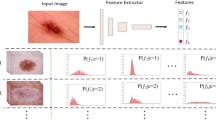
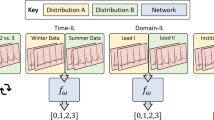
Abstract
Deep learning models have shown a great effectiveness in recognition of findings in medical images. However, they cannot handle the ever-changing clinical environment, bringing newly annotated medical data from different sources. To exploit the incoming streams of data, these models would benefit largely from sequentially learning from new samples, without forgetting the previously obtained knowledge. In this paper we introduce LifeLonger, a benchmark for continual disease classification on the MedMNIST collection, by applying existing state-of-the-art continual learning methods. In particular, we consider three continual learning scenarios, namely, task and class incremental learning and the newly defined cross-domain incremental learning. Task and class incremental learning of diseases address the issue of classifying new samples without re-training the models from scratch, while cross-domain incremental learning addresses the issue of dealing with datasets originating from different institutions while retaining the previously obtained knowledge. We perform a thorough analysis of the performance and examine how the well-known challenges of continual learning, such as the catastrophic forgetting exhibit themselves in this setting. The encouraging results demonstrate that continual learning has a major potential to advance disease classification and to produce a more robust and efficient learning framework for clinical settings. The code repository, data partitions and baseline results for the complete benchmark are publicly available\(^{1}\)(https://github.com/mmderakhshani/LifeLonger).
M. M. Derakhshani, I. Najdenkoska, T. van Sonsbeek—Equal contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo, A., Merino, A., Alférez, S., Molina, Á., Boldú, L., Rodellar, J.: A dataset of microscopic peripheral blood cell images for development of automatic recognition systems (2020)
Aljundi, R., Babiloni, F., Elhoseiny, M., Rohrbach, M., Tuytelaars, T.: Memory aware Synapses: Learning what (not) to forget. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11207, pp. 144–161. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01219-9_9
Baweja, C., Glocker, B., Kamnitsas, K.: Towards continual learning in medical imaging. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.02496 (2018)
Bilic, P., et al.: The liver tumor segmentation benchmark (lits). arxiv 2019. ArXiv (2019)
Castro, F.M., Marín-Jiménez, M.J., Guil, N., Schmid, C., Alahari, K.: End-to-End incremental learning. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11216, pp. 241–257. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01258-8_15
Chakraborti, T., Gleeson, F., Rittscher, J.: Contrastive representations for continual learning of fine-grained histology images. In: International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging (2021)
Chaudhry, A., Dokania, P.K., Ajanthan, T., Torr, P.H.S.: Riemannian walk for incremental learning: Understanding forgetting and intransigence. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11215, pp. 556–572. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01252-6_33
Derakhshani, M.M., Zhen, X., Shao, L., Snoek, C.: Kernel continual learning. In: ICML (2021)
Gonzalez, C., Sakas, G., Mukhopadhyay, A.: What is wrong with continual learning in medical image segmentation? ArXiv (2020)
Goodfellow, I.J., Mirza, M., Xiao, D., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: An empirical investigation of catastrophic forgetting in gradient-based neural networks. ArXiv (2013)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
Hou, S., Pan, X., Loy, C.C., Wang, Z., Lin, D.: Learning a unified classifier incrementally via rebalancing. In: CVPR (2019)
Kather, J.N., et al.: Predicting survival from colorectal cancer histology slides using deep learning: a retrospective multicenter study (2019)
Kemker, R., Kanan, C.: Fearnet: Brain-inspired model for incremental learning. In: ICLR (2018)
Kirkpatrick, J., et al.: Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 114, 3521–3526 (2017)
Lenga, M., Schulz, H., Saalbach, A.: Continual learning for domain adaptation in chest x-ray classification. In: Medical Imaging with Deep Learning (2020)
