Abstract
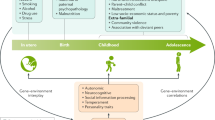
Conduct disorder (CD) is one of the most common psychiatric comorbidity in children with attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and is related to unfavorable clinical, relational, and behavioral outcomes. CD could be subtyped accordingly to age at onset (childhood-onset or adolescent-onset) or the presence or absence of callous unemotional traits. The etiopathogenesis of CD accompanying ADHD is complex and various factors such as enriched genetic risks, poor emotion regulation, temperamental risk characteristics, elevated levels of psychosocial adversity, and inappropriate parenting styles seem to contribute to the disorder. The presence and severity of CD symptoms should be cautiously assessed before making decisions on the intensity and nature of the intervention. Management of CD in ADHD primarily involves parent-based psychosocial interventions, and these interventions are more effective in early to middle childhood. Psychopharmacological agents such as stimulants and atypical antipsychotics may be also effective in certain cases. Further studies are needed to identify the developmental and causal pathways and better intervention strategies for CD in ADHD.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abram, K. M., Zwecker, N. A., Welty, L. J., Hershfield, J. A., Dulcan, M. K., & Teplin, L. A. (2015). Comorbidity and continuity of psychiatric disorders in youth after detention. JAMA Psychiatry, 72(1), 84. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1375
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. A. (2001). Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles : An integrated system of multi-informant assessment. In An integrated system of multi-informant assessment. ASEBA.
Alink, L. R. A., van IJzendoorn, M. H., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., Mesman, J., Juffer, F., & Koot, H. M. (2008). Cortisol and externalizing behavior in children and adolescents: Mixed meta-analytic evidence for the inverse relation of basal cortisol and cortisol reactivity with externalizing behavior. Developmental Psychobiology, 50(5), 427–450. https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.20300
Angold, A., Costello, E. J., & Erkanli, A. (1999). Comorbidity. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 40(1), 57–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-7610.00424
Anney, R. J. L., Lasky-Su, J., Ó’Dúshláine, C., Kenny, E., Neale, B. M., Mulligan, A., Franke, B., Zhou, K., Chen, W., Christiansen, H., Arias-Vásquez, A., Banaschewski, T., Buitelaar, J., Ebstein, R., Miranda, A., Mulas, F., Oades, R. D., Roeyers, H., Rothenberger, A., et al. (2008). Conduct disorder and ADHD: Evaluation of conduct problems as a categorical and quantitative trait in the international multicentre ADHD genetics study. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics : The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics, 147B(8), 1369–1378. https://doi.org/10.1002/AJMG.B.30871
APA. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Fifth Edition (DSM-5).
August, G. J., Realmuto, G. M., Joyce, T., & Hektner, J. M. (1999). Persistence and desistance of oppositional defiant disorder in a community sample of children with ADHD. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 38(10), 1262–1270. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199910000-00015
Azeredo, A., Moreira, D., & Barbosa, F. (2018). ADHD, CD, and ODD: Systematic review of genetic and environmental risk factors. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 82(December 2017), 10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2017.12.010
Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & Van Ijzendoorn, M. H. (2006). Gene-environment interaction of the dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) and observed maternal insensitivity predicting externalizing behavior in preschoolers. Developmental Psychobiology, 48(5), 406–409. https://doi.org/10.1002/DEV.20152
Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., Van IJzendoorn, M. H., Pijlman, F. T. A., Mesman, J., & Juffer, F. (2008). Experimental evidence for differential susceptibility: Dopamine D4 receptor polymorphism (DRD4 VNTR) moderates intervention effects on toddlers’ externalizing behavior in a randomized controlled trial. Developmental Psychology, 44(1), 293–300. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.44.1.293
Barker, E. D., Copeland, W., Maughan, B., Jaffee, S. R., & Uher, R. (2012). Relative impact of maternal depression and associated risk factors on offspring psychopathology. The British Journal of Psychiatry : The Journal of Mental Science, 200(2), 124–129. https://doi.org/10.1192/BJP.BP.111.092346
Barker, E. D., Séguin, J. R., White, H. R., Bates, M. E., Lacourse, É., Carbonneau, R., & Tremblay, R. E. (2007). Developmental trajectories of male physical violence and theft: Relations to neurocognitive performance. Archives of General Psychiatry, 64(5), 592–599. https://doi.org/10.1001/ARCHPSYC.64.5.592
Barkley, R. A. (1997). Behavioral inhibition, sustained attention, and executive functions: Constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychological Bulletin, 121(1), 65–94. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.121.1.65
Barkley, R. A. (2014). Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder : A handbook for diagnosis and treatment. Guilford Press.
Barkley, R. A., Fischer, M., Smallish, L., & Fletcher, K. (2004). Young adult follow-up of hyperactive children: Antisocial activities and drug use. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 45(2), 195–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1469-7610.2004.00214.X
Beauchaine, T. P., Gatzke-Kopp, L., & Mead, H. K. (2007). Polyvagal theory and developmental psychopathology: Emotion dysregulation and conduct problems from preschool to adolescence. Biological Psychology, 74(2), 174–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2005.08.008
Beauchaine, T. P., Hinshaw, S. P., & Pang, K. L. (2010). Comorbidity of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and early-onset conduct disorder: Biological, environmental, and developmental mechanisms. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 17(4), 327–336. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2850.2010.01224.x
Beauchaine, T. P., Katkin, E. S., Strassberg, Z., & Snarr, J. (2001). Disinhibitory psychopathology in male adolescents: Discriminating conduct disorder from attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder through concurrent assessment of multiple autonomic states. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 110(4), 610–624. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.110.4.610
Belanoff, J. K., Gross, K., Yager, A., & Schatzberg, A. F. (2001). Corticosteroids and cognition. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 35(3), 127–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3956(01)00018-8
Biederman, J., Petty, C. R., Dolan, C., Hughes, S., Mick, E., Monuteaux, M. C., & Faraone, S. V. (2008). The long-term longitudinal course of oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder in ADHD boys: Findings from a controlled 10-year prospective longitudinal follow-up study. Psychological Medicine, 38(7), 1027–1036. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291707002668
Biederman, J., & Faraone, S. V. (2005). Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. The Lancet, 366(9481), 237–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66915-2
Biederman, J., Mick, E., Faraone, S. V., Braaten, E., Doyle, A., Spencer, T., Wilens, T. E., Frazier, E., & Johnson, M. A. (2002). Influence of gender on attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children referred to a psychiatric clinic. American Journal of Psychiatry, 159(1), 36–42. https://doi.org/10.1176/APPI.AJP.159.1.36/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/J09F1.JPEG
Bilgiç, A., Uzun, N., Işık, Ü., Açıkel, S. B., Çoşkun, F., & Akça, Ö. F. (2021). The relationships of parent- and child-related psychiatric conditions with oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder symptoms in children with ADHD. Children’s Health Care, 50(4), 353–372. https://doi.org/10.1080/02739615.2021.1894938
Bilgiç, A., Yılmaz, S., Özcan, Ö., Tufan, A. E., Özmen, S., Öztop, D., Akça, Ö. F., Türkoğlu, S., & Yar, A. (2018). The relationship between parental affective temperament traits and disruptive behavior disorders symptoms in children with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 22(13), 1235–1245. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054716646449
Blair, R. J. R., & Lee, T. M. C. (2013). The social cognitive neuroscience of aggression, violence, and psychopathy. In Social neuroscience (Vol. 8, Issue 2, pp. 108–111). Social Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2012.757869.
