Abstract
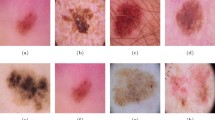
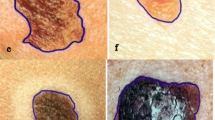
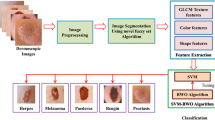
This study has conducted an investigation of the Redescending M-Estimators as alternative to strengthen an Intuitionistic Fuzzy C-Means algorithm against atypical information. In this regard, the objective function was stated taking into account the loss function, while the update expressions for membership matrix and prototypes vector were formulated by a derivative procedure, depending on the influence functions. The evaluated estimators were Huber Skipped Mean, Simple Cut, Tukey Biweight, Hampel’s Three Part Redescending, Andrew’s Sine, German-MacClure, Lorentzian, Asad-Qadir, Insha and Alamgir. The empirical study was performed using the ISIC 2017 dataset in order to make the skin lesion delimitation task, these images had inherent artifacts that were considered as atypical information; the performance was quantified by popular state-of-the-art metrics. The quantitative results show an outstanding performance of the Hampel’s Three Part Redescending with Jaccard Similarity Coefficient\(\,=0.905\pm 0.054\), Dice Measure\(\,=0.910\pm 0.060\), Misclassification Ratio\(\,=\,7.174\pm 0.864\) and Hausdorff Distance\(\,=6.281\pm 0.804\), in contrast all rest estimators.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adegun, A., Viriri, S.: Deep learning techniques for skin lesion analysis and melanoma cancer detection: a survey of state-of-the-art. Artificial Intelligence Review 54, 811–841 (2021)
Alamgir, A.A., Khan, S.A., Khan, D.M., Khalil, U.: A new efficient redescending m-estimator: Alamgir redescending m-estimator. Research Journal of Recent Sciences 2277, 2502 (2013)
Albahli, S., Nida, N., Irtaza, A., Yousaf, M.H., Mahmood, M.T.: Melanoma lesion detection and segmentation using yolov4-darknet and active contour. IEEE Access 8, 198403–198414 (2020)
Ali, A., Qadir, M.F.: A modified m-estimator for the detection of outliers. Pakistan journal of statistics and operation research (2005)
Andrews, D.F., Hampel, F.R.: Robust estimates of location. In: Robust Estimates of Location. Princeton University Press (2015)
Atanassov, K.T., Gargov, G.: Intuitionistic fuzzy logics. Springer (2017)
Beaton, A.E., Tukey, J.W.: The fitting of power series, meaning polynomials, illustrated on band-spectroscopic data. Technometrics 16(2), 147–185 (1974)
Bhattacharya, A., Freund, Y., Jaiswal, R.: On the k-means/median cost function. Inf. Process. Lett. 177, 106252 (2022)
Bindhu, A., Thanammal, K.: Segmentation of skin cancer using fuzzy u-network via deep learning. Meas.: Sens., 100677 (2023)
Chaira, T.: Fuzzy Set and its Extension: The Intuitionistic Fuzzy Set. Wiley (2019)
Codella, N., Rotemberg, V., Tschandl, P., Celebi, M.E., Dusza, S., Gutman, D., Helba, B., Kalloo, A., Liopyris, K., Marchetti, M., et al.: Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection 2018: a challenge hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC) (2019). arXiv:1902.03368
Do, T.T., Hoang, T., Pomponiu, V., Zhou, Y., Chen, Z., Cheung, N.M., Koh, D., Tan, A., Tan, S.H.: Accessible melanoma detection using smartphones and mobile image analysis. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 20(10), 2849–2864 (2018)
Durgarao, N., Sudhavani, G.: Diagnosing skin cancer via c-means segmentation with enhanced fuzzy optimization. IET Image Process. 15(10), 2266–2280 (2021)
Frigui, H., Krishnapuram, R.: A robust algorithm for automatic extraction of an unknown number of clusters from noisy data. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 17(12), 1223–1232 (1996)
Gallegos-Funes, F.J., Ponomaryov, V.I.: Real-time image filtering scheme based on robust estimators in presence of impulsive noise. R.-Time Imaging 10(2), 69–80 (2004)
Gamino-Sánchez, F., Hernández-Gutiérrez, I.V., Rosales-Silva, A.J., Gallegos-Funes, F.J., Mújica-Vargas, D., Ramos-Díaz, E., Carvajal-Gámez, B.E., Kinani, J.M.V.: Block-matching fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm for segmentation of color images degraded with gaussian noise. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 73, 31–49 (2018)
Hasan, M.K., Dahal, L., Samarakoon, P.N., Tushar, F.I., Martí, R.: DSNet: automatic dermoscopic skin lesion segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 120, 103738 (2020)
Huber, P.J., Ronchetti, E.M.: The basic types of estimates. Robust Stat., 43–72 (1981)
Ilesanmi, A.E., Chaumrattanakul, U., Makhanov, S.S.: A method for segmentation of tumors in breast ultrasound images using the variant enhanced deep learning. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 41(2), 802–818 (2021)
