Abstract
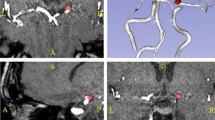
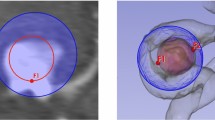
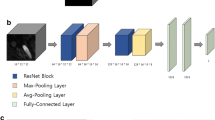
The diagnosis of unruptured intracranial aneurysms from time-of-flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography (TOF-MRA) images is a challenging clinical problem that is extremely difficult to automate. We propose to go beyond the mere detection of each aneurysm and also estimate its size and the orientation of its main axis for an immediate visualization in appropriate reformatted cut planes. To address this issue, and inspired by the idea behind YOLO architecture, a novel one-stage deep learning approach is described to simultaneously estimate the localization, size and orientation of each aneurysm in 3D images. It combines fast and approximate annotation, data sampling and generation to tackle the class imbalance problem, and a cosine similarity loss to optimize the orientation. We evaluate our approach on two large datasets containing 416 patients with 317 aneurysms using a 5-fold cross-validation scheme. Our method achieves a median localization error of 0.48 mm and a median 3D orientation error of 12.27 \(^\circ \)C, demonstrating an accurate localization of aneurysms and an orientation estimation that comply with clinical practice. Further evaluation is performed in a more classical detection setting to compare with state-of-the-art nnDetecton and nnUNet methods. Competitive performance is reported with an average precision of 76.60%, a sensitivity score of 82.93%, and 0.44 false positives per case. Code and annotations are publicly available at https://gitlab.inria.fr/yassis/DeepAnePose.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimura, H., Li, Q., Korogi, Y., et al.: Automated computerized scheme for detection of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in three-dimensional magnetic resonance angiography1. Acad. Radiol. 11(10), 1093–1104 (2004)
Assis, Y., Liao, L., Pierre, F., Anxionnat, R., Kerrien, E.: An efficient data strategy for the detection of brain aneurysms from mra with deep learning. In: Engelhardt, S., et al. (eds.) DGM4MICCAI/DALI -2021. LNCS, vol. 13003, pp. 226–234. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88210-5_22
Baumgartner, M., Jäger, P.F., Isensee, F., Maier-Hein, K.H.: nnDetection: a self-configuring method for medical object detection. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12905, pp. 530–539. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87240-3_51
Benner, T., Wisco, J.J., van der Kouwe, A.J., Fischl, B., et al.: Comparison of manual and automatic section positioning of brain MR images. Radiology 239(1), 246–254 (2006)
Bystrov, D., Pekar, V., Young, S., Dries, S.P., Heese, H.S., van Muiswinkel, A.M.: Automated planning of MRI scans of knee joints. In: Medical Imaging 2007: Visualization and Image-Guided Procedures, vol. 6509, pp. 1023–1031. SPIE (2007)
Çiçek, Ö., Abdulkadir, A., Lienkamp, S.S., Brox, T., Ronneberger, O.: 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: Ourselin, S., Joskowicz, L., Sabuncu, M.R., Unal, G., Wells, W. (eds.) MICCAI 2016. LNCS, vol. 9901, pp. 424–432. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49
Di Noto, T., Marie, G., Tourbier, S., et al.: Towards automated brain aneurysm detection in TOF-MRA: open data, weak labels, and anatomical knowledge. In: Neuroinformatics pp. 1–14 (2022)
Fedorov, A., Beichel, R., Kalpathy-Cramer, J., et al.: 3D slicer as an image computing platform for the quantitative imaging network. Magnetic Resonance Imaging 30(9), 1323–1341 (2012). https://slicer.org, pMID: 22770690
Isensee, F., Jaeger, P.F., Kohl, S.A., Petersen, J., Maier-Hein, K.H.: nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 18(2), 203–211 (2021)
Iskurt, A., Becerikli, Y., Mahmutyazicioglu, K.: Automatic identification of landmarks for standard slice positioning in brain MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 34(3), 499–510 (2011)
Jang, M., Kim, J., Park, J., et al.: Features of “false positive" unruptured intracranial aneurysms on screening magnetic resonance angiography. PloS one 15(9), e0238597 (2020)