Blomqvist, M., Holmberg, K., Lindblad, F., Fernell, E., Ek, U., & Dahllöf, G. (2007). Salivary cortisol levels and dental anxiety in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. European Journal of Oral Sciences, 115(1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0722.2007.00423.x
Booster, G. D., DuPaul, G. J., Eiraldi, R., & Power, T. J. (2012). Functional impairments in children with ADHD: Unique effects of age and comorbid status. Journal of Attention Disorders, 16(3), 179–189. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054710383239
Brookes, K. J., Mill, J., Guindalini, C., Curran, S., Xu, X., Knight, J., Chen, C. K., Huang, Y. S., Sethna, V., Taylor, E., Chen, W., Breen, G., & Asherson, P. (2006). A common haplotype of the dopamine transporter gene associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and interacting with maternal use of alcohol during pregnancy. Archives of General Psychiatry, 63(1), 74–81. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.63.1.74
Burke, J. D., Pardini, D. A., & Loeber, R. (2008). Reciprocal relationships between parenting behavior and disruptive psychopathology from childhood through adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 36(5), 679–692. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10802-008-9219-7
Burt, S. A., Krueger, R. F., McGue, M., & Iacono, W. G. (2001). Sources of covariation among attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, and conduct disorder: The importance of shared environment. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 110(4), 516–525. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.110.4.516
Çakaloz, B., Akay, A. P., & Böber, E. (2005). Dikkat eksikliǧi hiperaktivite bozukluǧu ve eşlik eden karşit olma karşi gelme bozukluǧu olan prepubertal erkek çocuklarda plazma kortizol düzeylerinin deǧerlendirilmesi. Klinik Psikofarmakoloji Bulteni, 15(4), 158–164.
Cappadocia, M. C., Desrocher, M., Pepler, D., & Schroeder, J. H. (2009). Contextualizing the neurobiology of conduct disorder in an emotion dysregulation framework. Clinical Psychology Review, 29(6), 506–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2009.06.001
Caspi, A., Langley, K., Milne, B., Moffitt, T. E., O’Donovan, M., Owen, M. J., Tomas, M. P., Poulton, R., Rutter, M., Taylor, A., Williams, B., & Thapar, A. (2008). A replicated molecular genetic basis for subtyping antisocial behavior in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 65(2), 203–210. https://doi.org/10.1001/ARCHGENPSYCHIATRY.2007.24
Caye, A., Spadini, A. V., Karam, R. G., Grevet, E. H., Rovaris, D. L., Bau, C. H. D., Rohde, L. A., & Kieling, C. (2016). Predictors of persistence of ADHD into adulthood: A systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 25(11), 1151–1159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-016-0831-8
Cecil, C. A. M., McCrory, E. J., Barker, E. D., Guiney, J., & Viding, E. (2018). Characterising youth with callous–unemotional traits and concurrent anxiety: Evidence for a high-risk clinical group. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 27(7), 885–898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-017-1086-8
Chamberlain, P. (2003). The Oregon multidimensional treatment foster care model: Features, outcomes, and progress in dissemination. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice, 10(4), 303–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1077-7229(03)80048-2
Choudhry, Z., Sengupta, S. M., Grizenko, N., Fortier, M. E., Thakur, G. A., Bellingham, J., & Joober, R. (2012). LPHN3 and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Interaction with maternal stress during pregnancy. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 53(8), 892–902. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1469-7610.2012.02551.X
Christiansen, H., Chen, W., Oades, R. D., Asherson, P., Taylor, E. A., Lasky-Su, J., Zhou, K., Banaschewski, T., Buschgens, C., Franke, B., Gabriels, I., Manor, I., Marco, R., Müller, U. C., Mulligan, A., Psychogiou, L., Rommelse, N. N. J., Uebel, H., Buitelaar, J., et al. (2008). Co-transmission of conduct problems with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Familial evidence for a distinct disorder. Journal of Neural Transmission 2008 115:2, 115(2), 163–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00702-007-0837-Y
Chronis, A. M., Pelham, W. E., Baumann, B. L., Kipp, H., Lahey, B. B., Williams, S. H., Jones, H. A., & Rathouz, P. J. (2007). Maternal depression and early positive parenting predict future conduct problems in young children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Developmental Psychology, 43(1), 70–82. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.43.1.70
Cloninger, C. R., Svrakic, D. M., & Przybeck, T. R. (1993). A psychobiological model of temperament and character. Archives of General Psychiatry, 50(12), 975–990. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820240059008
Colins, O. F., Andershed, H., Frogner, L., Lopez-Romero, L., Veen, V., & Andershed, A. K. (2014). A new measure to assess psychopathic personality in children: The child problematic traits inventory. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 36(1), 4–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-013-9385-y
Comer, J. S., Chow, C., Chan, P. T., Cooper-Vince, C., & Wilson, L. A. S. (2013). Psychosocial treatment efficacy for disruptive behavior problems in very young children: A meta-analytic examination. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 52(1), 26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2012.10.001
Connor, D. F., Edwards, G., Fletcher, K. E., Baird, J., Barkley, R. A., & Steingard, R. J. (2003). Correlates of comorbid psychopathology in children with ADHD. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 42(2), 193–200. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-200302000-00013
Costello, E. J., Mustillo, S., Erkanli, A., Keeler, G., & Angold, A. (2003). Prevalence and development of psychiatric disorders in childhood and adolescence. Archives of General Psychiatry, 60(8), 837–844. https://doi.org/10.1001/ARCHPSYC.60.8.837
Crowell, S. E., Beauchaine, T. P., Gatzke-Kopp, L., Sylvers, P., Mead, H., & Chipman-Chacon, J. (2006). Autonomic correlates of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and oppositional defiant disorder in preschool children. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 115(1), 174–178. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.115.1.174
Dadds, M. R., Cauchi, A. J., Wimalaweera, S., Hawes, D. J., & Brennan, J. (2012). Outcomes, moderators, and mediators of empathic-emotion recognition training for complex conduct problems in childhood. Psychiatry Research, 199(3), 201–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2012.04.033
Dalsgaard, S., Mortensen, P. B., Frydenberg, M., & Thomsen, P. H. (2013). Long-term criminal outcome of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Criminal Behaviour and Mental Health, 23(2), 86–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/CBM.1860
Dalsgaard, S., Østergaard, S. D., Leckman, J. F., Mortensen, P. B., & Pedersen, M. G. (2015). Mortality in children, adolescents, and adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A nationwide cohort study. The Lancet, 385(9983), 2190–2196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61684-6
De Sanctis, V. A., Newcorn, J. H., & Halperin, J. M. (2014). A prospective look at substance use and criminal behavior in urban ADHD youth: what is the role of maltreatment history on outcome? ADHD Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorders 2014 6:2, 6(2), 79–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12402-013-0124-8
De Vries, S. L. A., Hoeve, M., Assink, M., Stams, G. J. J. M., & Asscher, J. J. (2015). Practitioner review: Effective ingredients of prevention programs for youth at risk of persistent juvenile delinquency - Recommendations for clinical practice. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 56(2), 108–121. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12320
Deault, L. C. (2010). A systematic review of parenting in relation to the development of comorbidities and functional impairments in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 41(2), 168–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10578-009-0159-4
Diamond, A. (2013). Executive functions. In Annual Review of Psychology (Vol. 64, pp. 135–168). Annual Reviews Inc. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750.
