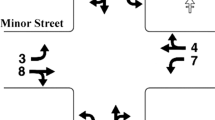
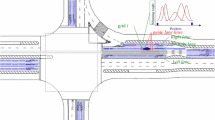
Abstract
The aim of traffic signal control (TSC) is to optimize vehicle traffic in urban road networks, via the control of traffic lights at intersections.
Supported by Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd, under work package 3 of the “Urban Traffic Flow Smoothening Models” NUS-STE joint laboratory.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camponogara, E., Kraus, W.: Distributed learning agents in urban traffic control. In: Pires, F.M., Abreu, S. (eds.) EPIA 2003. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2902, pp. 324–335. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24580-3_38
Chu, T., Wang, J., Codecà, L., Li, Z.: Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for large-scale traffic signal control. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 21(3), 1086–1095 (2019)
Chung, J., Gulcehre, C., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.3555 (2014)
Damani, M., Luo, Z., Wenzel, E., Sartoretti, G.: PRIMAL\(_2\): pathfinding via Reinforcement and Imitation Multi-Agent Learning - Lifelong. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6(2), 2666–2673 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2021.3062803
Gao, J., Shen, Y., Liu, J., Ito, M., Shiratori, N.: Adaptive traffic signal control: deep reinforcement learning algorithm with experience replay and target network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.02755 (2017)
Garg, D., Chli, M., Vogiatzis, G.: Deep reinforcement learning for autonomous traffic light control. In: 2018 3rd IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Engineering (ICITE), pp. 214–218. IEEE (2018)
Genders, W., Razavi, S.: Evaluating reinforcement learning state representations for adaptive traffic signal control. Procedia Comput. Sci. 130, 26–33 (2018)
Hunt, P., Robertson, D., Bretherton, R., Winton, R.: Scoot-a traffic responsive method of coordinating signals. Technical report (1981)
Li, L., Lv, Y., Wang, F.Y.: Traffic signal timing via deep reinforcement learning. IEEE/CAA J. Automatica Sinica 3(3), 247–254 (2016)
Luk, J.: Two traffic-responsive area traffic control methods: scat and scoot. Traffic Eng. Control 25(1) (1984)
Mousavi, S.S., Schukat, M., Howley, E.: Traffic light control using deep policy-gradient and value-function-based reinforcement learning. IET Intel. Transp. Syst. 11(7), 417–423 (2017)
Schulman, J., Wolski, F., Dhariwal, P., Radford, A., Klimov, O.: Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.06347 (2017)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
Wei, H., et al.: Presslight: learning max pressure control to coordinate traffic signals in arterial network. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 1290–1298 (2019)
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Dr. Teng Teck Hou for his feedback on earlier drafts of this manuscript as well as for research discussions during the elaboration of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Y., Damani, M., Sartoretti, G. (2022). Multi-agent Traffic Signal Control via Distributed RL with Spatial and Temporal Feature Extraction. In: Melo, F.S., Fang, F. (eds) Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. Best and Visionary Papers. AAMAS 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13441. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20179-0_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20179-0_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20178-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20179-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)