van der Kouwe, A.J., et al.: On-line automatic slice positioning for brain MR imaging. Neuroimage 27(1), 222–230 (2005)
Lall, R., Eddleman, C.S., Bendok, B.R., et al.: Unruptured intracranial aneurysms and the assessment of rupture risk based on anatomical and morphological factors: sifting through the sands of data. Neurosurg. Focus 26(5), E2 (2009)
Lecouvet, F.E., Claus, J., Schmitz, P., Denolin, V., Bos, C., Vande Berg, B.C.: Clinical evaluation of automated scan prescription of knee MR images. J. Magnetic Reson. Imaging Official J. Inter. Soc. Magnetic Reson. Med. 29(1), 141–145 (2009)
Lin, T.Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Dollár, P.: Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2980–2988 (2017)
Maier-Hein, L., et al.: Metrics reloaded: Pitfalls and recommendations for image analysis validation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.01653 (2022)
Miao, S., Lucas, J., Liao, R.: Automatic pose initialization for accurate 2D/3D registration applied to abdominal aortic aneurysm endovascular repair. In: Medical Imaging 2012: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, vol. 8316, pp. 243–250. SPIE (2012)
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.A.: V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 565–571. Ieee (2016)
Nakao, T., Hanaoka, S., Nomura, Y., el al.: Deep neural network-based computer-assisted detection of cerebral aneurysms in MR angiography. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 47(4), 948–953 (2018)
Reda, F.A., Zhan, Y., Zhou, X.S.: A Steering engine: learning 3-D anatomy orientation using regression forests. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 612–619. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_73
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: Yolov3: an incremental improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02767 (2018)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28 (2015)
Sichtermann, T., Faron, A., Sijben, R., et al.: Deep learning-based detection of intracranial aneurysms in 3D TOF-MRA. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 40(1), 25–32 (2019)
Stember, J.N., Chang, P., Stember, D.M., et al.: Convolutional neural networks for the detection and measurement of cerebral aneurysms on magnetic resonance angiography. J. Digit. Imaging 32(5), 808–815 (2019)
Timmins, K.M., van der Schaaf, I.C., Bennink, E., et al.: Comparing methods of detecting and segmenting unruptured intracranial aneurysms on TOF-MRAs: the ADAM challenge. Neuroimage 238, 118216 (2021)
Ueda, D., Yamamoto, A., Nishimori, M., et al.: Deep learning for MR angiography: automated detection of cerebral aneurysms. Radiology 290(1), 187–194 (2019)
Yang, X., Blezek, D.J., Cheng, L.T., et al.: Computer-aided detection of intracranial aneurysms in MR angiography. J. Digit. Imaging 24(1), 86–95 (2011)
Zhan, Y., Dewan, M., Harder, M., Krishnan, A., Zhou, X.S.: Robust automatic knee MR slice positioning through redundant and hierarchical anatomy detection. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 30(12), 2087–2100 (2011)
Zeng, K., Zhao, Y., Zhao, Y., et al.: Deep learning solution for medical image localization and orientation detection. Med. Image Anal. 81, 102529 (2022)
Zhou, Y., Barnes, C., Lu, J., Yang, J., Li, H.: On the continuity of rotation representations in neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5745–5753 (2019)
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by the Grand-Est Region and the University Hospital (CHRU) of Nancy, France.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Assis, Y., Liao, L., Pierre, F., Anxionnat, R., Kerrien, E. (2023). Aneurysm Pose Estimation with Deep Learning. In: Greenspan, H., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023. MICCAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14221. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43895-0_51
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43895-0_51
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43894-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43895-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)