Dick, D. M., Viken, R. J., Kaprio, J., Pulkkinen, L., & Rose, R. J. (2005). Understanding the covariation among childhood externalizing symptoms: Genetic and environmental influences on conduct disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity Ddsorder, and oppositional defiant disorder symptoms. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 33(2), 219–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-005-1829-8
Dishion, T. J., McCord, J., & Poulin, F. (1999). When interventions harm. Peer groups and problem behavior. The American Psychologist, 54(9), 755–764. https://doi.org/10.1037//0003-066X.54.9.755
Donfrancesco, R., Di Trani, M., Porfirio, M. C., Giana, G., Miano, S., & Andriola, E. (2015). Might the temperament be a bias in clinical study on attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?: Novelty seeking dimension as a core feature of ADHD. Psychiatry Research, 227(2–3), 333–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2015.02.014
Einziger, T., Levi, L., Zilberman-Hayun, Y., Auerbach, J. G., Atzaba-Poria, N., Arbelle, S., & Berger, A. (2018). Predicting ADHD symptoms in adolescence from early childhood temperament traits. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 46(2), 265–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-017-0287-4
Ercan, E. S., Polanczyk, G., Akyol Ardıc, U., Yuce, D., Karacetın, G., Tufan, A. E., Tural, U., Aksu, H., Aktepe, E., Rodopman Arman, A., Başgül, S., Bılac, O., Coşkun, M., Celık, G. G., Karakoc Demırkaya, S., Dursun, B. O., Durukan, İ., Fidan, T., Perdahlı Fiş, N., et al. (2019). The prevalence of childhood psychopathology in Turkey: A cross-sectional multicenter nationwide study (EPICPAT-T). Nordic Journal of Psychiatry, 73(2), 132–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/08039488.2019.1574892
Erskine, H. E., Ferrari, A. J., Nelson, P., Polanczyk, G. V., Flaxman, A. D., Vos, T., Whiteford, H. A., & Scott, J. G. (2013). Research review: Epidemiological modelling of attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder and conduct disorder for the global burden of disease study 2010. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 54(12), 1263–1274. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12144
Erskine, H. E., Ferrari, A. J., Polanczyk, G. V., Moffitt, T. E., Murray, C. J. L., Vos, T., Whiteford, H. A., & Scott, J. G. (2014). The global burden of conduct disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in 2010. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 55(4), 328–336. https://doi.org/10.1111/JCPP.12186
Erskine, H. E., Norman, R. E., Ferrari, A. J., Chan, G. C. K., Copeland, W. E., Whiteford, H. A., & Scott, J. G. (2016). Long-term outcomes of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and conduct disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 55(10), 841–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2016.06.016
Eskander, N. (2020). The psychosocial outcome of conduct and oppositional defiant disorder in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Cureus, 12(8), 8–13. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.9521
Eyberg, S., & Pincus, D. (1999). Eyberg Child Behavior Inventory & Sutter–Eyberg Student Behavior Inventory- Revised: Professional Manual. Psychological Assessment Resources.
Fairchild, G., Hawes, D. J., Frick, P. J., Copeland, W. E., Odgers, C. L., Franke, B., Freitag, C. M., & De Brito, S. A. (2019). Conduct disorder. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 5(1), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0095-y
Faraone, S. V., Biederman, J., Jetton, J. G., & Tsuang, M. T. (1997). Attention deficit disorder and conduct disorder: Longitudinal evidence for a familial subtype. Psychological Medicine, 27(2), 291–300. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291796004515
Faraone, S. V., Asherson, P., Banaschewski, T., Biederman, J., Buitelaar, J. K., Ramos-Quiroga, J. A., Rohde, L. A., Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S., Tannock, R., & Franke, B. (2015). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 1(1), 15020. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.20
Faraone, S. V., Biederman, J., & Monuteaux, M. C. (2000a). Toward guidelines for pedigree selection in genetic studies of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Genetic Epidemiology, 18(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-2272(200001)18:1<1::AID-GEPI1>3.0.CO;2-X
Faraone, S. V., Biederman, J., & Monuteaux, M. C. (2000b). Attention-deficit disorder and conduct disorder in girls: Evidence for a familial subtype. Biological Psychiatry, 48(1), 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3223(00)00230-4
Faraone, S. V., & Larsson, H. (2019). Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Molecular Psychiatry, 24(4), 562–575. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0
Foley, M., McClowry, S. G., & Castellanos, F. X. (2008). The relationship between attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and child temperament. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 29(2), 157–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APPDEV.2007.12.005
Fombonne, E. (1998). Increased rates of psychosocial disorders in youth. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 248(1), 14–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/S004060050013
Fonagy, P., Butler, S., Cottrell, D., Scott, S., Pilling, S., Eisler, I., Fuggle, P., Kraam, A., Byford, S., Wason, J., Smith, J. A., Anokhina, A., Ellison, R., Simes, E., Ganguli, P., Allison, E., & Goodyer, I. M. (2020). Multisystemic therapy versus management as usual in the treatment of adolescent antisocial behaviour (START): 5-year follow-up of a pragmatic, randomised, controlled, superiority trial. The Lancet Psychiatry, 7(5), 420–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30131-0
Forbes, M. K., Rapee, R. M., Camberis, A. L., & McMahon, C. A. (2017). Unique associations between childhood temperament characteristics and subsequent psychopathology symptom trajectories from childhood to early adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 45(6), 1221–1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-016-0236-7
Franke, B., Faraone, S. V., Asherson, P., Buitelaar, J., Bau, C. H. D., Ramos-Quiroga, J. A., Mick, E., Grevet, E. H., Johansson, S., Haavik, J., Lesch, K. P., Cormand, B., & Reif, A. (2012). The genetics of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults, a review. Molecular Psychiatry, 17(10), 960–987. https://doi.org/10.1038/MP.2011.138
Franke, B., Michelini, G., Asherson, P., Banaschewski, T., Bilbow, A., Buitelaar, J. K., Cormand, B., Faraone, S. V., Ginsberg, Y., Haavik, J., Kuntsi, J., Larsson, H., Lesch, K. P., Ramos-Quiroga, J. A., Réthelyi, J. M., Ribases, M., & Reif, A. (2018). Live fast, die young? A review on the developmental trajectories of ADHD across the lifespan. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 28(10), 1059–1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.08.001
Freitag, C. M., Hänig, S., Palmason, H., Meyer, J., Wüst, S., & Seitz, C. (2009). Cortisol awakening response in healthy children and children with ADHD: Impact of comorbid disorders and psychosocial risk factors. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 34(7), 1019–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PSYNEUEN.2009.01.018
Frick, P. J. (2012). Developmental pathways to conduct disorder: Implications for future directions in research, assessment, and treatment. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 41(3), 378–389. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2012.664815
Frick, P. J., & Morris, A. S. (2004). Temperament and developmental pathways to conduct problems. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 33(1), 54–68. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15374424JCCP3301_6
Frick, P. J., & Nigg, J. T. (2012). Current issues in the diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, and conduct disorder. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 8(1), 77–107. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032511-143150
Frick, P. J., Ray, J. V., Thornton, L. C., & Kahn, R. E. (2014). Can callous-unemotional traits enhance the understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of serious conduct problems in children and adolescents? A comprehensive review. Psychological Bulletin, 140(1), 1–57. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0033076
Friend, A., Defries, J. C., & Olson, R. K. (2008). Parental education moderates genetic influences on reading disability: Research article. Psychological Science, 19(11), 1124–1130. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02213.x
Gatti, U., Tremblay, R. E., & Vitaro, F. (2009). Iatrogenic effect of juvenile justice. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50(8), 991–998. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.02057.x
Gerra, G., Leonardi, C., Cortese, E., Zaimovic, A., Dell’Agnello, G., Manfredini, M., Somaini, L., Petracca, F., Caretti, V., Saracino, M. A., Raggi, M. A., & Donnini, C. (2007). Homovanillic acid (HVA) plasma levels inversely correlate with attention deficit-hyperactivity and childhood neglect measures in addicted patients. Journal of Neural Transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996), 114(12), 1637–1647. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00702-007-0793-6
Ghanizadeh, A. (2009). Psychiatric comorbidity differences in clinic-referred children and adolescents with ADHD according to the subtypes and gender. Journal of Child Neurology, 24(6), 679–684. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073808331086
Ghanizadeh, A., Mohammadi, M. R., & Moini, R. (2008). Comorbidity of psychiatric disorders and parental psychiatric disorders in a sample of Iranian children with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 12(2), 149–155. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054708314601
Godwin, J. W., Bierman, K. L., Coie, J. D., Crowley, D. M., Dodge, K. A., Greenberg, M. T., Lochman, J. E., McMahon, R. J., & Pinderhughes, E. E. (2020). The Fast Track intervention’s impact on behaviors of despair in adolescence and young adulthood. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(50), 31748–31753. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2016234117
Goodman, R., Ford, T., Simmons, H., Gatward, R., & Meltzer, H. (2003). Using the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) to screen for child psychiatric disorders in a community sample. International Review of Psychiatry, 15(1–2), 166–172. https://doi.org/10.1080/0954026021000046128
Gunter, T. D., Arndt, S., Riggins-Caspers, K., Wenman, G., & Cadoret, R. J. (2006). Adult outcomes of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and conduct disorder: Are the risks independent or additive? Annals of Clinical Psychiatry, 18(4), 233–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/10401230600948415
Hamshere, M. L., Langley, K., Martin, J., Agha, S. S., Stergiakouli, E., Anney, R. J. L., Buitelaar, J., Faraone, S. V., Lesch, K. P., Neale, B. M., Franke, B., Sonuga-Barke, E., Asherson, P., Merwood, A., Kuntsi, J., Medland, S. E., Ripke, S., Steinhausen, H. C., Freitag, C., et al. (2013). High loading of polygenic risk for ADHD in children with comorbid aggression. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 170(8), 909–916. https://doi.org/10.1176/APPI.AJP.2013.12081129
Harrison, J. E., Weber, S., Jakob, R., & Chute, C. G. (2021). ICD-11: An international classification of diseases for the twenty-first century. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 21. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12911-021-01534-6
Hendriks, A. M., Bartels, M., Colins, O. F., & Finkenauer, C. (2018). Childhood aggression: A synthesis of reviews and meta-analyses to reveal patterns and opportunities for prevention and intervention strategies. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 91, 278–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.03.021
Henggeler, S. W., Schoenwald, S. K., Borduin, C. M., Rowland, M. D., & Cunningham, P. B. (2009). Multisystemic therapy for antisocial behavior in children and adolescents (2nd ed.). Guilford Press.
