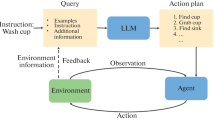
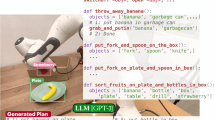
Abstract
Modern pretrained large language models (LLMs) are increasingly being used in zero-shot or few-shot learning modes. Recent years have seen increased interest in applying such models to embodied artificial intelligence and robotics tasks. When given in a natural language, the agent needs to build a plan based on this prompt. The best solutions use LLMs through APIs or models that are not publicly available, making it difficult to reproduce the results. In this paper, we use publicly available LLMs to build a plan for an embodied agent and evaluate them in three modes of operation: 1) the subtask evaluation mode, 2) the full autoregressive plan generation, and 3) the step-by-step autoregressive plan generation. We used two prompt settings: prompt-containing examples of one given task and a mixed prompt with examples of different tasks. Through extensive experiments, we have shown that the subtask evaluation mode, in most cases, outperforms others with a task-specific prompt, whereas the step-by-step autoregressive plan generation posts better performance in the mixed prompt setting.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, M., Brohan, A., Brown, N., Chebotar, Y., et al.: Do as i can and not as i say: grounding language in robotic affordances (2022)
Anderson, P., Fernando, B., Johnson, M., Gould, S.: SPICE: semantic propositional image caption evaluation. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9909, pp. 382–398. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46454-1_24
Black, S., Biderman, S., Hallahan, E., Anthony, Q., et al.: GPT-NeoX-20B: an open-source autoregressive language model (2022)
Brown, T., et al.: Language models are few-shot learners. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Chowdhery, A., Narang, S., Devlin, J., Bosma, M., et al.: PaLM: scaling language modeling with pathways (2022)
Driess, D., Xia, F., Sajjadi, M.S.M., Lynch, C., et al.: PaLM-E: an embodied multimodal language model (2023)
Gao, L., Biderman, S., Black, S., Golding, L., et al.: The pile: an 800GB dataset of diverse text for language modeling (2020)
Gramopadhye, M., Szafir, D.: Generating executable action plans with environmentally-aware language models (2022)
Huang, W., Abbeel, P., Pathak, D., Mordatch, I.: Language models as zero-shot planners: extracting actionable knowledge for embodied agents. In: ICML (2022)
Kolve, E., Mottaghi, R., Han, W., VanderBilt, E., et al.: AI2-THOR: an interactive 3D environment for visual AI (2017)
Kovalev, A.K., Panov, A.I.: Application of pretrained large language models in embodied artificial intelligence. Doklady Math. 106(S1), S85–S90 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064562422060138
Lin, B.Y., Huang, C., Liu, Q., Gu, W., Sommerer, S., Ren, X.: On grounded planning for embodied tasks with language models (2022)
Liu, Y., Ott, M., Goyal, N., Du, J., et al.: RoBERTa: a robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach (2019)
Logeswaran, L., Fu, Y., Lee, M., Lee, H.: Few-shot subgoal planning with language models (2022)
Mackenzie, J., Benham, R., Petri, M., Trippas, J.R., et al.: CC-News-En: a large English news corpus. In: CIKM (2020)
Min, S.Y., Chaplot, D.S., Ravikumar, P., Bisk, Y., Salakhutdinov, R.: FILM: following instructions in language with modular methods (2021)
OpenAI: Introducing ChatGPT (2022). https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt
Reimers, N., Gurevych, I.: Sentence-BERT: sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019). https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.10084
Shibata, Y., Kida, T., Fukamachi, S., Takeda, M., et al.: Byte pair encoding: a text compression scheme that accelerates pattern matching (1999)
Shridhar, M., Thomason, J., Gordon, D., Bisk, Y., et al.: ALFRED: a benchmark for interpreting grounded instructions for everyday tasks. In: CVPR (2020)
Singh, I., Blukis, V., Mousavian, A., Goyal, A., et al.: ProgPrompt: generating situated robot task plans using large language models (2022)
Song, C.H., Wu, J., Washington, C., Sadler, B.M., et al.: LLM-planner: few-shot grounded planning for embodied agents with large language models (2022)
Vedantam, R., Lawrence Zitnick, C., Parikh, D.: CIDEr: consensus-based image description evaluation. In: CVPR (2015)
Vemprala, S., Bonatti, R., Bucker, A., Kapoor, A.: ChatGPT for robotics: design principles and model abilities. Tech. rep., Microsoft (2023)
Wang, B., Komatsuzaki, A.: GPT-J-6B: a 6 billion parameter autoregressive language model (2021). https://github.com/kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax
Wei, J., et al.: Finetuned language models are zero-shot learners (2021)
Wei, J., et al.: Chain of thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models (2022)
Zhang, S., Roller, S., Goyal, N., Artetxe, M., et al.: OPT: open pre-trained transformer language models (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sarkisyan, C., Korchemnyi, A., Kovalev, A.K., Panov, A.I. (2023). Evaluation of Pretrained Large Language Models in Embodied Planning Tasks. In: Hammer, P., Alirezaie, M., Strannegård, C. (eds) Artificial General Intelligence. AGI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13921. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-33469-6_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-33469-6_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-33468-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-33469-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)