Abstract
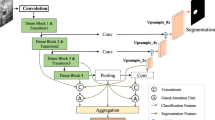
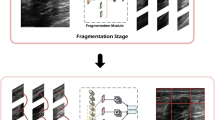
Segmentation of lymphoma from ultrasound image has become an important task in the diagnosis of lymphoma. There are two problems in the segmentation of lymphoma ultrasound images: (i) the fuzziness of structural boundaries in the image domain and (ii) the generalization of images scanned by different ultrasonic instruments. To solve these two problems, we propose an segmentation framework based on self-attention mechanism and stable learning, in which self-attention mechanism and stable learning are embedded in the baseline network. Self-Attention mechanism (TSA) learns non-local interaction of encoder coding features to alleviate the problem of information decay caused by multiple sampling. The Stable learning (SA) module uses random Fourier features (RFF) and sample weights to eliminate the dependence between features and solve the problem of false correlation features from images scanned by different instruments. In addition, counterfactual interpretation is used to generate instance level interpretation of our complex model. Experiments show that this method can effectively improve the accuracy and reliability of segmentation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, A., Ali, L.: Explainable medical image segmentation via generative adversarial networks and layer-wise relevance propagation. arXiv e-prints (2021)
Amiri, M., Brooks, R., Rivaz, H.: Fine-tuning U-Net for ultrasound image segmentation: different layers, different outcomes. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 67(12), 2510–2518 (2020)
Chen, L.-C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 833–851. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49
Contributors, M.: MMSegmentation: openmmlab semantic segmentation toolbox and benchmark (2020). https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmsegmentation
Mishra, D., Chaudhury, S., Sarkar, M., Soin, A.S.: Ultrasound image segmentation: a deeply supervised network with attention to boundaries. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 66(6), 1637–1648 (2018)
Draelos, R.L., Carin, L.: HiResCAM: faithful location representation in visual attention for explainable 3d medical image classification (2020)
Fu, J., et al.: Dual attention network for scene segmentation (2020)
Gu, R., et al.: CA-Net: comprehensive attention convolutional neural networks for explainable medical image segmentation (2020)
Hong, J.L., Kim, J.U., Lee, S., Kim, H.G., Yong, M.R.: Structure boundary preserving segmentation for medical image with ambiguous boundary (2020)
Hou, Q., Zhang, L., Cheng, M.M., Feng, J.: Strip pooling: rethinking spatial pooling for scene parsing. IEEE (2020)
Huang, L., Yuan, Y., Guo, J., Zhang, C., Chen, X., Wang, J.: Interlaced sparse self-attention for semantic segmentation. IEEE (2019)
Huang, L., Ruan, S., Decazes, P., Denoeux, T.: Lymphoma segmentation from 3D PET-CT images using a deep evidential network. arXiv e-prints arXiv:2201.13078 (2022)
Park, H., Lee, H.J., Kim, H.G., Ro, Y.M.: Endometrium segmentation on transvaginal ultrasound image using key-point discriminator. Med. Phys. 46(9), 3974–3984 (2019)
Li, H., et al.: DenseX-net: an end-to-end model for lymphoma segmentation in whole-body PET/CT images. IEEE Access 8, 8004–8018 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2963254
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(4), 640–651 (2015)
Martens, D., Provost, F.: Explaining documents’ classifications. Social Science Electronic Publishing
Nie, D., Wang, L., Xiang, L., Zhou, S., Shen, D.: Difficulty-aware attention network with confidence learning for medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 1085–1092 (2019)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Sahiner, B., et al.: Deep learning in medical imaging and radiation therapy. Med. Phys. 46(1), e1–e36 (2019)
Strudel, R., Garcia, R., Laptev, I., Schmid, C.: Segmenter: transformer for semantic segmentation (2021)
Swerdlow, S.H., Cook, J.R.: As the world turns, evolving lymphoma classifications - past, present and future. Hum. Pathol. 95, 55–77 (2019)
Tan, M., Le, Q.V.: Efficientnet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks (2019)
Vermeire, T., Martens, D.: Explainable image classification with evidence counterfactual (2020)
Wachter, S., Mittelstadt, B., Russell, C.: Counterfactual explanations without opening the black box: automated decisions and the GDPR. Social Science Electronic Publishing (2017)
Wang, Q., Wang, L., Wang, P.: Analysis of survival and prognostic factors in patients with malignant lymphoma after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Pract. J. Cancer 35(5), 4 (2020)
Xie, E., Wang, W., Yu, Z., Anandkumar, A., Alvarez, J.M., Luo, P.: Segformer: simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers (2021)
Yuan, C., et al.: Diffuse large b-cell lymphoma segmentation in PET-CT images via hybrid learning for feature fusion. Med. Phys. 48, 3665–3678 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.14847
Zang, X., Bascom, R., Gilbert, C., Toth, J., Higgins, W.: Methods for 2-d and 3-d endobronchial ultrasound image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63(7), 1426–1439 (2016)
Zeng, Y., Liu, Y.: Prognosis of patients with malignant lymphoma treated by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Lab. Med. Clin. 17(9), 4 (2020)
Zhao, H., Liu, D., Zhao, M., Li, Y.: Clinical review of 39 cases of lymphoma diagnosed by percutaneous ultrasound-guided peritoneal mass/lymph node biopsy. Chin. J. Emerg. Med. 28(6), 3 (2019)
Zhao, Y., Rada, L., Chen, K., Harding, S.P., Zheng, Y.: Automated vessel segmentation using infinite perimeter active contour model with hybrid region information with application to retinal images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 34(9), 1797–1807 (2015)
Zheng, S., Lu, J., Zhao, H., Zhu, X., Zhang, L.: Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers (2020)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Key R &D Program of China (No. 2019YFE0190500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Han, Y., Chen, D., Luo, Y., Dong, Y. (2022). Lymphoma Ultrasound Image Segmentation with Self-Attention Mechanism and Stable Learning. In: Pimenidis, E., Angelov, P., Jayne, C., Papaleonidas, A., Aydin, M. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2022. ICANN 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13529. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15919-0_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15919-0_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-15918-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-15919-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)