Herpertz, S. C., Wenning, B., Mueller, B., Qunaibi, M., Sass, H., & Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. (2001). Psychophysiological responses in ADHD boys with and without conduct disorder: Implications for adult antisocial behavior. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40(10), 1222–1230. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-200110000-00017
Hinshaw, S. P., Lahey, B. B., & Hart, E. L. (1993). Issues of taxonomy and comorbidity in the development of conduct disorder. Development and Psychopathology, 5(1–2), 31–49. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579400004247
Hirshfeld-Becker, D. R., Biederman, J., Faraone, S. V., Violette, H., Wrightsman, J., & Rosenbaum, J. F. (2002). Temperamental correlates of disruptive behavior disorders in young children: Preliminary findings. Biological Psychiatry, 51(7), 563–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3223(01)01299-9
Hur, Y. M. (2015). Genetic and environmental etiology of the relationship between childhood hyperactivity/inattention and conduct problems in a South Korean twin sample. Twin Research and Human Genetics, 18(3), 290–297. https://doi.org/10.1017/thg.2015.26
Inci, S. B., Ipci, M., Akyol Ardıç, U., & Ercan, E. S. (2019). Psychiatric comorbidity and demographic characteristics of 1,000 children and adolescents with ADHD in Turkey. Journal of Attention Disorders, 23(11), 1356–1367. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054716666954
İpçi, M., İnci İzmir, S. B., Türkçapar, M. H., Özdel, K., Akyol Ardiç, Ü., & Ercan, E. S. (2020). Psychiatric comorbidity in the subtypes of ADHD in children and adolescents with ADHD according to DSM-IV. Noro Psikiyatri Arsivi, 57(4), 283–289. https://doi.org/10.29399/NPA.24807
Isaksson, J., Nilsson, K. W., Nyberg, F., Hogmark, Å., & Lindblad, F. (2012). Cortisol levels in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 46(11), 1398–1405. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPSYCHIRES.2012.08.021
Işık, Ü., Bilgiç, A., Toker, A., & Kılınç, I. (2018). Serum levels of cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone, and oxytocin in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder combined presentation with and without comorbid conduct disorder. Psychiatry Research, 261(June 2017), 212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2017.12.076
Jaffee, S. R., Strait, L. B., & Odgers, C. L. (2012). From correlates to causes: Can quasi-experimental studies and statistical innovations bring us closer to identifying the causes of antisocial behavior? Psychological Bulletin, 138(2), 272–295. https://doi.org/10.1037/A0026020
Jensen, P. S., Martin, D., & Cantwell, D. P. (1997). Comorbidity in ADHD: Implications for research, practice, and DSM-V. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36(8), 1065–1079. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199708000-00014
Johnson, A. M., Hawes, D. J., Eisenberg, N., Kohlhoff, J., & Dudeney, J. (2017). Emotion socialization and child conduct problems: A comprehensive review and meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 54, 65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CPR.2017.04.001
Johnston, C., & Mash, E. J. (2001). Families of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Review and recommendations for future research. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 4(3), 183–207. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017592030434
Karalunas, S. L., Fair, D., Musser, E. D., Aykes, K., Iyer, S. P., & Nigg, J. T. (2014). Subtyping attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder using temperament dimensions: Toward biologically based nosologic criteria. JAMA Psychiatry, 71(9), 1015–1024. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.763
Karalunas, S. L., Gustafsson, H. C., Fair, D., Musser, E. D., & Nigg, J. T. (2019). Do we need an irritable subtype of ADHD? Replication and extension of a promising temperament profile approach to ADHD subtyping. Psychological Assessment, 31(2), 236–247. https://doi.org/10.1037/pas0000664
Kashdan, T. B., Jacob, R. G., Pelham, W. E., Lang, A. R., Hoza, B., Blumenthal, J. D., & Gnagy, E. M. (2004). Depression and anxiety in parents of children with ADHD and varying levels of oppositional defiant behaviors: Modeling relationships with family functioning. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology : The Official Journal for the Society of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, American Psychological Association, Division, 53, 33(1), 169–181. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15374424JCCP3301_16
Kaufman, J., Birmaher, B., Brent, D., Rao, U., Flynn, C., Moreci, P., Williamson, D., & Ryan, N. (1997). Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL): Initial reliability and validity data. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36(7), 980–988. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199707000-00021
Kerekes, N., Lundström, S., Chang, Z., Tajnia, A., Jern, P., Lichtenstein, P., Nilsson, T., & Anckarsäter, H. (2014). Oppositional defiant- and conduct disorder-like problems: Neurodevelopmental predictors and genetic background in boys and girls, in a nationwide twin study. PeerJ, 2014(1), e359. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.359
Kessler, R. C., Adler, L., Barkley, R., Biederman, J., Conners, C. K., Demler, O., Faraone, S. V., Greenhill, L. L., Howes, M. J., Secnik, K., Spencer, T., Ustun, T. B., Walters, E. E., & Zaslavsky, A. M. (2006). The Prevalence and Correlates of Adult ADHD in the United States: Results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. American Journal of Psychiatry, 163(4), 716–723. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.2006.163.4.716
Kim, J., Choi, I. Y., Dong, Y., Wang, W. T., Brooks, W. M., Weiner, C. P., & Lee, P. (2015). Chronic fetal hypoxia affects axonal maturation in Guinea pigs during development: A longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging and T2 mapping study. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging : JMRI, 42(3), 658–665. https://doi.org/10.1002/JMRI.24825
Kimonis, E. R., Frick, P. J., Skeem, J. L., Marsee, M. A., Cruise, K., Munoz, L. C., Aucoin, K. J., & Morris, A. S. (2008). Assessing callous-unemotional traits in adolescent offenders: Validation of the Inventory of Callous-Unemotional Traits. International Journal of Law and Psychiatry, 31(3), 241–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijlp.2008.04.002
Klein, R. G., Mannuzza, S., Ramos Olazagasti, M. A., Roizen, E., Hutchison, J. A., Lashua, E. C., & Castellanos, F. X. (2012). Clinical and functional outcome of childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder 33 years later. Archives of General Psychiatry, 69(12), 1295–1303. https://doi.org/10.1001/ARCHGENPSYCHIATRY.2012.271
Koisaari, T., Michelsson, K., Holopainen, J. M., Maksimainen, R., Päivänsalo, J., Rantala, K., & Tervo, T. (2015). Traffic and criminal behavior of adults with attention deficit–Hyperactivity with a prospective follow-up from birth to the age of 40 years. Traffic Injury Prevention, 16(8), 824–830. https://doi.org/10.1080/15389588.2015.1029068
Kreppner, J. M., O’Connor, T. G., Rutter, M., Beckett, C., Castle, J., Croft, C., Dunn, J., & Groothues, C. (2001). Can Inattention/Overactivity Be an Institutional Deprivation Syndrome? Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 2001 29:6, 29(6), 513–528. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012229209190
Kuja-Halkola, R., Lichtenstein, P., D’Onofrio, B. M., & Larsson, H. (2015). Codevelopment of ADHD and externalizing behavior from childhood to adulthood. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 56(6), 640–647. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12340
Kumsta, R., Stevens, S., Brookes, K., Schlotz, W., Castle, J., Beckett, C., Kreppner, J., Rutter, M., & Sonuga-Barke, E. (2010). 5HTT genotype moderates the influence of early institutional deprivation on emotional problems in adolescence: Evidence from the English and Romanian Adoptee (ERA) study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 51(7), 755–762. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02249.x
