load-profiles-for-different-final-customers-and-appliances/
Lien, S.K., Ivanko, D., Sartori, I.: Domestic hot water decomposition from measured total heat load in Norwegian buildings. SINTEF Academic Press, 2020. Accessed: Jan. 17, 2023. https://ntnuopen.ntnu.no/ntnu-xmlui/handle/11250/2684373
Zaeri, N., Gunay, H.B., Ashouri, A.: Unsupervised energy disaggregation using time series decomposition for commercial buildings. In: Proceedings of the 9th ACM International Conference on Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, Cities, and Transportation, Boston Massachusetts: ACM, pp. 373–377, November 2022. https://doi.org/10.1145/3563357.3566155
Amayri, M., Silva, C.S., Pombeiro, H., Ploix, S.: Flexibility characterization of residential electricity consumption: A machine learning approach. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 32, 100801 (2022)
Najafi, B., Di Narzo, L., Rinaldi, F., Arghandeh, R.: Machine learning based disaggregation of air-conditioning loads using smart meter data. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib.Distrib. 14(21), 4755–4762 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-gtd.2020.0698
Miller, C., Meggers, F.: Mining electrical meter data to predict principal building use, performance class, and operations strategy for hundreds of non-residential buildings. Energy Build. 156, 360–373 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.09.056
Kaselimi, M., Doulamis, N., Doulamis, A., Voulodimos, A., Protopapadakis, E.: Bayesian-optimized bidirectional LSTM regression model for non-intrusive load monitoring. In: ICASSP 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, United Kingdom: IEEE, pp. 2747–2751, May 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8683110
Xia, M., Liu, W., Wang, K., Song, W., Chen, C., Li, Y.: Non-intrusive load disaggregation based on composite deep long short-term memory network. Expert Syst. Appl. 160, 113669 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113669
Wang, J., El Kababji, S., Graham, C., Srikantha, P.: Ensemble-based deep learning model for non-intrusive load monitoring. In: 2019 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference (EPEC), pp. 1–6, October 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/EPEC47565.2019.9074816
Davies, P., Dennis, J., Hansom, J., Martin, W., Stankevicius, A., Ward, L.: Deep neural networks for appliance transient classification. In: ICASSP 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), May 2019, pp. 8320–8324. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8682658
Li, C., Zheng, R., Liu, M., Zhang, S.: A fusion framework using integrated neural network model for non-intrusive load monitoring. In: 2019 Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Guangzhou, China: IEEE, pp. 7385–7390, July 2019. https://doi.org/10.23919/ChiCC.2019.8865721
Wang, T.S., Ji, T.Y., Li, M.S.: A new approach for supervised power disaggregation by using a denoising autoencoder and recurrent LSTM network. In: 2019 IEEE 12th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), Toulouse, France: IEEE, pp. 507–512, August 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/DEMPED.2019.8864870
Harell, A., Makonin, S., Bajic, I.V.: Wavenilm: a causal neural network for power disaggregation from the complex power signal. In: ICASSP 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, United Kingdom: IEEE, pp. 8335–8339, May 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8682543
Xia, M., Liu, W., Wang, K., Zhang, X., Xu, Y.: Non-intrusive load disaggregation based on deep dilated residual network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 170, 277–285 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2019.01.034
Xia, M., Liu, W., Xu, Y., Wang, K., Zhang, X.: Dilated residual attention network for load disaggregation. Neural Comput. Appl. 31(12), 8931–8953 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04414-3
Kaselimi, M., Doulamis, N., Voulodimos, A., Protopapadakis, E., Doulamis, A.: Context aware energy disaggregation using adaptive bidirectional LSTM models. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 11(4), 3054–3067 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSG.2020.2974347
Kaselimi, M., Voulodimos, A., Protopapadakis, E., Doulamis, N., Doulamis, A.: EnerGAN: a generative adversarial network for energy disaggregation. In: ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, pp. 1578–1582, May 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9054342
Kaselimi, M., Doulamis, N., Voulodimos, A., Doulamis, A., Protopapadakis, E.: EnerGAN++: a generative adversarial gated recurrent network for robust energy disaggregation. IEEE Open J. Signal Process. 2, 1–16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/OJSP.2020.3045829
Liu, H., Liu, C., Tian, L., Zhao, H., Liu, J.: Non-intrusive load disaggregation based on deep learning and multi-feature fusion. In: 2021 3rd International Conference on Smart Power & Internet Energy Systems (SPIES), Shanghai, China: IEEE, pp. 210–215, September 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/SPIES52282.2021.9633819
Kianpoor, N., Hoff, B., Østrem, T.: Deep adaptive ensemble filter for non-intrusive residential load monitoring. Sensors 23(4), Art. no. 4, Jan. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23041992
Zou, M., Zhu, S., Gu, J., Korunovic, L.M., Djokic, S.Z.: Heating and lighting load disaggregation using frequency components and convolutional bidirectional long short-term memory method. Energies 14(16), Art. no. 16, Jan. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14164831
Hosseini, S.S., Delcroix, B., Henao, N., Agbossou, K., Kelouwani, S.: A case study on obstacles to feasible NILM solutions for energy disaggregation in quebec residences. Power 2, 4 (2022)
Li, H.: A Non-intrusive home load identification method based on adaptive reinforcement learning algorithm. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 853(1), 012030 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/853/1/012030
Zaouali, K., Ammari, M.L., Bouallegue, R.: LSTM-based reinforcement q learning model for non intrusive load monitoring. In: Barolli, L., Hussain, F., Enokido, T. (eds.) Advanced Information Networking and Applications, pp. 1–13. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-99619-2_1
NVE and SSB, Oppvarming i boliger. Kartlegging av oppvarmingsutstyr of effektiviseringstiltak i husholdningene. NVE Rapport 85–2014 (2014). Accessed 23 Mar 2023. https://publikasjoner.nve.no/rapport/2014/rapport2014_85.pdf
Acknowledgment
This article has been written within the research project “Coincidence factors and peak loads of buildings in the Norwegian low carbon society” (COFACTOR). The authors gratefully acknowledge the support from the Research Council of Norway (project number 326891), research partners, industry partners and data providers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lien, S.K., Najafi, B., Rajasekharan, J. (2024). Advances in Machine-Learning Based Disaggregation of Building Heating Loads: A Review. In: Jørgensen, B.N., da Silva, L.C.P., Ma, Z. (eds) Energy Informatics. EI.A 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14467. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-48649-4_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-48649-4_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-48648-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-48649-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)