Abstract
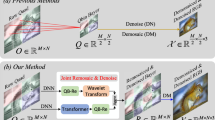
The color filter array widely used in smart phones is mainly Quad Bayer and Bayer. Quad Bayer color filter array (QBC) is a filter shared by four pixels, which can improve the image quality by averaging four pixels in the 2\(\,\times \,\)2 neighborhood under low light conditions. From low-resolution Bayer to full-resolution Bayer has become a very challenging research, especially in the presence of noise. Considering denoise and remosaic, we propose a general two-stage framework JRD-QBC (Joint Remosaic and Denoise in Quad Bayer CFA), including denoise and remosaic. To begin with, for the denoise phase, in order to ensure the difference of each color channel recovery, we convert the input to hollow QBC, and then enter our backbone network, including source encoder module, feature refinement module and final prediction module. After that, get a clean QBC and then use the same network structure to remosaic to generate Bayer. Extensive experiments demonstrate the proposed two-stage method has a good effect in quantitative indicators and subjective vision.
X. Wu and Z. Fan—Both authors contributed equally to this research.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Sharif, S., Naqvi, R.A., Biswas, M.: Beyond joint demosaicking and denoising: an image processing pipeline for a pixel-bin image sensor. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 233–242 (2021)
Abdelhamed, A., Lin, S., Brown, M.S.: A high-quality denoising dataset for smartphone cameras. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1692–1700 (2018)
Aharon, M., Elad, M., Bruckstein, A.: K-SVD: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(11), 4311–4322 (2006)
Anaya, J., Barbu, A.: Renoir-a dataset for real low-light image noise reduction. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 51, 144–154 (2018)
Buades, A., Coll, B., Morel, J.M.: A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In: 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2005), vol. 2, pp. 60–65. IEEE (2005)
Chen, C., Chen, Q., Xu, J., Koltun, V.: Learning to see in the dark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3291–3300 (2018)
Chen, Y., Pock, T.: Trainable nonlinear reaction diffusion: a flexible framework for fast and effective image restoration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(6), 1256–1272 (2016)
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K.: Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(8), 2080–2095 (2007)
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K.: Image restoration by sparse 3D transform-domain collaborative filtering. In: Image Processing: Algorithms and Systems VI, vol. 6812, pp. 62–73. SPIE (2008)
Elad, M., Aharon, M.: Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(12), 3736–3745 (2006)
Foi, A., Trimeche, M., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K.: Practical poissonian-gaussian noise modeling and fitting for single-image raw-data. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 17(10), 1737–1754 (2008)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hirakawa, K., Parks, T.W.: Joint demosaicing and denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(8), 2146–2157 (2006)
Jain, V., Seung, S.: Natural image denoising with convolutional networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 21 (2008)
Kim, B.-H., Song, J., Ye, J.C., Baek, J.H.: PyNET-CA: enhanced PyNET with channel attention for end-to-end mobile image signal processing. In: Bartoli, A., Fusiello, A. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12537, pp. 202–212. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67070-2_12
Lehtinen, J., et al.: Noise2noise: learning image restoration without clean data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.04189 (2018)
Lukac, R., Plataniotis, K.N.: Color filter arrays: design and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 51(4), 1260–1267 (2005)
Lukac, R., Plataniotis, K.N.: Universal demosaicking for imaging pipelines with an RGB color filter array. Pattern Recogn. 38(11), 2208–2212 (2005)
Mairal, J., Bach, F., Ponce, J., Sapiro, G., Zisserman, A.: Non-local sparse models for image restoration. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2272–2279. IEEE (2009)
Mildenhall, B., Barron, J.T., Chen, J., Sharlet, D., Ng, R., Carroll, R.: Burst denoising with kernel prediction networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2502–2510 (2018)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Wang, Y., Huang, H., Xu, Q., Liu, J., Liu, Y., Wang, J.: Practical deep raw image denoising on mobile devices. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12351, pp. 1–16. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58539-6_1
Wilson, P.: Bayer pattern. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/bayer-pattern
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A.A., Shechtman, E., Wang, O.: The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 586–595 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Li, K., Li, K., Wang, L., Zhong, B., Fu, Y.: Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 286–301 (2018)
Zhu, F., Chen, G., Heng, P.A.: From noise modeling to blind image denoising. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 420–429 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, X., Fan, Z., Zheng, J., Wu, Y., Zhang, F. (2023). Learning to Joint Remosaic and Denoise in Quad Bayer CFA via Universal Multi-scale Channel Attention Network. In: Karlinsky, L., Michaeli, T., Nishino, K. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022 Workshops. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13805. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25072-9_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25072-9_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25071-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25072-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)