Lahey, B. B., Loeber, R., Quay, H. C., Applegate, B., Shaffer, D., Waldman, I., Hart, E. L., McBurnett, K., Frick, P. J., Jensen, P. S., Dulcan, M. K., Canino, G., & Bird, H. R. (1998). Validity of DSM-IV subtypes of conduct disorder based on age of onset. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 37(4), 435–442. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199804000-00022
Lam, A. K. S., & Ho, T. P. (2010). Early adolescent outcome of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in a Chinese population: 5-year follow-up study. Hong Kong Medical Journal, 16(4), 257–264.
Langley, K., Heron, J., O’Donovan, M. C., Owen, M. J., & Thapar, A. (2010). Genotype link with extreme antisocial behavior: The contribution of cognitive pathways. Archives of General Psychiatry, 67(12), 1317–1323. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.163
Laucht, M., Skowronek, M. H., Becker, K., Schmidt, M. H., Esser, G., Schulze, T. G., & Rietschel, M. (2007). Interacting effects of the dopamine transporter gene and psychosocial adversity on attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms among 15-year-olds from a high-risk community sample. Archives of General Psychiatry, 64(5), 585–590. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.64.5.585
Lee, Y. H., & Song, G. G. (2018). BDNF 196 G/a and COMT Val158Met polymorphisms and susceptibility to ADHD: A meta-analysis. Journal of Attention Disorders, 22(9), 872–877. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054715570389
Li, J. J., & Lee, S. S. (2012). Association of positive and negative parenting behavior with childhood ADHD: Interactions with offspring monoamine oxidase a (MAO-A) genotype. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40(2), 165–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-011-9553-z
Lichtenstein, P., Halldner, L., Zetterqvist, J., Sjölander, A., Serlachius, E., Fazel, S., Långström, N., & Larsson, H. (2012). Medication for attention deficit–hyperactivity disorder and criminality. New England Journal of Medicine, 367(21), 2006–2014. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMOA1203241/SUPPL_FILE/NEJMOA1203241_DISCLOSURES.PDF
Liu, J. (2011). Early health risk factors for violence: Conceptualization, review of the evidence, and implications. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 16(1), 63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AVB.2010.12.003
Liu, J., & Raine, A. (2006). The effect of childhood malnutrition on externalizing behavior. Current Opinion in Pediatrics, 18(5), 565–570. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.MOP.0000245360.13949.91
Loeber, R., & Hay, D. (1997). Key issues in the development of aggression and violence from childhood to early adulthood. Annual Review of Psychology, 48, 371–410. https://doi.org/10.1146/ANNUREV.PSYCH.48.1.371
Lorber, M. F. (2004). Psychophysiology of aggression, psychopathy, and conduct problems: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 130(4), 531–552. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.130.4.531
Lukkari, S., Hakko, H., Herva, A., Pouta, A., Riala, K., & Räsänen, P. (2012). Exposure to obstetric complications in relation to subsequent psychiatric disorders of adolescent inpatients: Specific focus on gender differences. Psychopathology, 45(5), 317–326. https://doi.org/10.1159/000336073
Lundström, S., Forsman, M., Larsson, H., Kerekes, N., Serlachius, E., Långström, N., & Lichtenstein, P. (2014). Childhood neurodevelopmental disorders and violent criminality: A sibling control study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 44(11), 2707–2716. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10803-013-1873-0/TABLES/4
Lynam, D. R. (1998). Early identification of the fledgling psychopath: Locating the psychopathic child in the current nomenclature. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 107(4), 566–575. https://doi.org/10.1037//0021-843X.107.4.566
Lynam, D. R., Caspi, A., Moffit, T. E., Wikström, P.-O., Loeber, R., & Novak, S. (2000). The interaction between impulsivity and neighborhood context on offending: The effects of impulsivity are stronger in poorer neighborhoods. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 109(4), 563–574. https://doi.org/10.1037//0021-843X.109.4.563
Mannuzza, S., Klein, R. G., Bessler, A., Malloy, P., & LaPadula, M. (1993). Adult outcome of hyperactive boys: Educational achievement, occupational rank, and psychiatric status. Archives of General Psychiatry, 50(7), 565–576. https://doi.org/10.1001/ARCHPSYC.1993.01820190067007
Mannuzza, S., Klein, R. G., Konig, P. H., & Giampino, T. L. (1989). Hyperactive boys almost grown up: IV. Criminality and its relationship to psychiatric status. Archives of General Psychiatry, 46(12), 1073–1079. https://doi.org/10.1001/ARCHPSYC.1989.01810120015004
Mannuzza, S., Klein, R. G., & Moulton, J. L. (2008). Lifetime criminality among boys with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A prospective follow-up study into adulthood using official arrest records. Psychiatry Research, 160(3), 237–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PSYCHRES.2007.11.003
Martel, M. M. (2009). Research review: A new perspective on attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Emotion dysregulation and trait models. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50(9), 1042–1051. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02105.x
Martel, M. M., Gremillion, M. L., & Roberts, B. (2012). Temperament and common disruptive behavior problems in preschool. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(7), 874–879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2012.07.011
Martel, M. M., Gremillion, M. L., Roberts, B. A., Zastrow, B. L., & Tackett, J. L. (2014). Longitudinal prediction of the one-year course of preschool ADHD symptoms: Implications for models of temperament–ADHD associations. Personality and Individual Differences, 64, 58–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2014.02.018
Martel, M. M., & Nigg, J. T. (2006). Child ADHD and personality/temperament traits of reactive and effortful control, resiliency, and emotionality. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 47(11), 1175–1183. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01629.x
Martel, M. M., Nigg, J. T., & Von Eye, A. (2009). How do trait dimensions map onto ADHD symptom domains? Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37(3), 337–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-008-9255-3
Martin, N. C., Levy, F., Pieka, J., & Hay, D. A. (2006). A genetic study of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder, oppositional defiant disorder and Reading disability: Aetiological overlaps and implications. International Journal of Disability, Development and Education, 53(1), 21–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/10349120500509992
Matthys, W., Vanderschuren, L. J. M. J., & Schutter, D. J. L. G. (2013). The neurobiology of oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder: Altered functioning in three mental domains. Development and Psychopathology, 25(1), 193–207. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579412000272
McCart, M. R., & Sheidow, A. J. (2016). Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for adolescents with disruptive behavior. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 45(5), 529–563. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2016.1146990
Meier, M. H., Slutske, W. S., Arndt, S., & Cadoret, R. J. (2008). Impulsive and callous traits are more strongly associated with delinquent behavior in higher risk neighborhoods among boys and girls. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 117(2), 377–385. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.117.2.377
Merwood, A., Asherson, P., & Larsson, H. (2013). Genetic associations between the ADHD symptom dimensions and Cloninger’s temperament dimensions in adult twins. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 23(6), 416–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.10.003