Jain, A.K., Dubes, R.C.: Algorithms for Clustering Data. Prentice-Hall, Inc. (1988)
Jayapriya, K., Jacob, I.J.: Hybrid fully convolutional networks-based skin lesion segmentation and melanoma detection using deep feature. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 30(2), 348–357 (2020)
Jiang, L., Yang, W.: A modified fuzzy c-means algorithm for segmentation of magnetic resonance images. In: Proceedings of the VIIth Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (2003)
Kersten, P.R.: Fuzzy order statistics and their application to fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 7(6), 708–712 (1999)
Khachay, M., Khachay, D.: Attainable accuracy guarantee for the k-medians clustering in [0, 1]. Optim. Lett. 13(8), 1837–1853 (2019)
Klomsae, A., Auephanwiriyakul, S., Theera-Umpon, N.: A string grammar possibilistic-fuzzy c-medians. Soft Comput. 23(17), 7637–7653 (2019)
Mújica-Vargas, D., Gallegos-Funes, F.J., Rosales-Silva, A.J.: A fuzzy clustering algorithm with spatial robust estimation constraint for noisy color image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 34(4), 400–413 (2013)
Mújica-Vargas, D., de Jesús Rubio, J., Kinani, J.M.V., Gallegos-Funes, F.J.: An efficient nonlinear approach for removing fixed-value impulse noise from grayscale images. J. R.-Time Image Process. 14(3), 617–633 (2018)
Mújica-Vargas, D., Rendón-Castro, A., Matuz-Cruz, M., Garcia-Aquino, C.: Multi-core median redescending m-estimator for impulsive denoising in color images. In: Mexican Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 261–271. Springer (2021)
Nawaz, M., Mehmood, Z., Nazir, T., Naqvi, R.A., Rehman, A., Iqbal, M., Saba, T.: Skin cancer detection from dermoscopic images using deep learning and fuzzy k-means clustering. Microsc. Res. Tech. 85(1), 339–351 (2022)
Nida, N., Irtaza, A., Javed, A., Yousaf, M.H., Mahmood, M.T.: Melanoma lesion detection and segmentation using deep region based convolutional neural network and fuzzy c-means clustering. Int. J. Med. Inform. 124, 37–48 (2019)
Pander, T., Przybyła, T.: Fuzzy-based algorithm for QRS detection. In: International Workshop on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets and Generalized Nets, pp. 202–215. Springer (2019)
Pitas, I., Venetsanopoulos, A.N.: Nonlinear Digital Filters: Principles and Applications, vol. 84. Springer Science & Business Media (2013)
Raju, D.N., Shanmugasundaram, H., Sasikumar, R.: Fuzzy segmentation and black widow-based optimal SVM for skin disease classification. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 59(10), 2019–2035 (2021)
Rupesh, Y.K., Behnam, P., Pandla, G.R., Miryala, M., Bojnordi, M.N.: Accelerating \(k\)-medians clustering using a novel 4T-4R RRAM cell. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 26(12), 2709–2722 (2018)
Szmidt, E.: Distances and Similarities in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets, vol. 307. Springer (2014)
Tukey, J.W.: A survey of sampling from contaminated distributions. In: Contributions to Probability and Statistics, pp. 448–485 (1960)
Ullah, I., Qadir, M.F., Ali, A.: Insha’s redescending m-estimator for robust regression: a comparative study. Pak. J. Stat. Oper. Res., 135–144 (2006)
Wang, X., Jiang, X., Ding, H., Zhao, Y., Liu, J.: Knowledge-aware deep framework for collaborative skin lesion segmentation and melanoma recognition. Pattern Recognit. 120, 108075 (2021)
Xu, Z.: Intuitionistic fuzzy aggregation operators. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 15(6), 1179–1187 (2007)
Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., Zhu, L.: A parameterized approximation algorithm for the chromatic k-median problem. IEEE Access 9, 31678–31683 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank to CONACYT, as well as TecNM-CENIDET for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mújica-Vargas, D., Carvajal-Gámez, B., Martínez-Rebollar, A., Rubio, J.d.J. (2023). Redescending M-Estimators Analysis on the Intuitionistic Fuzzy Clustering Algorithm for Skin Lesion Delimitation. In: Rivera, G., Cruz-Reyes, L., Dorronsoro, B., Rosete, A. (eds) Data Analytics and Computational Intelligence: Novel Models, Algorithms and Applications. Studies in Big Data, vol 132. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-38325-0_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-38325-0_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-38324-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-38325-0
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)