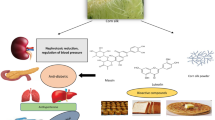
Abstract
Nutraceuticals are food-based substances originating from herb and medicine formulations for the prophylaxis and therapy of diseases. Starting from fourteenth century till now, corn intake is important owing to its high content of vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, dietary fibres, bioactive compounds with health advantages. The corn phenolics like ferulic acid, syringic acid, caffeic acid exhibit antibacterial, antimicrobial and chemopreventive effects and alleviates oxidative stress, cytokine production, NFκB activation. The corn carotenoids like lutein, zeaxanthin, β-cryptoxanthin, α- and β-carotene exhibit antioxidant and anti-carcinogenic qualities, inactivating free radical antioxidants, enhance immune function. The corn fatty acids like linoleic acid, oleic acid, myristic acid, palmitic acid enhance the levels of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids in plasma phospholipids, which improves cardiovascular health. Nearly all essential vitamins and minerals are present in corn byproducts which can aid in normal functioning of body. The corn dietary fibres can improve digestive health acting as prebiotic and laxative too. Regular consumption of corn byproducts can decrease risk of neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases, cancer, type 2 diabetes, obesity, etc. improving overall health.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Egbuna C, Tupas GD (eds) (2020) Functional foods and nutraceuticals – bioactive components, formulations and innovations, 1st edn. Springer Nature, Cham, Switzerland, p 646
Li YO, Komarek AR (2017) Dietary fibre basics: health, nutrition, analysis, and applications. Food Qual Saf 1(1):47–59
Watson SA (1988) Corn marketing, processing, and utilization. Corn Corn Improve 18:881–940
Hasanudin K, Hashim P, Mustafa S (2012) Corn silk (Stigma maydis) in healthcare: a phytochemical and pharmacological review. Molecules 17(8):9697–9715
Siyuan S, Tong L, Liu R (2018) Corn phytochemicals and their health benefits. Food Sci Human Wellness 7(3):185–195
Wang Y, Ning Y, Yuan C, Cui B, Liu G, Zhang Z (2021) The protective mechanism of a debranched corn starch/konjac glucomannan composite against dyslipidemia and gut microbiota in high-fat-diet induced type 2 diabetes. Food Funct 12(19):9273–9285
Tsuda T, Horio F, Uchida K, Aoki H, Osawa T (2003) Dietary cyanidin 3-O-β-D-glucoside-rich purple corn color prevents obesity and ameliorates hyperglycemia in mice. J Nutr 133(7):2125–2130
Makbul SAA, Jahan N, Ansari AA (2020) Cereals and grains as functional food in unani system of medicine. In: Egbuna C, Dable Tupas G (eds) Functional foods and nutraceuticals. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42319-3_15
Thomsen MH (2005) Complex media from processing of agricultural crops for microbial fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68(5):598–606
Adom KK, Liu RH (2002) Antioxidant activity of grains. J Agric Food Chem 50(21):6182–6187
Rackis JJ, Sessa DJ, Honig DH (1979) Flavor problems of vegetable food proteins. J Am Oil Chem Soc 56(3Part2):262–271
Streit L (2019) What’s the difference between corn flour and cornstarch? Accessed 22 Oct 2021. <https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/cornstarch-vs-corn-flour#bottom-line>
Quratulain, cornmeal vs. corn flour – what’s the difference? Accessed 24 Oct 2021. <https://theculinaryprofessor.com/cornmeal-vs-corn-flour/>
Siegel N, Schwarz C (2016) Mushrooms of the Redwood Coast: a comprehensive guide to the fungi of coastal northern California. Ten Speed Press
Huang SW, Frankel EN, German JB (1995) Effects of individual tocopherols and tocopherol mixtures on the oxidative stability of corn oil triglycerides. J Agric Food Chem 43(9):2345–2350
Parker K, Salas M, Nwosu VC (2010) High fructose corn syrup: production, uses and public health concerns. Biotechnol Mol Biol Rev 5(5):71–78
Aiyer PV (2005) Amylases and their applications. Afr J Biotechnol 4(13)
Parekh M, Blaschek HP (1999) Butanol production by hypersolvent-producing mutant Clostridium beijerinckii BA101 in corn steep water medium containing maltodextrin. Biotechnol Lett 21(1):45–48
Shahzad MA, Nisa M, Sarwar M (2011) Influence of replacing corn grain by enzose (corn dextrose) on nutrient utilization, thyroid hormones, plasma metabolites, and weight gain in growing lambs. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 24(7):946–951
Crestani CE, Silva AR, Bernardo A, Costa CB, Giulietti M (2021) Crystalline fructose production: a conceptual design with experimental data and operating cost analysis. Chem Eng Commun 27:1–3
Wang XJ, Zheng XQ, Kopparapu NK, Cong WS, Deng YP, Sun XJ, Liu XL (2014) Purification and evaluation of a novel antioxidant peptide from corn protein hydrolysate. Process Biochem 49(9):1562–1569