Michelson, D., Davenport, C., Dretzke, J., Barlow, J., & Day, C. (2013). Do evidence-based interventions work when tested in the “real world?” a systematic review and meta-analysis of parent management training for the treatment of child disruptive behavior. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 16(1), 18–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-013-0128-0
Mier, D., Kirsch, P., & Meyer-Lindenberg, A. (2010). Neural substrates of pleiotropic action of genetic variation in COMT: A meta-analysis. Molecular Psychiatry, 15(9), 918–927. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2009.36
Moffitt, T. E. (1990). Juvenile delinquency and attention deficit disorder: Boys’ developmental trajectories from age 3 to age 15. Child Development, 61(3), 893. https://doi.org/10.2307/1130972
Moffitt, T. E. (2017). Life-course-persistent versus adolescence-limited antisocial behavior. Developmental and Life-Course Criminological Theories, 75–103. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315094908-4
Moffitt, T. E., Arseneault, L., Jaffee, S. R., Kim-Cohen, J., Koenen, K. C., Odgers, C. L., Slutske, W. S., & Viding, E. (2008). Research review: DSM-V conduct disorder: Research needs for an evidence base. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49(1), 3–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01823.x
Moffitt, T. E., Caspi, A., Harrington, H., & Milne, B. J. (2002). Males on the life-course-persistent and adolescence-limited antisocial pathways: Follow-up at age 26 years. Development and Psychopathology, 14(1), 179–207. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579402001104
Moffitt, T. E., & Scott, S. (2009). Conduct disorders of childhood and adolescence. Rutter’s Child and Adolescent Psychiatry: Fifth Edition, 543–564. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444300895.CH35
Mohammadi, M. R., Zarafshan, H., Khaleghi, A., Ahmadi, N., Hooshyari, Z., Mostafavi, S. A., Ahmadi, A., Alavi, S. S., Shakiba, A., & Salmanian, M. (2021). Prevalence of ADHD and its comorbidities in a population-based sample. Journal of Attention Disorders, 25(8), 1058–1067. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054719886372
Mohr-Jensen, C., & Steinhausen, H. C. (2016). A meta-analysis and systematic review of the risks associated with childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder on long-term outcome of arrests, convictions, and incarcerations. Clinical Psychology Review, 48, 32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CPR.2016.05.002
Murray, J., Burgess, S., Zuccolo, L., Hickman, M., Gray, R., & Lewis, S. J. (2016). Moderate alcohol drinking in pregnancy increases risk for children’s persistent conduct problems: Causal effects in a Mendelian randomisation study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 57(5), 575–584. https://doi.org/10.1111/JCPP.12486
Nadder, T. S., Rutter, M., Silberg, J. L., Maes, H. H., & Eaves, L. J. (2002). Genetic effects on the variation and covariation of attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and oppositional-defiant disorder/conduct disorder (ODD/CD) symptomatologies across informant and occasion of measurement. Psychological Medicine, 32(1), 39–53. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033291701004792
Nadder, T. S., Silberg, J. L., Eaves, L. J., Maes, H. H., & Meyer, J. M. (1998). Genetic effects on ADHD symptomatology in 7- to 13-year-old twins: Results from a telephone survey. Behavior Genetics, 28(2), 83–99. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021686906396
NICE Clinical Guidelines. (2017). Antisocial behaviour and conduct disorders in children and young people: recognition and management. Antisocial Behaviour and Conduct Disorders in Children and Young People: Recognition and Management.
Nigg, J. T. (2006). Temperament and developmental psychopathology. In Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines (Vol. 47, Issues 3–4, pp. 395–422). J Child Psychol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01612.x.
Nigg, J. T., Goldsmith, H. H., & Sachek, J. (2004). Temperament and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: The development of a multiple pathway model. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 33(1), 42–53. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15374424JCCP3301_5
Nikolas, M. A., & Burt, S. A. (2010). Genetic and environmental influences on ADHD symptom dimensions of inattention and hyperactivity: A meta-analysis. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 119(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018010
Nock, M. K., Kazdin, A. E., Hiripi, E., & Kessler, R. C. (2006). Prevalence, subtypes, and correlates of DSM-IV conduct disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Psychological Medicine, 36(5), 699–710. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291706007082
Noordermeer, S. D. S., Luman, M., & Oosterlaan, J. (2016). A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Neuroimaging in Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) and Conduct Disorder (CD) Taking Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Into Account. Neuropsychology Review, 26(1), 44–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-015-9315-8
Northover, C., Thapar, A., Langley, K., Fairchild, G., & van Goozen, S. H. M. (2016). Cortisol levels at baseline and under stress in adolescent males with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, with or without comorbid conduct disorder. Psychiatry Research, 242, 130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PSYCHRES.2016.05.052
Odgers, C. L., Caspi, A., Broadbent, J. M., Dickson, N., Hancox, R. J., Harrington, H., Poulton, R., Sears, M. R., Thomson, W. M., & Moffitt, T. E. (2007). Prediction of differential adult health burden by conduct problem subtypes in males. Archives of General Psychiatry, 64(4), 476. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.64.4.476
Pardini, D. A., & Fite, P. J. (2010). Symptoms of conduct disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and callous-unemotional traits as unique predictors of psychosocial maladjustment in boys: Advancing an evidence base for DSM-V. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 49(11), 1134–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JAAC.2010.07.010
Pennington, B. F., McGrath, L. M., Rosenberg, J., Barnard, H., Smith, S. D., Willcutt, E. G., Friend, A., DeFries, J. C., & Olson, R. K. (2009). Gene × environment interactions in Reading disability and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Developmental Psychology, 45(1), 77–89. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014549
Pfiffner, L. J., McBurnett, K., Rathouz, P. J., & Judice, S. (2005). Family correlates of oppositional and conduct disorders in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 33(5), 551–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10802-005-6737-4
Pluess, M., Belsky, J., & Neuman, R. J. (2009). Prenatal smoking and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: DRD4-7R as a plasticity gene. Biological Psychiatry, 66(4), e5–e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.04.019
Polanczyk, G. V., Salum, G. A., Sugaya, L. S., Caye, A., & Rohde, L. A. (2015). Annual research review: A meta-analysis of the worldwide prevalence of mental disorders in children and adolescents. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 56(3), 345–365. https://doi.org/10.1111/JCPP.12381
Powers, C. J., Bierman, K. L., & Coffman, D. L. (2016). Restrictive educational placements increase adolescent risks for students with early-starting conduct problems. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 57(8), 899–908. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12487
Pratt, T. C., Cullen, F. T., Blevins, K. R., Daigle, L., & Unnever, J. D. (2002). The relationship of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder to crime and delinquency: A meta-analysis. International Journal of Police Science and Management, 4(4), 344–360. https://doi.org/10.1350/ijps.4.4.344.10873
