Abstract
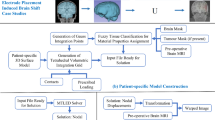
Our motivation is to enable non-specialists to use sophisticated biomechanical models in the clinic. To further this goal, in this study, we constructed a framework within 3D Slicer for automatically generating and solving patient-specific biomechanical models of the brain. This framework allows determining automatically patient-specific geometry from MRI data, generating patient-specific computational grid, defining boundary conditions and external loads, assigning material properties to intracranial constituents and solving the resulting set of differential equations. We used the Meshless Total Lagrangian Explicit Dynamics (MTLED) algorithm to solve these equations. We demonstrated the effectiveness and appropriateness of our framework on a case study of brain tissue deformations caused by placement of electrodes on the brain surface in intracranial electroencephalography (iEEG).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bezdek, J. C., Ehrlich, R., & Full, W. (1984). FCM: The fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Computers & Geosciences, 10(2–3), 191–203.
Ciarlet, P. G. (1988). Mathematical elasticity. North Hollad.
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis: I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage, 9(2), 179–194.
Dora, L., Agrawal, S., Panda, R., & Abraham, A. (2017). State-of-the-art methods for brain tissue segmentation: A review. IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering, 10, 235–249.
Fedorov, A., Beichel, R., Kalpathy Cramer, J., Finet, J., Fillion Robin, J.-C., Pujol, S., Bauer, C., Jennings, D., Fennessy, F., Sonka, M., Buatti, J., Aylward, S., Miller, J., Pieper, S., & Kikinis, R. (2012). 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the quantitative imaging network. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 30(9), 1323–1341.
Geuzaine, C., & Remacle, J. F. (2009). Gmsh: A 3-D finite element mesh generator with built-in pre- and post-processing facilities. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 79(11), 1309–1331.
Horton, A., Wittek, A., Joldes, G. R., & Miller, K. (2010). A meshless total Lagrangian explicit dynamics algorithm for surgical simulation. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering, 26, 977–998.
Jin, X., Joldes, G. R., Miller, K., Yang, K. H., & Wittek, A. (2014). Meshless algorithm for soft tissue cutting in surgical simulation. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering, 17, 800–817.
Joldes, G., Bourantas, G., Zwick, B., Chowdhury, H., Wittek, A., Agrawal, S., Mountris, K., Hyde, D., Warfield, S. K., & Miller, K. (2019). Suite of meshless algorithms for accurate computation of soft tissue deformation for surgical simulation. Medical Image Analysis, 56, 152–171.
Joldes, G., Wittek, A., & Miller, K. (2009). Suite of finite element algorithms for accurate computation of soft tissue deformation for surgical simulation. Medical Image Analysis, 13(6), 912–919.
Joldes, G. R., Chowdhury, H. A., Wittek, A., Doyle, B., & Miller, K. (2015). Modified moving least squares with polynomial bases for scattered data approximation. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 266, 893–902.
Joldes, G. R., Wittek, A., & Miller, K. (2011). An adaptive dynamic relaxation method for solving nonlinear finite element problems. Application to brain shift estimation. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering, 27(2), 173–185.
Joldes, G. R., Wittek, A., Miller, K., & Morriss, L. (2008). Realistic and efficient brain-skull interaction model for brain shift computation. In Computational Biomechanics for Medicine III Workshop, MICCAI.
Joldes, G. R., Wittek, A., Warfield, S. K., & Miller, K. (2012). Performing brain image warping using the deformation field predicted by a biomechanical model (pp. 89–96). Springer.
Li, M., Miller, K., Joldes, G. R., Kikinis, R., & Wittek, A. (2016). Biomechanical model for computing deformations for whole-body image registration: A meshless approach. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering, 32(12).
Li, M., Wittek, A., Joldes, G. R., & Miller, K. (2016). Fuzzy tissue classification for non-linear patient-specific biomechanical models for whole-body image registration. In G. R. Joldes, B. Doyle, A. Wittek, P. M. F. Nielsen & K. Miller (Eds.), Computational biomechanics for medicine: Imaging, modeling and computing (pp. 85–96). Springer International Publishing.
Miga, M. I., Sun, K., Chen, I., Clements, L. W., Pheiffer, T. S., Simpson, A. L., & Thompson, R. C. (2016). Clinical evaluation of a model-updated image-guidance approach to brain shift compensation: Experience in 16 cases. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 11(8), 1467–1474.
Miller, K., Chinzei, K., Orssengo, G., & Bednarz, P. (2000). Mechanical properties of brain tissue in-vivo: Experiment and computer simulation. Journal of Biomechanics, 33, 1369–1376.
