Abstract
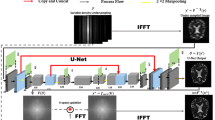
Magnetic Resonance (MR) image reconstruction from under-sampled acquisition promises faster scanning time. To this end, current State-of-The-Art (SoTA) approaches leverage deep neural networks and supervised training to learn a recovery model. While these approaches achieve impressive performances, the learned model can be fragile on unseen degradation, e.g. when given a different acceleration factor. These methods are also generally deterministic and provide a single solution to an ill-posed problem; as such, it can be difficult for practitioners to understand the reliability of the reconstruction. We introduce DiffuseRecon, a novel diffusion model-based MR reconstruction method. DiffuseRecon guides the generation process based on the observed signals and a pre-trained diffusion model, and does not require additional training on specific acceleration factors. DiffuseRecon is stochastic in nature and generates results from a distribution of fully-sampled MR images; as such, it allows us to explicitly visualize different potential reconstruction solutions. Lastly, DiffuseRecon proposes an accelerated, coarse-to-fine Monte-Carlo sampling scheme to approximate the most likely reconstruction candidate. The proposed DiffuseRecon achieves SoTA performances reconstructing from raw acquisition signals in fastMRI and SKM-TEA. Code will be open-sourced at www.github.com/cpeng93/DiffuseRecon.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akçakaya, M., Moeller, S., Weingärtner, S., Uğurbil, K.: Scan-specific robust artificial-neural-networks for k-space interpolation (RAKI) reconstruction: database-free deep learning for fast imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 81(1), 439–453 (2019)
Chung, H., Chul Ye, J.: Score-based diffusion models for accelerated MRI (2021)
Desai, A.D., et al.: Skm-tea: a dataset for accelerated MRI reconstruction with dense image labels for quantitative clinical evaluation. In: Thirty-Fifth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Datasets and Benchmarks Track (Round 2) (2021)
Dhariwal, P., Nichol, A.: Diffusion models beat GANs on image synthesis. CoRR abs/2105.05233 (2021). https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.05233
Eo, T., et al.: KIKI-net: cross-domain convolutional neural networks for reconstructing undersampled magnetic resonance images. Magn. Reson. Med. 80(5), 2188–2201 (2018)
Guo, P., Valanarasu, J.M.J., Wang, P., Zhou, J., Jiang, S., Patel, V.M.: Over-and-under complete convolutional RNN for MRI reconstruction. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12906, pp. 13–23. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_2
Guo, P., Wang, P., Zhou, J., Jiang, S., Patel, V.M.: Multi-institutional collaborations for improving deep learning-based magnetic resonance image reconstruction using federated learning. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2021, virtual, June 19–25, 2021, pp. 2423–2432. Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE (2021)
Hammernik, K., et al.: Learning a variational network for reconstruction of accelerated MRI data. Magn. Reson. Med. 79(6), 3055–3071 (2018)
Han, Y., Sunwoo, L., Ye, J.C.: \({k}\) -space deep learning for accelerated MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(2), 377–386 (2020)
Ho, J., Jain, A., Abbeel, P.: Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In: Larochelle, H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M., Lin, H. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2020, NeurIPS 2020, 6–12 December, 2020, virtual (2020)
Jalal, A., Arvinte, M., Daras, G., Price, E., Dimakis, A.G., Tamir, J.I.: Robust compressed sensing MRI with deep generative priors. In: Ranzato, M., Beygelzimer, A., Dauphin, Y.N., Liang, P., Vaughan, J.W. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, NeurIPS 2021, 6–14 December 2021, virtual, pp. 14938–14954 (2021)
Kong, Z., Ping, W.: On fast sampling of diffusion probabilistic models. CoRR abs/2106.00132 (2021). https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00132
Lustig, M., Donoho, D., Pauly, J.M.: Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Med. 58(6), 1182–95 (2007)
Nichol, A.Q., Dhariwal, P.: Improved denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In: Meila, M., Zhang, T. (eds.) Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2021, 18–24 July 2021, Virtual Event. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 139, pp. 8162–8171. PMLR (2021), http://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/nichol21a.html
Qin, C., Schlemper, J., Caballero, J., Price, A.N., Hajnal, J.V., Rueckert, D.: Convolutional recurrent neural networks for dynamic MR image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(1), 280–290 (2019)
Ravishankar, S., Bresler, Y.: MR image reconstruction from highly undersampled k-space data by dictionary learning. IEEE TMI 30(5), 1028–41 (2011)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Salimans, T., Ho, J.: Progressive distillation for fast sampling of diffusion models. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2022)
Schlemper, J., Caballero, J., Hajnal, J.V., Price, A.N., Rueckert, D.: A deep cascade of convolutional neural networks for dynamic MR image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging 37(2), 491–503 (2018)
Song, J., Meng, C., Ermon, S.: Denoising diffusion implicit models. In: 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2021, Virtual Event, Austria, 3–7 May, 2021. OpenReview.net (2021)
Song, Y., Shen, L., Xing, L., Ermon, S.: Solving inverse problems in medical imaging with score-based generative models. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2022). https://openreview.net/forum?id=vaRCHVj0uGI
Sriram, A., Zbontar, J., Murrell, T., Zitnick, C.L., Defazio, A., Sodickson, D.K.: Grappanet: combining parallel imaging with deep learning for multi-coil MRI reconstruction. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June, 2020, pp. 14303–14310. Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE (2020)
Valanarasu, J.M.J., Sindagi, V.A., Hacihaliloglu, I., Patel, V.M.: KiU-Net: towards accurate segmentation of biomedical images using over-complete representations. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12264, pp. 363–373. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_36
Wang, S., et al.: Accelerating magnetic resonance imaging via deep learning. In: 2016 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 514–517 (2016)
Yang, G., et al.: Dagan: deep de-aliasing generative adversarial networks for fast compressed sensing MRI reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(6), 1310–1321 (2018)
Zbontar, J., et al.: fastmri: an open dataset and benchmarks for accelerated MRI. CoRR abs/1811.08839 (2018)
Zhou, B., Zhou, S.K.: Dudornet: Learning a dual-domain recurrent network for fast MRI reconstruction with deep T1 prior. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June, 2020, pp. 4272–4281. Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Peng, C., Guo, P., Zhou, S.K., Patel, V.M., Chellappa, R. (2022). Towards Performant and Reliable Undersampled MR Reconstruction via Diffusion Model Sampling. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022. MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13436. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16446-0_59
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16446-0_59
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16445-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16446-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)