Abstract
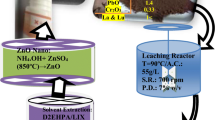
The development of a processing technique that could eliminate impurities from copper smelter dust (WCD) while maintaining a desirable level of revenue metals in the final concentrate is seen as a useful strategy. Not to mention the profit that can be realized if done economically to support the handling of WCD that has been accumulated. The recovery of contained copper values as CuO nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) precipitates, instead of copper cathode slabs, is more appealing. The study’s goal was to create CuO-NPs from the leach solution of low-grade WCD from South Africa. The goal was accomplished by first preparing a copper precursor. This was achieved by adding 0.5 M solution of Na2CO3 dropwise to purified CuSO4 Solution. The copper precursor preparation process was optimized at various test temperatures (25, 55, and 85 °C) and stirring rates (340, 740, and 1480 rpm). The copper precursor was then thermally decomposed at various temperatures (650, 750, and 850 °C) and times (1, 2, 3 h). The obtained results demonstrated that angular to spherical CuO-NPs with a mean diameter of 35 ± 5 nm were successfully synthesized using a thermal decomposition approach at optimal conditions (copper precursor: 85 °C/340 rpm and CuO-NPs: 750 °C/2 h). This process does not need organic solvents, pricey raw ingredients, or difficult machinery.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others

References
D.O. Okanigbe, A.P.I. Popoola, A.A. Adeleke, Characterization of copper smelter dust for copper recovery. Procedia Manuf. 7, 121–126 (2017)
X. Zhang, D. Zhang, X. Ni, J. Song, H. Zheng, Synthesis and electrochemical properties of different sizes of the CuO particles. J. Nanopart. Res. 10(5), 839–844 (2008)
M.A. Rafea, N. Roushdy, Determination of the optical band gap for amorphous and nanocrystalline copper oxide thin films prepared by SILAR technique. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 42(1), 015413 (2008)
T. Kida, T. Oka, M. Nagano, Y. Ishiwata, X.G. Zheng, Synthesis and application of stable copper oxide nanoparticle suspensions for nanoparticulate film fabrication. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90(1), 107–110 (2007)
N. Topnani, S. Kushwaha, T. Athar, Wet synthesis of copper oxide nanopowder. Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1(2), M67–M73 (2010)
M.A. Dar, Y.S. Kim, W.B. Kim, J.M. Sohn, H.S. Shin, Structural and magnetic properties of CuO nanoneedles synthesized by hydrothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254(22), 7477–7481 (2008)
J. Wang, S. He, Z. Li, X. Jing, M. Zhang, Synthesis of claw-like CuO and its catalytic activity in the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Mater. Sci. Pol. 27(2), 501–507 (2009)
X. Zhang, D. Zhang, X. Ni, H. Zheng, Optical and electrochemical properties of nanosized CuO via thermal decomposition of copper oxalate. Solid State Electron. 52(2), 245–248 (2008)
C. Li, Y. Yin, H. Hou, N. Fan, F. Yuan, Y. Shi, Q. Meng, Preparation and characterization of Cu(OH)2 and CuO nanowires by the coupling route of microemulsion with homogenous precipitation. Solid State Commun. 150(13–14), 585–589 (2010)
B.J. Hansen, N. Kouklin, G. Lu, I.K. Lin, J. Chen, X. Zhang, Transport, analyte detection, and opto-electronic response of p-type CuO nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(6), 2440–2447 (2010)
C.T. Hsieh, J.M. Chen, H.H. Lin, H.C. Shih, Field emission from various CuO nanostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83(16), 3383–3385 (2003)
C.C. Li, M.H. Chang, Colloidal stability of CuO nanoparticles in alkanes via oleate modifications. Mater. Lett. 58(30), 3903–3907 (2004)
M.H. Chang, H.S. Liu, C.Y. Tai, Preparation of copper oxide nanoparticles and its application in nanofluid. Powder Technol. 207(1–3), 378–386 (2011)
S. Anandan, X. Wen, S. Yang, Room temperature growth of CuO nanorod arrays on copper and their application as a cathode in dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Chem. Phys. 93(1), 35–40 (2005)
X.P. Gao, J.L. Bao, G.L. Pan, H.Y. Zhu, P.X. Huang, F. Wu, D.Y. Song, Preparation and electrochemical performance of polycrystalline and single crystalline CuO nanorods as anode materials for Li ion battery. J. Phys. Chem. B 108(18), 5547–5551 (2004)
C.L. Carnes, K.J. Klabunde, The catalytic methanol synthesis over nanoparticle metal oxide catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 194(1–2), 227–236 (2003)
Y. Kobayashi, T. Maeda, K. Watanabe, K. Ihara, Y. Yasuda, T. Morita, Preparation of CuO nanoparticles by metal salt-base reaction in aqueous solution and their metallic bonding property. J. Nanopart. Res. 13(10), 5365–5372 (2011)
L. Sun, Z. Zhang, Z. Wang, Z. Wu, H. Dang, Synthesis and characterization of CuO nanoparticles from liquid ammonia. Mater. Res. Bull. 40(6), 1024–1027 (2005)