Prencipe, A., Kesek, A., Cohen, J., Lamm, C., Lewis, M. D., & Zelazo, P. D. (2011). Development of hot and cool executive function during the transition to adolescence. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 108(3), 621–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2010.09.008
Pringsheim, T., Hirsch, L., Gardner, D., & Gorman, D. A. (2015). The pharmacological management of oppositional behaviour, conduct problems, and aggression in children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, and conduct disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysi. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. Revue Canadienne de Psychiatrie, 60(2), 42–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/070674371506000203
Prior, M., Smart, D., Sanson, A., & Oberklaid, F. (2001). Longitudinal predictors of behavioural adjustment in pre-adolescent children. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 35(3), 297–307. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1614.2001.00903.x
Propper, C., Willoughby, M., Halpern, C. T., Carbone, M. A., & Cox, M. (2007). Parenting quality, DRD4, and the prediction of externalizing and internalizing behaviors in early childhood. Developmental Psychobiology, 49(6), 619–632. https://doi.org/10.1002/DEV.20249
Purcell, S. (2002). Variance components models for gene-environment interaction in twin analysis. Twin Research, 5(6), 554–571. https://doi.org/10.1375/136905202762342026
Raine, A. (2002). Biosocial studies of antisocial and violent behavior in children and adults: A review. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 30(4), 311–326. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015754122318
Raine, A., Brennan, P., & Mednick, S. A. (1997). Interaction between birth complications and early maternal rejection in predisposing individuals to adult violence: Specificity to serious, early-onset violence. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 154(9), 1265–1271. https://doi.org/10.1176/AJP.154.9.1265
Randazzo, W. T., Dockray, S., & Susman, E. J. (2008). The stress response in adolescents with inattentive type ADHD symptoms. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 39(1), 27–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-007-0068-3
Reif, A., Rösler, M., Freitag, C. M., Schneider, M., Eujen, A., Kissling, C., Wenzler, D., Jacob, C. P., Retz-Junginger, P., Thome, J., Lesch, K. P., & Retz, W. (2007). Nature and nurture predispose to violent behavior: Serotonergic genes and adverse childhood environment. Neuropsychopharmacology, 32(11), 2375–2383. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301359
Rettew, D. C., Copeland, W., Stanger, C., & Hudziak, J. J. (2004). Associations between temperament and DSM-IV externalizing disorders in children and adolescents. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 25(6), 383–391. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004703-200412000-00001
Retz, W., Ginsberg, Y., Turner, D., Barra, S., Retz-Junginger, P., Larsson, H., & Asherson, P. (2021). Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), antisociality and delinquent behavior over the lifespan. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 120(November 2020), 236–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.11.025
Reyes, M., Croonenberghs, J., Augustyns, I., & Eerdekens, M. (2006). Long-term use of risperidone in children with disruptive behavior disorders and subaverage intelligence: Efficacy, safety, and tolerability. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 16(3), 260–272. https://doi.org/10.1089/cap.2006.16.260
Rösler, M., Retz, W., Retz-Junginger, P., Hengesch, G., Schneider, M., Supprian, T., Schwitzgebel, P., Pinhard, K., Dovi-Akue, N., Wender, P., & Thome, J. (2004). Prevalence of attention deficit−/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and comorbid disorders in young male prison inmates*. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 2004 254:6, 254(6), 365–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00406-004-0516-Z
Rothbart, M. K., & Bates, J. E. (1998). Temperament. In W. Damon & N. Eisenberg (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology: Social, emotional, and personality development (pp. 105–176).
Rowe, R., Maughan, B., Pickles, A., Costello, E. J., & Angold, A. (2002). The relationship between DSM-IV oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder: Findings from the Great Smoky Mountains study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 43(3), 365–373.
Rubia, K. (2011). “Cool” inferior frontostriatal dysfunction in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder versus “hot” ventromedial orbitofrontal-limbic dysfunction in conduct disorder: A review. Biological Psychiatry, 69(12), e69–e87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.023
Rutter, M. (2007). Gene-environment interdependence. In Developmental science (Vol. 10, Issue 1, pp. 12–18). Developmental Science. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7687.2007.00557.x.
Sagar, R., Patra, B. N., & Patil, V. (2019). Clinical practice guidelines for the management of conduct disorder. Indian Journal of Psychiatry, 61(8), S270–S276. https://doi.org/10.4103/PSYCHIATRY.INDIANJPSYCHIATRY_539_18
Sanders, M. R. (2012). Development, evaluation, and multinational dissemination of the triple P-positive parenting program. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 8(1), 345–379. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032511-143104
Satterfield, J. H., Hoppe, C. M., & Schell, A. M. (1982). A prospective study of delinquency in 110 adolescent boys with attention deficit disorder and 88 normal adolescent boys. American Journal of Psychiatry, 139(6), 795–798. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.139.6.795
Satterfield, J. H., Faller, K. J., Crinella, F. M., Schell, A. M., Swanson, J. M., & Homer, L. D. (2007). A 30-year prospective follow-up study of hyperactive boys with conduct problems: Adult criminality. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 46(5), 601–610. https://doi.org/10.1097/chi.0b013e318033ff59
Schmeck, K., & Poustka, F. (2001). Temperament and disruptive behavior disorders. Psychopathology, 34(3), 159–163. https://doi.org/10.1159/000049300
Schoofs, D., Preuß, D., & Wolf, O. T. (2008). Psychosocial stress induces working memory impairments in an n-back paradigm. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 33(5), 643–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PSYNEUEN.2008.02.004
Scott, S., Knapp, M., Henderson, J., & Maughan, B. (2001). Financial cost of social exclusion: Follow up study of antisocial children into adulthood. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.), 323(7306), 191–194. https://doi.org/10.1136/BMJ.323.7306.191
Scotto Rosato, N., Correll, C. U., Pappadopulos, E., Chait, A., Crystal, S., & Jensen, P. S. (2012). Treatment of maladaptive aggression in youth: CERT guidelines II. Treatments and Ongoing Management. Pediatrics, 129(6), e1577–e1586. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2010-1361
Seeger, G., Schloss, P., Schmidt, M. H., Rüter-Jungfleisch, A., & Henn, F. A. (2004). Gene-environment interaction in hyperkinetic conduct disorder (HD + CD) as indicated by season of birth variations in dopamine receptor (DRD4) gene polymorphism. Neuroscience Letters, 366(3), 282–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.05.049
Sexton, T., & Turner, C. W. (2010). The effectiveness of functional family therapy for youth with behavioral problems in a community practice setting. Journal of Family Psychology, 24(3), 339–348. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019406
Shaffer, D., Fisher, P., & Lucas, C. (2004). The Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children (DISC). In M. J. Hilsenroth & D. L. Segal (Eds.), Comprehensive handbook of psychological assessment, Vol. 2. Personality assessment (pp. 256–270).
