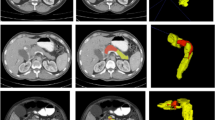
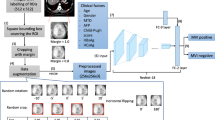
Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly lethal cancer in which the tumor-vascular involvement greatly affects the resectability and, thus, overall survival of patients. However, current prognostic prediction methods fail to explicitly and accurately investigate relationships between the tumor and nearby important vessels. This paper proposes a novel learnable neural distance that describes the precise relationship between the tumor and vessels in CT images of different patients, adopting it as a major feature for prognosis prediction. Besides, different from existing models that used CNNs or LSTMs to exploit tumor enhancement patterns on dynamic contrast-enhanced CT imaging, we improved the extraction of dynamic tumor-related texture features in multi-phase contrast-enhanced CT by fusing local and global features using CNN and transformer modules, further enhancing the features extracted across multi-phase CT images. We extensively evaluated and compared the proposed method with existing methods in the multi-center (n = 4) dataset with 1,070 patients with PDAC, and statistical analysis confirmed its clinical effectiveness in the external test set consisting of three centers. The developed risk marker was the strongest predictor of overall survival among preoperative factors and it has the potential to be combined with established clinical factors to select patients at higher risk who might benefit from neoadjuvant therapy.
H. Dong—Work was done during an internship at Alibaba DAMO Academy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attiyeh, M.A., et al.: Survival prediction in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by quantitative computed tomography image analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 25(4), 1034–1042 (2018)
Bian, Y., et al.: Artificial intelligence to predict lymph node metastasis at CT in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Radiology 306(1), 160–169 (2023)
Cheng, N.M., et al.: Deep learning for fully automated prediction of overall survival in patients with oropharyngeal cancer using FDG-PET imaging. Clin. Cancer Res. 27(14), 3948–3959 (2021)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: ICLR (2021)
Ducreux, M., et al.: Cancer of the pancreas: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 26, v56–v68 (2015)
Feng, Y., Wang, J., An, D., Gu, X., Xu, X., Zhang, M.: End-to-end evidential-efficient net for radiomics analysis of brain MRI to predict oncogene expression and overall survival. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2022. LNCS, vol. 13433, pp. 282–291. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16437-8_27
Haoqiang Fan, H.S., Guibas, L.: A point set generation network for 3D object reconstruction from a single image. In: CVPR (2017)
Huttenlocher, D.P., Rucklidge, W.J., Klanderman, G.A.: Comparing images using the hausdorff distance under translation. In: Proceedings 1992 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2002)
Katzman, J.L., Shaham, U., Cloninger, A., Bates, J., Jiang, T., Kluger, Y.: Deepsurv: personalized treatment recommender system using a cox proportional hazards deep neural network. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 18(1), 24 (2018)
Koay, E.J., et al.: Computed tomography-based biomarker outcomes in a prospective trial of preoperative folfirinox and chemoradiation for borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 3, 1–15 (2019)
Koehler, G., Isensee, F., Maier-Hein, K.: A noisy nnU-Net student for semi-supervised abdominal organ segmentation. In: Ma, J., Wang, B. (eds.) MICCAI 2022. LNCS, vol. 13816, pp. 128–138. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23911-3_12
Lou, B., et al.: An image-based deep learning framework for individualising radiotherapy dose: a retrospective analysis of outcome prediction. Lancet Digit. Health 1(3), e136–e147 (2019)
Mehta, S., Rastegari, M.: Mobilevit: light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer. In: ICLR (2022)
Prokesch, R.W., Chow, L.C., Beaulieu, C.F., Bammer, R., Jeffrey, R.B., Jr.: Isoattenuating pancreatic adenocarcinoma at multi-detector row CT: secondary signs. Radiology 224(3), 764–768 (2002)
Saeed, N., Sobirov, I., Al Majzoub, R., Yaqub, M.: TMSS: an end-to-end transformer-based multimodal network for segmentation and survival prediction. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2022. LNCS, vol. 13437, pp. 319–329. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16449-1_31
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., Jemal, A.: Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 69(1), 7–34 (2019)
Tang, Z., et al.: Deep learning of imaging phenotype and genotype for predicting overall survival time of glioblastoma patients. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(6), 2100–2109 (2020)
Tempero, M.A., et al.: Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, version 2.2021, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 19(4), 439–457 (2021)
Tsai, S., et al.: Importance of normalization of ca19-9 levels following neoadjuvant therapy in patients with localized pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. 271(4), 740–747 (2020)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Guyon, I., et al. (eds.) NeurIPS, vol. 30. Curran Associates, Inc. (2017)
Yao, J., et al.: Deep learning for fully automated prediction of overall survival in patients undergoing resection for pancreatic cancer: a retrospective multicenter study. Ann. Surg. 278(1), e68–e79 (2023)
Yao, J., et al.: Deepprognosis: Preoperative prediction of pancreatic cancer survival and surgical margin via comprehensive understanding of dynamic contrast-enhanced CT imaging and tumor-vascular contact parsing. Med. Image Anal. 73, 102150 (2021)
Yuan, M., et al.: Devil is in the queries: advancing mask transformers for real-world medical image segmentation and out-of-distribution localization. In: CVPR, pp. 23879–23889 (2023)
Zhang, L., et al.: Robust pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma segmentation with multi-institutional multi-phase partially-annotated CT scans. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12264, pp. 491–500. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_48
Zheng, H., et al.: Multi-transSP: multimodal transformer for survival prediction of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2022, pp. 234–243. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16449-1_23
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Alibaba Group through Alibaba Research Intern Program. Bin Dong and Li Zhang was partly supported by NSFC 12090022 and 11831002, and Clinical Medicine Plus X-Young Scholars Project of Peking University PKU2023LCXQ041. Yu Shi was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82071885).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dong, H. et al. (2023). Improved Prognostic Prediction of Pancreatic Cancer Using Multi-phase CT by Integrating Neural Distance and Texture-Aware Transformer. In: Greenspan, H., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023. MICCAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14224. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43904-9_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43904-9_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43903-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43904-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)