P.J. Cai, M. Shi, Large scale synthesis of shuttle like CuO nanocrystals by microwave irradiation, in Advanced Materials Research, vol. 92, (Trans Tech Publications Ltd., 2010), pp. 117–123
D. Han, H. Yang, C. Zhu, F. Wang, Controlled synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Triton X-100-based water-in-oil reverse micelles. Powder Technol. 185(3), 286–290 (2008)
R. Ranjbar-Karimi, A. Bazmandegan-Shamili, A. Aslani, K. Kaviani, Sonochemical synthesis, characterization and thermal and optical analysis of CuO nanoparticles. Phys. B Condens. Matter 405(15), 3096–3100 (2010)
N. Liu, D. Wu, H. Wu, C. Liu, F. Luo, A versatile and “green” electrochemical method for synthesis of copper and other transition metal oxide and hydroxide nanostructures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 107(2–3), 511–517 (2008)
Q. Liu, H. Liu, Y. Liang, Z. Xu, G. Yin, Large-scale synthesis of single-crystalline CuO nanoplatelets by a hydrothermal process. Mater. Res. Bull. 41(4), 697–702 (2006)
W. Jia, E. Reitz, P. Shimpi, E.G. Rodriguez, P.X. Gao, Y. Lei, Spherical CuO synthesized by a simple hydrothermal reaction: Concentration-dependent size and its electrocatalytic application. Mater. Res. Bull. 44(8), 1681–1686 (2009)
W. Jisen, Y. Jinkai, S. Jinquan, B. Ying, Synthesis of copper oxide nanomaterials and the growth mechanism of copper oxide nanorods. Mater. Des. 25(7), 625–629 (2004)
W. Wang, Y. Zhan, X. Wang, Y. Liu, C. Zheng, G. Wang, Synthesis and characterization of CuO nanowhiskers by a novel one-step, solid-state reaction in the presence of a nonionic surfactant. Mater. Res. Bull. 37(6), 1093–1100 (2002)
F. Bakhtiari, Synthesis and characterization of tenorite (CuO) nanoparticles from smelting furnace dust (SFD). J. Min. Metall. B Metall. 49(1), 21–21 (2013)
J. Zhu, D. Li, H. Chen, X. Yang, L. Lu, X. Wang, Highly dispersed CuO nanoparticles prepared by a novel quick-precipitation method. Mater. Lett. 58(26), 3324–3327 (2004)
R. Wu, Z. Ma, Z. Gu, Y. Yang, Preparation and characterization of CuO nanoparticles with different morphology through a simple quick-precipitation method in DMAC–water mixed solvent. J. Alloys Compd. 504(1), 45–49 (2010)
R. Ahmadi, M.H. Hosseini, A. Masoudi, Avrami behavior of magnetite nanoparticles formation in co-precipitation process. J. Min. Metall. B Metall. 47(2), 211–218 (2011)
H. Fan, L. Yang, W. Hua, X. Wu, Z. Wu, S. Xie, B. Zou, Controlled synthesis of monodispersed CuO nanocrystals. Nanotechnology 15(1), 37 (2003)
F. Bakhtiari, E. Darezereshki, One-step synthesis of tenorite (CuO) nano-particles from Cu4(SO4)(OH)6 by direct thermal-decomposition method. Mater. Lett. 65(2), 171–174 (2011)
S. Thimmaiah, M. Rajamathi, N. Singh, P. Bera, F. Meldrum, N. Chandrasekhar, R. Seshadri, A solvothermal route to capped nanoparticles of γ-Fe2O3 and CoFe2O4. J. Mater. Chem. 11(12), 3215–3221 (2001)
J. Yang, G.H. Cheng, J.H. Zeng, S.H. Yu, X.M. Liu, Y.T. Qian, Shape control and characterization of transition metal diselenides MSe2 (M=Ni, Co, Fe) prepared by a solvothermal-reduction process. Chem. Mater. 13(3), 848–853 (2001)
K. Byrappa, M. Yoshimura, Handbook of Hydrothermal Technology (William Andrew, 2012)
A. Umer, S. Naveed, N. Ramzan, M.S. Rafique, Selection of a suitable method for the synthesis of copper nanoparticles. Nano 7(05), 1230005 (2012)
K. Byrappa, Growth of quartz crystals, in Bulk Crystal Growth of Electronic, Optical and Optoelectronic Materials, (Wiley, 2005), pp. 387–406
E. Darezereshki, F. Bakhtiari, A novel technique to synthesis of tenorite (CuO) nanoparticles from low concentration CuSO4 solution. J. Min. Metall. B Metall. 47(1), 73–78 (2011)
D.O. Okanigbe, Production of copper and copper oxide nano-particles from leach solution of low grade copper smelter dust. Thesis, Dissertation, 2019.
S. Makaka, M. Aziz, A. Nesbitt, Copper recovery in a bench-scale carrier facilitated tubular supported liquid membrane system. J. Min. Metall. B Metall. 46, 67 (2010)
N. Koga, J.M. Criado, H. Tanaka, Reaction pathway and kinetics of the thermal decomposition of synthetic brochantite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 49(3), 1467–1475 (1997)
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to acknowledge the support received from Tshwane University of Technology, the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, and National Research Foundation in Pretoria, South Africa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Okanigbe, D.O. (2023). Extraction of Copper Oxide (II): Copper Oxide Nanoparticles. In: Ogochukwu Okanigbe, D., Popoola, A.P. (eds) Resource Recovery and Recycling from Waste Metal Dust. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22492-8_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22492-8_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-22491-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-22492-8
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)