Miller, K., Horton, A., Joldes, G. R., & Wittek, A. (2012). Beyond finite elements: A comprehensive, patient-specific neurosurgical simulation utilizing a meshless method. Journal of biomechanics, 45(15), 2698–2701.
Miller, K., & Lu, J. (2013). On the prospect of patient-specific biomechanics without patient-specific properties of tissues. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 27, 154–166.
Miller, K., Wittek, A., & Joldes, G. (2011). Biomechanical modeling of the brain for computer-assisted neurosurgery. In Biomechanics of the brain (pp. 111–136). Springer.
Neal, M. L., & Kerckhoffs, R. (2010). Current progress in patient-specific modeling. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 11, 15.
Otsu, N. (1979). A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 9(1), 62–66.
Pinter, C., Lasso, A., & Fichtinger, G. (2019). Polymorph segmentation representation for medical image computing. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 171, 19–26.
Pruthi, S., Dawant, B., & Parker, S. L. (2020). Initial experience with using a structured light 3D scanner and image registration to plan bedside subdural evacuating port system placement.
Safdar, S., Joldes, G., Zwick, B., Bourantas, G., Kikinis, R., Wittek, A., & Miller, K. (2021). Automatic framework for patient-specific biomechanical computations of organ deformation (pp. 3–16). Springer.
Ségonne, F., Dale, A. M., Busa, E., Glessner, M., Salat, D., Hahn, H. K., & Fischl, B. (2004). A hybrid approach to the skull stripping problem in MRI. NeuroImage, 22(3), 1060–1075.
Sorkine, O., Cohen-Or, D., Lipman, Y., Alexa, M., Rössl, C., & Seidel, H. P. (2004). Laplacian surface editing. In Proceedings of the 2004 Eurographics/ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Geometry Processing.
Sullivan, C., & Kaszynski, A. (2019). PyVista: 3D plotting and mesh analysis through a streamlined interface for the Visualization Toolkit (VTK). Journal of Open Source Software, 4(37), 1450.
Valette, S., Chassery, J. M., & Prost, R. (2008). Generic remeshing of 3D triangular meshes with metric-dependent discrete Voronoi diagrams. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 14(2), 369–381.
Waldron, K. J., & Kinzel, G. L. (2004). Kinematics, dynamics, and design of machinery. Wiley.
Lorensen, W. E., & Cline, H. E. (1987). Marching cubes: A high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. In SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics, (Vol. 21, pp. 163–169). Association for Computing Machinery.
Wittek, A., Grosland, N., Joldes, G., Magnotta, V., & Miller, K. (2016). From finite element meshes to clouds of points: A review of methods for generation of computational biomechanics models for patient-specific applications. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 44(1), 3–15.
Wittek, A., Hawkins, T., & Miller, K. (2009). On the unimportance of constitutive models in computing brain deformation for image-guided surgery. Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology, 8, 77–84.
Wittek, A., Joldes, G., Couton, M., Warfield, S. K., & Miller, K. (2010). Patient-specific non-linear finite element modelling for predicting soft organ deformation in real-time; Application to non-rigid neuroimage registration. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, 103, 292–303.
Wittek, A., Joldes, G. R., & Miller, K. (2019). Finite element algorithms for computational biomechanics of the brain (pp. 243–272). Springer.
Wittek, A., Miller, K., Kikinis, R., & Warfield, S. K. (2007). Patient-specific model of brain deformation: Application to medical image registration. Journal of Biomechanics, 40, 919–929.
Zhang, J. Y., Joldes, G. R., Wittek, A., & Miller, K. (2013). Patient-specific computational biomechanics of the brain without segmentation and meshing. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering, 29(2), 293–308.
Zwick, B.F., Bourantas, G.C., Safdar, S., Joldes, G.R., Hyde, D.E., Warfield, S.K., Wittek, A., & Miller, K. (2022). Patient-specific solution of the electrocorticography forward problem in deforming brain (preprint on ArXiv:2109.07164, submitted to Neuroimage).
Acknowledgements
The funding from NHMRC grants APP1162030; APP1144519 is gratefully acknowledged. The first author acknowledges scholarship funding from University Postgraduate Award. We also wish to thank 3D Slicer on-line community https://discourse.slicer.org/ whose members have made many valuable contributions. Our special thanks go to Dr. Andras Lasso of Laboratory for Percutaneous Surgery (PerkLab).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Safdar, S. et al. (2022). Automatic Framework for Patient-Specific Biomechanical Computations of Organ Deformation: An Epilepsy (EEG) Case Study. In: Nielsen, P.M., Nash, M.P., Li, X., Miller, K., Wittek, A. (eds) Computational Biomechanics for Medicine. MICCAI 2021. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-09327-2_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-09327-2_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-09326-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-09327-2
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)