Abstract
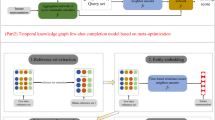
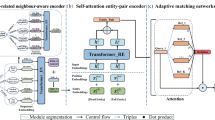
Temporal knowledge graph completion (TKGC) aims to predict the missing links among the entities in a temporal knowledge graph (TKG). Most previous TKGC methods only consider predicting the missing links among the entities seen in the training set, while they are unable to achieve great performance in link prediction concerning newly-emerged unseen entities. Recently, a new task, i.e., TKG few-shot out-of-graph (OOG) link prediction, is proposed, where TKGC models are required to achieve great link prediction performance concerning newly-emerged entities that only have few-shot observed examples. In this work, we propose a TKGC method FITCARL that combines few-shot learning with reinforcement learning to solve this task. In FITCARL, an agent traverses through the whole TKG to search for the prediction answer. A policy network is designed to guide the search process based on the traversed path. To better address the data scarcity problem in the few-shot setting, we introduce a module that computes the confidence of each candidate action and integrate it into the policy for action selection. We also exploit the entity concept information with a novel concept regularizer to boost model performance. Experimental results show that FITCARL achieves stat-of-the-art performance on TKG few-shot OOG link prediction. Code and supplementary appendices are provided (https://github.com/ZifengDing/FITCARL/tree/main).
Z. Ding and J. Wu—Equal contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
TITer can model unseen entities, but it is not designed for few-shot setting and requires a substantial number of associated facts. Besides, both TITer and CluSTeR are TKG forecasting methods, where models are asked to predict future links given the past TKG information (different from TKGC, see Appendix B for discussion).
- 2.
For each query quadruple in the form of \((\tilde{e}_q, r_q, e', t_q)\), we derive its LP query as \((e', r_q^{-1}, ?, t_q)\). \(r_q^{-1}\) is \(r_q\)’s inverse relation. The agent always starts from \((e', t_q)\).
- 3.
Both original and inverse relations are trained in pre-training.
- 4.
All LP queries are transformed into object prediction in TKG few-shot OOG LP.
References
Abboud, R., Ceylan, İ.İ., Lukasiewicz, T., Salvatori, T.: Boxe: a box embedding model for knowledge base completion. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Ammanabrolu, P., Hausknecht, M.J.: Graph constrained reinforcement learning for natural language action spaces. In: ICLR. OpenReview.net (2020)
Baek, J., Lee, D.B., Hwang, S.J.: Learning to extrapolate knowledge: transductive few-shot out-of-graph link prediction. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Balazevic, I., Allen, C., Hospedales, T.M.: Tucker: tensor factorization for knowledge graph completion. In: EMNLP/IJCNLP (1), pp. 5184–5193. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019)
Bordes, A., Usunier, N., García-Durán, A., Weston, J., Yakhnenko, O.: Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. In: NIPS, pp. 2787–2795 (2013)
Boschee, E., Lautenschlager, J., O’Brien, S., Shellman, S., Starz, J., Ward, M.: ICEWS Coded Event Data (2015)
Chen, K., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Li, A.: Rotateqvs: representing temporal information as rotations in quaternion vector space for temporal knowledge graph completion. In: ACL (1), pp. 5843–5857. Association for Computational Linguistics (2022)
Chen, M., Zhang, W., Zhang, W., Chen, Q., Chen, H.: Meta relational learning for few-shot link prediction in knowledge graphs. In: EMNLP/IJCNLP (1), pp. 4216–4225. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019)
Cho, K., et al.: Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In: EMNLP, pp. 1724–1734. ACL (2014)
Ding, Z., He, B., Ma, Y., Han, Z., Tresp, V.: Learning meta representations of one-shot relations for temporal knowledge graph link prediction. CoRR abs/2205.10621 (2022)
Ding, Z., Ma, Y., He, B., Han, Z., Tresp, V.: A simple but powerful graph encoder for temporal knowledge graph completion. In: NeurIPS 2022 Temporal Graph Learning Workshop (2022)
Ding, Z., et al.: Forecasting question answering over temporal knowledge graphs. CoRR abs/2208.06501 (2022)
Ding, Z., Wu, J., He, B., Ma, Y., Han, Z., Tresp, V.: Few-shot inductive learning on temporal knowledge graphs using concept-aware information. In: 4th Conference on Automated Knowledge Base Construction (2022)
Guo, J., Kok, S.: Bique: biquaternionic embeddings of knowledge graphs. In: EMNLP (1), pp. 8338–8351. Association for Computational Linguistics (2021)
Hamaguchi, T., Oiwa, H., Shimbo, M., Matsumoto, Y.: Knowledge transfer for out-of-knowledge-base entities: a graph neural network approach. In: IJCAI, pp. 1802–1808. ijcai.org (2017)
He, Y., Wang, Z., Zhang, P., Tu, Z., Ren, Z.: VN network: embedding newly emerging entities with virtual neighbors. In: CIKM, pp. 505–514. ACM (2020)
Jung, J., Jung, J., Kang, U.: Learning to walk across time for interpretable temporal knowledge graph completion. In: KDD, pp. 786–795. ACM (2021)
Lacroix, T., Obozinski, G., Usunier, N.: Tensor decompositions for temporal knowledge base completion. In: ICLR. OpenReview.net (2020)
Leblay, J., Chekol, M.W.: Deriving validity time in knowledge graph. In: WWW (Companion Volume), pp. 1771–1776. ACM (2018)