Sharp, C. (2002). Sex differences in antisocial behaviour: Conduct disorder, delinquency and violence in the Dunedin longitudinal study. By T. Moffitt, A. Caspi, M. Rutter and P. Silva. Psychological Medicine, 32(8), 1475–1478. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291702216670
Sibley, M. H., Pelham, W. E., Molina, B. S. G., Gnagy, E. M., Waschbusch, D. A., Biswas, A., MacLean, M. G., Babinski, D. E., & Karch, K. M. (2011). The delinquency outcomes of boys with ADHD with and without comorbidity. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 39(1), 21–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10802-010-9443-9/TABLES/2
Silva, D., Colvin, L., Glauert, R., & Bower, C. (2014). Contact with the juvenile justice system in children treated with stimulant medication for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A population study. The Lancet. Psychiatry, 1(4), 278–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(14)70302-5
Sinclair, I., Parry, E., Biehal, N., Fresen, J., Kay, C., Scott, S., & Green, J. (2016). Multi-dimensional Treatment Foster Care in England: Differential effects by level of initial antisocial behaviour. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 25(8), 843–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-015-0799-9
Smoller, J. W., Kendler, K., Craddock, N., Lee, P. H., Neale, B. M., Nurnberger, J. N., Ripke, S., Santangelo, S., Sullivan, P. S., Neale, B. N., Purcell, S., Anney, R., Buitelaar, J., Fanous, A., Faraone, S. F., Hoogendijk, W., Lesch, K. P., Levinson, D. L., Perlis, R. P., et al. (2013). Identification of risk loci with shared effects on five major psychiatric disorders: A genome-wide analysis. The Lancet, 381(9875), 1371–1379. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62129-1
Snoek, H., Van Goozen, S. H. M., Matthys, W., Buitelaar, J. K., & Van Engeland, H. (2004). Stress responsivity in children with externalizing behavior disorders. Development and Psychopathology, 16(2), 389–406. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579404044578
Steinberg, E. A., & Drabick, D. A. G. (2015). A developmental psychopathology perspective on ADHD and comorbid conditions: The role of emotion regulation. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 46(6), 951–966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-015-0534-2
Stevens, S. E., Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S., Kreppner, J. M., Beckett, C., Castle, J., Colvert, E., Groothues, C., Hawkins, A., & Rutter, M. (2008). Inattention/overactivity following early severe institutional deprivation: Presentation and associations in early adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 36(3), 385–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-007-9185-5
Stuss, D. T., & Alexander, M. P. (2000). Executive functions and the frontal lobes: A conceptual view. Psychological Research, 63(3–4), 289–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004269900007
Swanson, J. M., Arnold, L. E., Molina, B. S. G., Sibley, M. H., Hechtman, L. T., Hinshaw, S. P., Abikoff, H. B., Stehli, A., Owens, E. B., Mitchell, J. T., Nichols, Q., Howard, A., Greenhill, L. L., Hoza, B., Newcorn, J. H., Jensen, P. S., Vitiello, B., Wigal, T., Epstein, J. N., et al. (2017). Young adult outcomes in the follow-up of the multimodal treatment study of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Symptom persistence, source discrepancy, and height suppression. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 58(6), 663–678. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12684
Szatmari, P., Boyle, M., & Offord, D. R. (1989). ADDH and conduct disorder: Degree of diagnostic overlap and differences among correlates. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 28(6), 865–872. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-198911000-00010
Taylor, E., Chadwick, O., Heptinstall, E., & Danckaerts, M. (1996). Hyperactivity and conduct problems as risk factors for adolescent development. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 35(9), 1213–1226. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199609000-00019
Thapar, A., Harrington, R., & McGuffin, P. (2001). Examining the comorbidity of ADHD-related behaviours and conduct problems using a twin study design. British Journal of Psychiatry, 179(SEPT.), 224–229. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.179.3.224
Thapar, A., Van Den Bree, M., Fowler, T., Langley, K., & Whittinger, N. (2006). Predictors of antisocial behaviour in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 15(2), 118–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-006-0511-1
Thapar, A., & Van Goozen, S. (2018). Conduct disorder in ADHD. In Oxford textbook of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (pp. 193–199).
Turgay, A., Binder, C., Snyder, R., & Fisman, S. (2002). Long-term safety and efficacy of risperidone for the treatment of disruptive behavior disorders in children with subaverage IQs. Pediatrics, 110(3), e34–e34. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.110.3.e34
Tuvblad, C., Zheng, M., Raine, A., & Baker, L. A. (2009). A common genetic factor explains the covariation among ADHD ODD and CD symptoms in 9-10 year old boys and girls. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37(2), 153–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-008-9278-9
van der Stouwe, T., Asscher, J. J., Stams, G. J. J. M., Deković, M., & van der Laan, P. H. (2014). The effectiveness of Multisystemic Therapy (MST): A meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 34(6), 468–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2014.06.006
Van Goozen, S. H. M., Fairchild, G., Snoek, H., & Harold, G. T. (2007). The evidence for a neurobiological model of childhood antisocial behavior. Psychological Bulletin, 133(1), 149–182. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.133.1.149
Van Goozen, S. H. M., Langley, K., Northover, C., Hubble, K., Rubia, K., Schepman, K., O’Donovan, M. C., & Thapar, A. (2016). Identifying mechanisms that underlie links between COMT genotype and aggression in male adolescents with ADHD. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 57(4), 472–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12464
Van Lang, N. D. J., Tulen, J. H. M., Kallen, V. L., Rosbergen, B., Dieleman, G., & Ferdinand, R. F. (2007). Autonomic reactivity in clinically referred children attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder versus anxiety disorder. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 16(2), 71–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-006-0575-y
Viken, R. J., Kaprio, J., Koskenvuo, M., & Rose, R. J. (1999). Longitudinal analyses of the determinants of drinking and of drinking to intoxication in adolescent twins. Behavior Genetics, 29(6), 455–461. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021631122461
Wåhlstedt, C., Thorell, L. B., & Bohlin, G. (2009). Heterogeneity in ADHD: Neuropsychological pathways, comorbidity and symptom domains. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37(4), 551–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10802-008-9286-9
Webster-Stratton, C., & Reid, M. J. (2003). Treating conduct problems and strengthening social and emotional competence in young children. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 11(3), 130–143. https://doi.org/10.1177/10634266030110030101
Welner, Z., Reich, W., Herjanic, B., Jung, K. G., & Amado, H. (1987). Reliability, validity, and parent-child agreement studies of the Diagnostic Interview for Children and Adolescents (DICA). Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 26(5), 649–653. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-198709000-00007
Werthamer-Larsson, L., Kellam, S., & Wheeler, L. (1991). Effect of first-grade classroom environment on shy behavior, aggressive behavior, and concentration problems. American Journal of Community Psychology, 19(4), 585–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00937993
Yoshimasu, K., Barbaresi, W. J., Colligan, R. C., Voigt, R. G., Killian, J. M., Weaver, A. L., & Katusic, S. K. (2012). Childhood ADHD is strongly associated with a broad range of psychiatric disorders during adolescence: A population-based birth cohort study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53(10), 1036–1043. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2012.02567.x
Young, A. H., Sahakian, B. J., Robbins, T. W., & Cowen, P. J. (1999). The effects of chronic administration of hydrocortisone on cognitive function in normal male volunteers. Psychopharmacology, 145(3), 260–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/S002130051057
Zelazo, P. D., & Carlson, S. M. (2012). Hot and cool executive function in childhood and adolescence: Development and plasticity. Child Development Perspectives, 6(4), 354–360. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-8606.2012.00246.x
Zhou, K., Chen, W., Buitelaar, J., Banaschewski, T., Oades, R. D., Franke, B., Sonuga-Barke, E., Ebstein, R., Eisenberg, J., Gill, M., Manor, I., Miranda, A., Mulas, F., Roeyers, H., Rothenberger, A., Sergeant, J., Steinhausen, H. C., Lasky-Su, J., Taylor, E., et al. (2008). Genetic heterogeneity in ADHD: DAT1 gene only affects probands without CD. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics : The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics, 147B(8), 1481–1487. https://doi.org/10.1002/AJMG.B.30644
Zuckerman, M. (1994). Behavioral expressions and biosocial bases of sensation seeking. Cambridge University Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bilgiç, A., Akça, Ö.F., Işık, Ü., Ercan, E.S. (2023). Conduct Disorder in ADHD. In: Matson, J.L. (eds) Clinical Handbook of ADHD Assessment and Treatment Across the Lifespan. Autism and Child Psychopathology Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41709-2_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41709-2_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-41708-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-41709-2
eBook Packages: Behavioral Science and PsychologyBehavioral Science and Psychology (R0)