Abstract
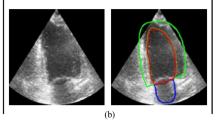
Echocardiogram illustrates what the capacity it owns of detecting the global and regional functions of the heart. With obvious benefits of non-invasion, visuality and mobility, it has become an indispensable technology for clinical evaluation of cardiac function. However, the uncertainty in measurement of ultrasonic equipment and inter-reader variability are always inevitable. Regarding of this situation, researchers have proposed many methods for cardiac function assessment based on deep learning. In this paper, we propose UDeep, an encoder-decoder model for left ventricular segmentation of echocardiography, which pays attention to both multi-scale high-level semantic information and multi-scale low-level fine-grained information. Our model maintains sensitivity to semantic edges, so as to accurately segment the left ventricle. The encoder extracts multiple scales high-level semantic features through a computation efficient backbone named Separated Xception and the Atrous Spacial Pyramid Pooling module. A new decoder module consisting of several Upsampling Fusion Modules (UPFMs), at the same time, is applied to fuse features of different levels. To improve the generalization of our model to different echocardiography images, we propose Pseudo-Segmentation Penalty loss function. Our model accurately segments the left ventricle with a Dice Similarity Coefficient of 0.9290 on the test set of echocardiography videos dataset.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bui, A.L., Horwich, T.B., Fonarow, G.C.: Epidemiology and risk profile of heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 8(1), 30–41 (2011)
McMurray, J.J., Stewart, S.: Epidemiology, aetiology, and prognosis of heart failure. Heart 83(5), 596–602 (2000)
Ziaeian, B., Fonarow, G.C.: Epidemiology and aetiology of heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 13(6), 368–378 (2016)
Chen, L.-C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 833–851. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Ouyang, D., et al.: Video-based AI for beat-to-beat assessment of cardiac function. Nature 580(7802), 252–256 (2020)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(4), 640–651 (2015)
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., Cipolla, R.: SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(12), 2481–2495 (2017)
Noh, H., Hong, S., Han, B.: Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1520–1528 (2015)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: Bengio, Y., LeCun, Y. (eds.) 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015, Conference Track Proceedings (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(9), 1904–1916 (2015)
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., Yuille, A.L.: DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(4), 834–848 (2017)
Chen, L., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. CoRR abs/1706.05587 (2017)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2881–2890 (2017)
Cho, K., et al.: Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. Comput. Sci. (2014)
Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O., Le, Q.V.: Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 3104–3112 (2014)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Li, X., Zhong, Z., Wu, J., Yang, Y., Lin, Z., Liu, H.: Expectation-maximization attention networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9167–9176 (2019)
Chen, J., et al.: TransUNet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. CoRR abs/2102.04306 (2021)
Zhang, J., et al.: Fully automated echocardiogram interpretation in clinical practice: feasibility and diagnostic accuracy. Circulation 138(16), 1623–1635 (2018)
Liu, F., Wang, K., Liu, D., Yang, X., Tian, J.: Deep pyramid local attention neural network for cardiac structure segmentation in two-dimensional echocardiography. Med. Image Anal. 67, 101873 (2021)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1026–1034 (2015)
Paszke, A., Chaurasia, A., Kim, S., Culurciello, E.: ENet: a deep neural network architecture for real-time semantic segmentation. CoRR abs/1606.02147 (2016)
Qi, H., et al.: Deformable convolutional networks-COCO detection and segmentation challenge 2017 entry. In: ICCV COCO Challenge Workshop, vol. 15, pp. 764–773 (2017)
Russakovsky, O., et al.: ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 115(3), 211–252 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y
Hu, P., Caba, F., Wang, O., Lin, Z., Sclaroff, S., Perazzi, F.: Temporally distributed networks for fast video semantic segmentation. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020, pp. 8815–8824. Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE (2020)
Lou, A., Guan, S., Loew, M.H.: DC-UNet: rethinking the u-Net architecture with dual channel efficient CNN for medical images segmentation. CoRR abs/2006.00414 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, E., Cai, Z., Lai, Jh. (2022). Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation of Echocardiography Videos via Multi-level Features Selection. In: Yu, S., et al. Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision. PRCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13535. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18910-4_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18910-4_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-18909-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-18910-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)