Li, J., Tang, T., Zhao, W.X., Wei, Z., Yuan, N.J., Wen, J.: Few-shot knowledge graph-to-text generation with pretrained language models. In: ACL/IJCNLP (Findings). Findings of ACL, vol. ACL/IJCNLP 2021, pp. 1558–1568. Association for Computational Linguistics (2021)
Li, Z., et al.: Search from history and reason for future: two-stage reasoning on temporal knowledge graphs. In: ACL/IJCNLP (1), pp. 4732–4743. Association for Computational Linguistics (2021)
Lin, Y., Liu, Z., Sun, M., Liu, Y., Zhu, X.: Learning entity and relation embeddings for knowledge graph completion. In: AAAI, pp. 2181–2187. AAAI Press (2015)
Messner, J., Abboud, R., Ceylan, İ.İ.: Temporal knowledge graph completion using box embeddings. In: AAAI, pp. 7779–7787. AAAI Press (2022)
Mirtaheri, M., Rostami, M., Ren, X., Morstatter, F., Galstyan, A.: One-shot learning for temporal knowledge graphs. In: 3rd Conference on Automated Knowledge Base Construction (2021)
Nickel, M., Tresp, V., Kriegel, H.: A three-way model for collective learning on multi-relational data. In: ICML, pp. 809–816. Omnipress (2011)
Sadeghian, A., Armandpour, M., Colas, A., Wang, D.Z.: Chronor: rotation based temporal knowledge graph embedding. In: AAAI, pp. 6471–6479. AAAI Press (2021)
Saxena, A., Tripathi, A., Talukdar, P.P.: Improving multi-hop question answering over knowledge graphs using knowledge base embeddings. In: ACL, pp. 4498–4507. Association for Computational Linguistics (2020)
Schlichtkrull, M., Kipf, T.N., Bloem, P., van den Berg, R., Titov, I., Welling, M.: Modeling relational data with graph convolutional networks. In: Gangemi, A., et al. (eds.) ESWC 2018. LNCS, vol. 10843, pp. 593–607. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93417-4_38
Sheng, J., et al.: Adaptive attentional network for few-shot knowledge graph completion. In: EMNLP (1), pp. 1681–1691. Association for Computational Linguistics (2020)
Sun, H., Zhong, J., Ma, Y., Han, Z., He, K.: Timetraveler: reinforcement learning for temporal knowledge graph forecasting. In: EMNLP (1), pp. 8306–8319. Association for Computational Linguistics (2021)
Tresp, V., Esteban, C., Yang, Y., Baier, S., Krompaß, D.: Learning with memory embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.07972 (2015)
Trouillon, T., Welbl, J., Riedel, S., Gaussier, É., Bouchard, G.: Complex embeddings for simple link prediction. In: ICML, JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, vol. 48, pp. 2071–2080. JMLR.org (2016)
Tucker, L.R.: The extension of factor analysis to three-dimensional matrices. In: Gulliksen, H., Frederiksen, N. (eds.) Contributions to Mathematical Psychology, pp. 110–127. Holt, Rinehart and Winston, New York (1964)
Vashishth, S., Sanyal, S., Nitin, V., Talukdar, P.P.: Composition-based multi-relational graph convolutional networks. In: ICLR. OpenReview.net (2020)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: NIPS, pp. 5998–6008 (2017)
Vinyals, O., Blundell, C., Lillicrap, T., Kavukcuoglu, K., Wierstra, D.: Matching networks for one shot learning. In: NIPS, pp. 3630–3638 (2016)
Wang, P., Han, J., Li, C., Pan, R.: Logic attention based neighborhood aggregation for inductive knowledge graph embedding. In: AAAI, pp. 7152–7159. AAAI Press (2019)
Wang, R., et al.: Learning to sample and aggregate: few-shot reasoning over temporal knowledge graphs. In: NeurIPS (2022)
Wu, J., Cao, M., Cheung, J.C.K., Hamilton, W.L.: Temp: temporal message passing for temporal knowledge graph completion. In: EMNLP (1), pp. 5730–5746. Association for Computational Linguistics (2020)
Xiong, W., Yu, M., Chang, S., Guo, X., Wang, W.Y.: One-shot relational learning for knowledge graphs. In: EMNLP, pp. 1980–1990. Association for Computational Linguistics (2018)
Xu, C., Chen, Y., Nayyeri, M., Lehmann, J.: Temporal knowledge graph completion using a linear temporal regularizer and multivector embeddings. In: NAACL-HLT, pp. 2569–2578. Association for Computational Linguistics (2021)
Xu, C., Nayyeri, M., Alkhoury, F., Yazdi, H.S., Lehmann, J.: Tero: a time-aware knowledge graph embedding via temporal rotation. In: COLING, pp. 1583–1593. International Committee on Computational Linguistics (2020)
Yang, B., Yih, W., He, X., Gao, J., Deng, L.: Embedding entities and relations for learning and inference in knowledge bases. In: ICLR (Poster) (2015)
Zhang, F., Zhang, Z., Ao, X., Zhuang, F., Xu, Y., He, Q.: Along the time: timeline-traced embedding for temporal knowledge graph completion. In: CIKM, pp. 2529–2538. ACM (2022)
Zhang, Y., Dai, H., Kozareva, Z., Smola, A.J., Song, L.: Variational reasoning for question answering with knowledge graph. In: AAAI, pp. 6069–6076. AAAI Press (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ding, Z., Wu, J., Li, Z., Ma, Y., Tresp, V. (2023). Improving Few-Shot Inductive Learning on Temporal Knowledge Graphs Using Confidence-Augmented Reinforcement Learning. In: Koutra, D., Plant, C., Gomez Rodriguez, M., Baralis, E., Bonchi, F. (eds) Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases: Research Track. ECML PKDD 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14171. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43418-1_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43418-1_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43417-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43418-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)