Li, Z., Hoiem, D.: Learning without forgetting. In: PAMI (2017)
Li, Z., Zhong, C., Wang, R., Zheng, W.-S.: Continual learning of new diseases with dual distillation and ensemble strategy. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12261, pp. 169–178. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59710-8_17
Litjens, G., et al.: A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 42, 60–88 (2017)
Liu, X., et al.: A comparison of deep learning performance against health-care professionals in detecting diseases from medical imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Digital Health 1, e271–e297 (2019)
Lomonaco, V., et al.: Avalanche: an end-to-end library for continual learning. In: CVPR (2021)
Lopez-Paz, D., Ranzato, M.: Gradient episodic memory for continual learning. In: NeurIPS (2017)
Masana, M., Liu, X., Twardowski, B., Menta, M., Bagdanov, A.D., van de Weijer, J.: Class-incremental learning: survey and performance evaluation on image classification. ArXiv (2020)
McCloskey, M., Cohen, N.J.: Catastrophic interference in connectionist networks: The sequential learning problem. In: Psychology of Learning and Motivation (1989)
Memmel, M., Gonzalez, C., Mukhopadhyay, A.: Adversarial continual learning for multi-domain hippocampal segmentation. In: Domain Adaptation and Representation Transfer, and Affordable Healthcare and AI for Resource Diverse Global Health (2021)
Nguyen, C.V., Li, Y., Bui, T.D., Turner, R.E.: Variational continual learning. In: ICLR (2018)
Ostapenko, O., Puscas, M., Klein, T., Jahnichen, P., Nabi, M.: Learning to remember: a synaptic plasticity driven framework for continual learning. In: CVPR (2019)
Rebuffi, S.A., Kolesnikov, A.I., Sperl, G., Lampert, C.H.: iCaRL: Incremental classifier and representation learning. In: CVPR (2017)
Ring, M.B.: Child: a first step towards continual learning. Learning to learn (1998)
Rusu, A.A., et al.: Progressive neural networks. In: NeurIPS (2016)
Shin, H., Lee, J.K., Kim, J., Kim, J.: Continual learning with deep generative replay. In: NeurIPS (2017)
Srivastava, S., Yaqub, M., Nandakumar, K., Ge, Z., Mahapatra, D.: Continual domain incremental learning for chest x-ray classification in low-resource clinical settings. In: Domain Adaptation and Representation Transfer, and Affordable Healthcare and AI for Resource Diverse Global Health (2021)
Van de Ven, G.M., Tolias, A.S.: Three scenarios for continual learning. ArXiv (2019)
Wu, Y., et al.: Large scale incremental learning. In: CVPR (2019)
Xiang, Y., Fu, Y., Ji, P., Huang, H.: Incremental learning using conditional adversarial networks. In: CVPR (2019)
Yang, J., Shi, R., Ni, B.: Medmnist classification decathlon: a lightweight automl benchmark for medical image analysis. In: ISBI (2021)
Yang, Y., Cui, Z., Xu, J., Zhong, C., Wang, R., Zheng, W.-S.: Continual learning with bayesian model based on a fixed pre-trained feature extractor. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12905, pp. 397–406. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87240-3_38
Zenke, F., Poole, B., Ganguli, S.: Continual learning through synaptic intelligence. In: ICML (2017)
Zhang, J., Gu, R., Wang, G., Gu, L.: Comprehensive importance-based selective regularization for continual segmentation across multiple sites. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12901, pp. 389–399. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_37
Zheng, E., Yu, Q., Li, R., Shi, P., Haake, A.: A continual learning framework for uncertainty-aware interactive image segmentation. In: AAAI (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the Inception Institute of Artificial Intelligence, the University of Amsterdam and the allowance Top consortia for Knowledge and Innovation (TKIs) from the Netherlands Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Derakhshani, M.M. et al. (2022). LifeLonger: A Benchmark for Continual Disease Classification. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022. MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13432. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16434-7_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16434-7_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16433-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16434-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)