Shukla R, Cheryan M (2001) Zein: the industrial protein from corn. Ind Crop Prod 13(3):171–192
Hazrol MD, Sapuan SM, Zainudin ES, Zuhri MY, Abdul Wahab NI (2021) Corn starch (Zea mays) biopolymer plastic reaction in combination with sorbitol and glycerol. Polymers 13(2):242
Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia (2021). Accessed 22 Oct 2021. <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cornmeal>
Cornflakes with Milk for Breakfast is a Really Healthy Option (2021). Accessed 22 Oct 2021. <https://www.herzindagi.com/diet-nutrition/benefits-cornflakes-for-breakfast-nutrition-weight-loss-healthy-heart-article-170754>
Ogori AF (2020) Source, extraction and constituents of fats and oils. J Food Sci Nutr 6(2):100060
Moeller SM, Fryhofer SA, Osbahr AJ III, Robinowitz CB (2009) Council on science and public health, American medical association. The effects of high fructose syrup. J Am Coll Nutr 28(6):619–626. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2009.10719794
The Surprising Facts About Dietary Fiber Indigestable Dextrin (2021) Accessed 27 Oct 2021. <https://www.otsuka.co.jp/en/health-and-illness/fiber/about/type/dextrin/>
Tiberian J (2021) Read your food labels: watch out for maltodextrin. Accessed 25 Oct 2021. <https://www.mdvip.com/about-mdvip/blog/read-your-food-labels-watch-out-maltodextrin>
Fletcher J (2018) Everything you need to know about dextrose. Accessed 27 Oct 2021 <https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322243#uses-in-food>
Brennan D (2021) What to know about dextrose. Accessed 27 Oct 2021. <https://www.webmd.com/diet/what-to-know-dextrose#1>
What is Crystalline Fructose in Food: Uses, Health Benefits, Side Effects (2020) Accessed 27 Oct 2021. <https://foodadditives.net/sweeteners/crystalline-fructose/>
High Fructose Corn Syrup and Fructose, the Differences (2019) Accessed 27 Oct 2021. <http://fructosefacts.org/about/high-fructose-corn-syrup-and-fructose-the-differences/>
What is Hydrolyzed Corn Protein and Its Uses in Food? (2019) Accessed 27 Oct 2021. <https://foodadditives.net/flavor-enhancer/hydrolyzed-corn-protein/>
Lorenzo G, Sosa M, Califano A (2018) Alternative proteins and pseudocereals in the development of gluten-free pasta. In: Alternative and replacement foods. Academic Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 433–458
Grembecka M (2015) Sugar alcohols—their role in the modern world of sweeteners: a review. Eur Food Res Technol 241(1):1–4
Choi DJ, Kim SL, Choi JW, Park YI (2014) Neuroprotective effects of corn silk maysin via inhibition of H2O2-induced apoptotic cell death in SK-N-MC cells. Life Sci 109(1):57–64
Fazel Nabavi S, Pandima Devi K, Sheeja Malar D, Sureda A, Daglia M, Mohammad NS (2015) Ferulic acid and Alzheimer’s disease: promises and pitfalls. Mini Rev Med Chem 15(9):776–788. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557515666150522102545
Ferreira PS, Victorelli FD, Fonseca-Santos B, Chorilli M (2019) A review of analytical methods for p-coumaric acid in plant-based products, beverages, and biological matrices. Crit Rev Anal Chem 49(1):21–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2018.1459173
Alam MA, Subhan N, Hossain H, Hossain M, Reza HM, Rahman MM, Ullah MO (2016) Hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives: a potential class of natural compounds for the management of lipid metabolism and obesity. Nutr Metabol 13(1):1–3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-016-0080-3
Srinivasulu C, Ramgopal M, Ramanjaneyulu G, Anuradha CM, Kumar CS (2018) Syringic acid (SA)–a review of its occurrence, biosynthesis, pharmacological and industrial importance. Biomed Pharmacother 108:547–557
Calixto-Campos C, Carvalho TT, Hohmann MS, Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Fattori V, Manchope MF, Zarpelon AC, Baracat MM, Georgetti SR, Casagrande R, Verri WA Jr (2015) Vanillic acid inhibits inflammatory pain by inhibiting neutrophil recruitment, oxidative stress, cytokine production, and NFκB activation in mice. J Nat Prod 78(8):1799–1808. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00246
Ullah R, Ikram M, Park TJ, Ahmad R, Saeed K, Alam SI, Rehman IU, Khan A, Khan I, Jo MG, Kim MO (2021) Vanillic acid, a bioactive phenolic compound, counteracts LPS-induced neurotoxicity by regulating c-Jun N-terminal kinase in mouse brain. Int J Mol Sci 22(1):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010361
Birková A, Hubková B, Bolerázska B, Mareková M, Čižmárová B (2020) Caffeic acid: a brief overview of its presence, metabolism, and bioactivity. Bioact Compd Health Dis 3(4):74–81
Hseu YC, Korivi M, Lin FY, Li ML, Lin RW, Wu JJ, Yang HL (2018) Trans-cinnamic acid attenuates UVA-induced photoaging through inhibition of AP-1 activation and induction of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant genes in human skin fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sci 90(2):123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2018.01.004
