Abstract
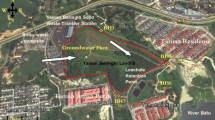
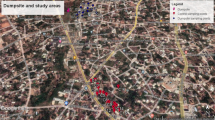
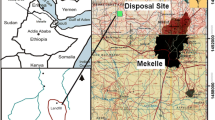
Samples of leachate from the Osisioma open dumpsite and water from four boreholes from the surrounding residence were collected using the four cardinal point model. The sampled boreholes were assigned BH 1, BH 2, BH 3, and BH 4 with distances of 80, 251, 348, and 455 (m) respectively from the location of the dumpsite which is at the center as regards to the cardinal point model used. Physicochemical and microbiological parameters were analyzed to determine the quality of the water. pH, Conductivity, Temperature, TDS, Colour, alkalinity, DO, BOD, COD, Nitrate, Nitrate-Nitrogen, Iron, Chlorine, Chromium, Copper, Arsenic, Lead, Zinc, total bacterial count, E. coli and total coliform count were analyzed. pH ranged from 5.2 to 6.3 in borehole water indicating toxic pollution and was neutral (7.1) in the leachate sample. The temperature of borehole water and leachate ranged from 26.70 to 29.70 °C, Colour (Platinum Cobalt Unit) ranged from 13 to 13850PCU in borehole water and leachate. The concentrations of, Lead, Chromium, Copper, Nitrate, Chlorine, Zinc and Iron ranged from; Lead 0.001 in BH 3 to 0.125 in BH 1, Copper 0.00 in BH 3 to 0.08 in BH 4, Chromium 0.014 in BH 3 to 0.037 in BH 2, Nitrate 234.2 in BH 4 to 343.0 in BH 1, Chlorine 0.35 in BH 3 to 1.71 in BH 4, Zinc; 0.09 mg/L in BH 3 to 0.25 in BH 4 and Iron 0.19 in BH 3 to 0.42 in BH 4 respectively. Alkalinity in water sample was below the WHO permissible limit. Arsenic and Iron were above the permissible limits in BH 1 (0.031 and 0.40 mg/L) and BH 4 (0.020 and 0.42 mg/L). Lead also exceeded the limit in BH 1 at 0.125 mg/L. DO, nitrate, nitrate-nitrogen and chlorine exceeded the limits across all the boreholes water sampled. In the microbiological analysis, Total Bacteria Count, E. coli, and Total Coliform Count were analyzed with mean values of 62.00, 6.50 and 23.75 respectively. All the microbial parameters analyzed exceeded WHO permissible limits which make the water unfit for direct consumption. The variations in concentration of microbiological parameters were in respect to distance from the dumpsite and elevation of the sampling points. There is therefore a need for major water treatment to be carried out on the borehole water before human consumption. Dumping of fresh refuse in the study area should be discouraged with the use of sanctions and fines on defaulters. Government should adopt eco-friendly solid waste disposal management systems such as sorting before disposal, incineration, landfill, waste conversion to biogas and compost as well as provision of portable water to reduce indiscriminate borehole construction to preserve the soil structure.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams D (2001) Lesson 2—interpreting a mineral analysis information sheet. http://animalrangeextension.montana.edu/LoL/Module3b/3-Mineral2.htm. Accessed 20 June 2016
Afolayan OS, Ogundele FO, Omotayo A (2012) Comparative analysis of the effect of closed and operational landfills in groundwater quality in Solous, Lagos, Nigeria. J Appl Technol Environ Sanit 2(1):67–76
Akinbiyi R (1992) Improving the urban environment. Afr Health 15(1):26–28
Aluko OO (2001) Characterization and treatment of leachate from a municipal solid waste landfill site in Ibadan. MPH dissertation, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria, pp 83–85
Amadi AN, Olasehinde PI, Yisa J, Okosun EA, Nwankwoala HO, Alkali YB (2012) Geostatistical assessment of groundwater quality from coastal aquifers of eastern Niger delta, Nigeria. Geosciences 2(3):51–59
Anju A, Dipu S, Salom Gnana Thanga V (2015) Effect of municipal solid waste leachate on ground water quality of Thiruvananthapuram district, Kerala, India. Appl Ecol Environ Sci 3(5):151–157. http://pubs.sciepub.com/aees/3/5/5
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association Inc., Washington, DC, New York
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC, New York
Ashwani KT, Abhay KS (2014) Hydro geochemical investigation and groundwater quality assessment of Pratapgarh district, Uttar Pradesh. J Geol Soc India 83:329–343
Brodkin E, Copes R, Mattman A, Kennedy J, Kling, R, Yassi A (2007) Lead and mercury exposures: interpretation and action. Can Med Assoc J 176(1):59–63
Civeria AC, Lavado MO (2008) Foreign materials and top soils; test of soil toxicity on boreholes, detrimental effects: physical properties, structural stability and water retention. Am J Chem 1(1):37–43
Ejeona UU, Umah NO (2000) Investigation on environmental hazard in Onitsha physio-chemical properties of soil: soil contamination density, caused by dumpsites. Sci Total Environ 345(1):10–14
Jagloo K (2002) Groundwater risk analysis in the vicinity of a landfill, a case study in Mauritius. M.Sc. thesis, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm
Johnson CJ, Bonrud PJ, Dosch TL, Kilness AW, Senger KA, Busch DC, Meyer MR (1987) Fatal outcome of methemoglobinamia in an infant. J Am Med Assoc 257:279–2797
Mohammad IN, Sahil S, Saqib F, Mohammad AD, Jayalakshmi R (2014) The effect of dumping site leachate on groundwater quality. A case study of Srinagar city, India. Int J Civ Struct Environ Infrastruct Eng Res Dev 4(1):1–8. ISSN (P): 2249-6866; ISSN (E): 2249-7978
Mor S, Ravindra K, Dahiya RP, Chandra A (2006) Leachate characterization and assessment of groundwater pollution near municipal solid waste landfill site. Environ Monit Assess 118:435–456
Payne M (2008) Lead in drinking water. Can Med Assoc J 179:253–254. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.071483
Sanborn MD, Abelsohn A, Campbell M, Weir E (2002) Identifying and managing adverse environmental health effects: 3. Lead exposure. Can Med Assoc J 166:1287–1292
Ugwu SA, Nwosu JI (2009) Effect of waste dumps on groundwater in Choba using geophysical method. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 13(1):85–89
World Health Organization (2010) Water for health. In: World Health Organization standard guidelines for drinking water quality
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Osuagwu, E.C., Uwaga, A.M., Inemeawaji, H.P. (2023). Effects of Leachate from Osisioma Open Dumpsite in Aba, Abia State, Nigeria on Surrounding Borehole Water Quality. In: Sherif, M., Singh, V.P., Sefelnasr, A., Abrar, M. (eds) Water Resources Management and Sustainability. Water Science and Technology Library, vol 121. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-24506-0_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-24506-0_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-24505-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-24506-0
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)