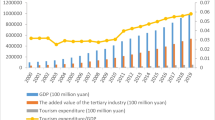
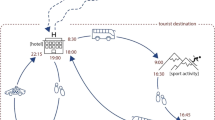
Abstract
In the international literature, several studies have analyzed the impact of HSR on tourists' behavior with qualitative and quantitative approaches. However, they have not been able to solve the problem of capturing the spatial and temporal variation by fitting a regression model at a local point. The spatial heterogeneity within local models, such as Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) models, provides a better platform allowing exploring the different spatial relationships between HSR and tourism. In this chapter, a spatio-temporal analysis has been proposed to evaluate the variables affecting tourists ‘choices, specifically the impact of HSR on both Chinese and Foreign tourists. Two advanced methods were adopted: firstly, we used the Weighted Regression with Poisson distribution (GWPR) modelling approach, which considers the problem of the temporal and spatial autocorrelation differently with respect to the Generalized Estimating Equations method. The results of this study support the use of the GWPR as a promising tool for tourism planning, especially because it makes it possible to model non-stationary spatially counting data. As far as the authors know, this methodology has never been applied in the international literature to this context. Secondly, we combined both temporal autocorrelation and spatial autocorrelation by applying models of Geographical and Temporal Weighted Regression (GTWR) types to take into account the local effects from the temporal point of view.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pagliara, F., Mauriello, F., Garofalo, A.: Exploring the interdependences between High Speed Rail systems and tourism: some evidence from Italy. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 106, 300–308 (2017)
Pagliara, F., Mauriello, F.: Modelling the impact of high speed rail on tourists with geographically weighted poisson regression. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 132, 780–790 (2020)
Yin, P., Pagliara, F., Wilson, A.: How does high-speed rail affect tourism? a case study of the capital region of China. Sustainability 11(2), 472 (2019)
Cao, J., Liu, X.C., Wang, Y., Li, Q.: Accessibility impacts of China’s high-speed rail network. J. Transp. Geogr. 28, 12–21 (2013)
Jiao, J., Wang, J., Jin, F.: Impacts of high-speed rail lines on the city network in China. J. Transp. Geogr. 60, 257–266 (2017)
Shaw, S.L., Fang, Z., Lu, S., Tao, R.: Impacts of high speed rail on railroad network accessibility in China. J. Transp. Geogr. 40, 112–122 (2014)
Wang, W.C., Chang, Y.J., Wang, H.C.: An application of the spatial autocorrelation method on the change of real estate prices in Taitung City. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 8(6), 249 (2019)
Chen, Z., Haynes, K.E.: Impact of high-speed rail on international tourism demand in China. Appl. Econ. Lett. 22(1), 57–60 (2015)
Degen, W., Jia, Q., Yu, N.: Spatial pattern and evolution of urban tourism field strength in China under high speed railway network. Acta Geogr. Sin. 71(10), 1784–1800 (2016)
Xin, W., Tongqiao, Z.: The influence of high speed railway network on the development and layout of China’s regional tourism industry. Econ. Geogr. 30(7), 1189–1194 (2010)
Feng, F., Linhao, C.: The opening of high-speed railway and the development of tourism in station cities: engine or corridor? Econ. Manag. 42(2), 175–191 (2020)
Chen, Z., Haynes, K.E., Zhou, Y., Dai, Z.: High speed rail and China’s new economic geography: Impact assessment from the regional science perspective. Edward Elgar Publishing, Chapter 6, pp. 148–168 (2019)
Taotao, D., Lei, Z., Mulan, M.: Research on the impact of Yangtze River delta high speed railway network on urban tourism development. Econ. Manag. 38(1), 137–146 (2016)
Yuhua, Z., Jun, C.: Heterogeneous impact of high speed rail on tourism development of station cities: a study based on double difference method. Tour. Sci. 32(6), 79–92 (2018)
Lei, L., Lin, L., Chenglin, M., Xiaolong, S.: Evolution of spatial structure of tourism flow in typical tourism cities in the era of high speed railway network: a case study of Huangshan City. Econ. Geogr. 39(5), 207–216 (2019)
Yin, P., Lin, Z., Prideaux, B.: The impact of high-speed railway on tourism spatial structures between two adjoining metropolitan cities in China: Beijing and Tianjin. J. Transp. Geogr. 80, 102495 (2019)
Yin, P., Tonghao, Z., Hanyan, Y.: Study on the change characteristics of urban tourism spatial function of Beijing Tianjin Hebei under the influence of high speed railway. Tour. Guide 4(1), 30–44 (2020)
Ziyang, W., Dan, L., Yuting, Z.: Research on the impact of high speed railway on tourism development based on grey correlation analysis: a case study of Xiamen City. Logist. Eng. Manage. 42(8), 163–165 (2020)
Yongze, Y., Yu, F., Haitao, Z.: The impact of the opening of high speed railway on the development of regional tourism. Res. Financ. 1, 31–38 (2020)
Tinessa, F., Papola, A., Marzano, V.: The importance of choosing appropriate random utility models in complex choice contexts. In: 5th IEEE International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS), pp. 884–888, IEEE, Naples, Italy (2017)
Tinessa, F., Marzano, V., Papola, A., Montanino, M., Simonelli, F.: CoNL route choice model: numerical assessment on a real dataset of trajectories. In: 6th International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS), pp. 1–10, IEEE, Cracow, Poland (2019)
Washington, S.P., Karlaftis, M.G., Mannering, F.: Statistical and Econometric Methods for Transportation Data Analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2010)
Montella, A., Marzano, V., Mauriello, F., Vitillo, R., Fasanelli, R., Pernetti, M., Galante, F.: Development of macro-level safety performance functions in the city of Naples. Sustainability 11(7), 1871 (2019)
Cafiso, S., Montella, A., D’Agostino, C., Mauriello, F., Galante, F.: Crash modification functions for pavement surface condition and geometric design indicators. Accid. Anal. Prev. 149, 105887 (2021)
Jobson, J.D.: Applied Multivariate Data Analysis: Regression and Experimental Design. Springer, New York (1991)
Agresti, A.: Categorical Data Analysis. John Wiley, New Jersey (2002)
Fitzmaurice, G.M., Laird, N.M., Ware, J.H.: Applied Longitudinal Analysis, vol. 998. John Wiley & Sons (2012)
Fotheringham, A.S., Brunsdon, C., Charlton, M.: Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships. Wiley, Chichester (2002)
Nakaya, T., Fotheringham, A.S., Brunsdon, C., Charlton, M.: Geographically weighted Poisson regression for disease association mapping. Stat. Med. 24, 2695–2717 (2005)
Kopczewska, K.: Applied Spatial Statistics and Econometrics Data Analysis in R. Routledge (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mauriello, F., Chen, Z., Pagliara, F. (2023). A Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression Approach for Analyzing the Effect of High-Speed Rail on Tourism in China. In: Pagliara, F. (eds) Socioeconomic Impacts of High-Speed Rail Systems. IW-HSR 2022. Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26340-8_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26340-8_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-26339-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-26340-8
eBook Packages: Economics and FinanceEconomics and Finance (R0)