Masella R, Santangelo C, D’archivio M, LiVolti G, Giovannini C, Galvano F (2012) Protocatechuic acid and human disease prevention: biological activities and molecular mechanisms. Curr Med Chem 19(18):2901–2917. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986712800672102
Bartlett HE, Eperjesi F (2007) Effect of lutein and antioxidant dietary supplementation on contrast sensitivity in age-related macular disease: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 61(9):1121–1127. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602626
Mares J (2016) Lutein and zeaxanthin isomers in eye health and disease. Annu Rev Nutr 36:571–602. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071715-05111
Jia YP, Sun L, Yu HS, Liang LP, Li W, Ding H, Song XB, Zhang LJ (2017) The pharmacological effects of lutein and zeaxanthin on visual disorders and cognition diseases. Molecules 22(4):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040610
Yamaguchi M (2008) β-cryptoxanthin and bone metabolism: the preventive role in osteoporosis. J Health Sci 54(4):356–369
Elvira-Torales LI, García-Alonso J, Periago-Castón MJ (2019) Nutritional importance of carotenoids and their effect on liver health: a review. Antioxidants 8(7):229
Galanakis CM (ed) (2016) Nutraceutical and functional food components: effects of innovative processing techniques. Academic Press, Cambridge, MA
Blair HC, Robinson LJ, Huang CL, Sun L, Friedman PA, Schlesinger PH, Zaidi M (2011) Calcium and bone disease. Biofactors 37(3):159–167. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.143
Geiger H, Wanner C (2012) Magnesium in disease. Clin Kidney J 5(Suppl_1):i25–i38. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndtplus/sfr165
Moe SM (2008) Disorders involving calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium. Prim Care 35(2):215–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2008.01.007
Patience JF (1990) A review of the role of acid-base balance in amino acid nutrition. J Anim Sci 68(2):398–408
Constantin MU, Alexandru I (2011) The role of sodium in the body. Balneo-Res J 2(1):70–74
Evans GW (1986) Zinc and its deficiency diseases. Clin Physiol Biochem 4(1):94–98
Soetan KO, Olaiya CO, Oyewole OE (2010) The importance of mineral elements for humans, domestic animals and plants-a review. Afr J Food Sci 4(5):200–222
Suwannasom N, Kao I, Pruß A, Georgieva R, Bäumler H (2020) Riboflavin: the health benefits of a forgotten natural vitamin. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):950
Gasperi V, Sibilano M, Savini I, Catani MV (2019) Niacin in the central nervous system: an update of biological aspects and clinical applications. Int J Mol Sci 20(4):974
Dalto DB, Matte JJ (2017) Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) and the glutathione peroxidase system; a link between one-carbon metabolism and antioxidation. Nutrients 9(3):189
Arya SS, Pavitra K (2012) Folate: its health benefits. Agro Food Industry Hi-Tech 23(4):XXVIII-XI
Iqbal K, Khan A, Khattak MM (2004) Biological significance of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) in human health-a review. Pak J Nutr 3(1):5–13
Rizvi S, Raza ST, Faizal Ahmed AA, Abbas S, Mahdi F (2014) The role of vitamin E in human health and some diseases. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J 14(2):e157
Halder M, Petsophonsakul P, Akbulut AC, Pavlic A, Bohan F, Anderson E, Maresz K, Kramann R, Schurgers L (2019) Vitamin K: double bonds beyond coagulation insights into differences between vitamin K1 and K2 in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci 20(4):896
Vilchez C, Touchburn SP, Chavez ER, Chan CW (1990) The influence of supplemental corn oil and free fatty acids on the reproductive performance of Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Poult Sci 69(9):1533–1538
Chowdhury R, Steur M, Patel PS, Franco OH (2016) Individual fatty acids in cardiometabolic disease. In: Handbook of lipids in human function. AOCS Press, pp 207–318
Carta G, Murru E, Banni S, Manca C (2017) Palmitic acid: physiological role, metabolism and nutritional implications. Front Physiol 8:902. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00902
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Palai, S., Kesh, S.S. (2022). Corn Byproducts as Source of Nutraceuticals. In: Egbuna, C., Sawicka, B., Khan, J. (eds) Food and Agricultural Byproducts as Important Source of Valuable Nutraceuticals. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98760-2_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98760-2_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-98759-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-98760-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)