Abstract
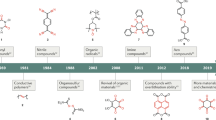
The world is moving for electromobility as well as associated decarbonization. The era and community related to it are moving towards the fourth industrial revolution comprising of digital technology and electronic devices. The organic electrode materials (OEMs) obtained from biomass serve to be the best option for sustainable and green lithium batteries due to various features such as low costing, availability in large amounts, high sustainability, environmental compassion, and recyclability. The research on organic electrodes is mainly based on material level despite the performing ability of batteries. The current chapter focuses on the history of organic electrode materials and prospects of elevation, and the challenges faced by organic electrode materials for practical use in the form of density of OEMs and intrinsic electronic conductivity. Later the comprehensive optimization is performed. Finally, we have focused on developing high-quality stimulation for research to obtain future commercialization of OEMs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohammad, F., Arfin, T., Al-Lohedan, H.A.: Biocompatible polylactic acid-reinforced nickel-arsenate composite: studies of electrochemical conductivity, mechanical stability, and cell viability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C102, 42–149 (2019)
Arfin, T.: Emerging trends in lab-on-a-chip for biosensing applications. In: Hussain, C.M., Shukla, S.K., Joshi, G.M. (eds.) Functionalized Nanomaterials Based Devices for Environmental Applications, pp. 199–218. Elsevier, Netherlands (2021)
Mohammad, F., Arfin, T., Al-Lohedan, H.A.: Enhanced biological activity and biosorption performance of trimethyl chitosan-loaded cerium oxide particles. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 45, 33–43 (2017)
Sophia, A.C., Arfin, T., Lima, E.C.: Recent developments in adsorption of dyes using graphene-based nanomaterials. In: Naushad, M. (ed.) A New Generation Material Graphene: Applications in Water Technology, pp. 439–471. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2019)
Arfin, T., Bushra, R., Mohammad, F.: Electrochemical sensor for the sensitive detection of o-nitrophenol using graphene oxide-poly(ethyleneimine) dendrimer-modified glassy carbon electrode. Graph. Technol. 1(1), 1–15 (2016)
Arfin T, Rafiuddin: Transport studies of nickel arsenate membrane. J. Electroanal. Chem. 636(1), 113–122 (2009)
Arfin, T., Jabeen, F., Kriek, R.J.: An electrochemical and theoretical comparison of ionic transport through a polystyrene based titanium-vanadium (1:2) phosphate membrane. Desalination 274(1–3), 206–211 (2011)
Obulapuram, P.K., Arfin, T., Mohammad, F., Khiste, S.K., Chavali, M., Albalawi, A.N., Al-Lohedan, H.A.: Adsorption, equilibrium isotherm, and thermodynamic studies towards the removal of reactive orange 16 dye using Cu(I)-polyaniline composite. Polymers 13(20), 3490 (2021)
Obulapuram, P.K., Arfin, T., Mohammad, F., Kumari, K., Khiste, S.K., Al-Lohedan, H.A., Chavali, M.: Surface-enhanced biocompatibility and adsorption capacity of a zirconium phosphate-coated polyaniline composite. ACS Omega 6(49), 33614–33626 (2021)
Arfin, T., Tarannum, A.: Rapid determination of lead ions using polyaniline-zirconium (IV) iodatebased ion selective electrode. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7(1), 102811 (2019)
Wang, J.: Organic-phase biosensors-new tools for flow analysis: a short review. Talanta 40(12), 1905–1909 (1993)
Wang, J., Lin, M.S.: Mixed plant tissue carbon paste bioelectrode. Anal. Chem. 60(15), 1545–1548 (1988)
Kaku, S., Nakanishi, S., Horiguchi, K.: Enzyme immunoelectrode for insulin incorporating a membrane partially treated with water vapor plasma. Anal. Chim. Acta 225, 283–292 (1989)
Warsinke, A., Benkert, A., Scheller, F.W.: Electrochemical immunoassays. Fresen. J. Anal. Chem. 366, 622–634 (2000)
Sadik, O.A., John, M.J., Wallace, G.G., Barnett, D., Clarke, C., Laing, D.G.: Pulsed amperometric detection of thaumatin using antibody-containing poly(pyrrole) electrodes. Analyst 119, 1997–2000 (1994)
Bagel, O., Limoges, B., Schollhorn, B., Degrand, C.: Subfemtomolar determination of alkaline phosphatase at a disposable screen-printed electrode modified with a perfluorosulfonated lonomer film. Anal. Chem. 69(22), 4688–4694 (1997)
Scheller, F.W., Bauer, C.G., Makower, A., Wollenberger, U., Warsinke, A., Bier, F.F.: Coupling of immunoassays with enzymatic recycling electrodes. Anal. Lett. 34(8), 1233–1245 (2007)
Kojima, K., Hiratsuka, A., Suzuki, H., Yano, K., Ikebukuro, K., Karube, I.: Electrochemical protein chip with arrayed immunosensors with antibodies immobilized in a plasma-polymerized film. Anal. Chem. 75(5), 1116–1122 (2003)
Zak, J., Kuwana, T.: Chemically modified electrodes and electrocatalysis. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 150(1–2), 645–664 (1983)
Ugo, P., Moretto, L.M.: Ion-exchange voltammetry at polymer-coated electrodes: principles and analytical prospects. Electroanalysis 7(12), 1105–1113 (1995)
Mohammad, F., Arfin, T., Saba, N., Jawaid, M., Al-Lohedan, H.A.: Electrical conductivity and biological efficacy of ethyl cellulose and polyaniline-based composites. In: Khan, A., Jawaid, M., Khan, A.A.P., Asiri, A.M. (eds.) Electrically Conductive Polymers and Polymer Composites: From Synthesis to Biomedical Applications, pp. 181–197. Wiley-VCH Verlag, Germany (2018)
Arfin, T., Bushra, R., Kriek, R.J.: Ionic conductivity of alkali halides across a polyaniline-zirconium(IV)-arsenate membrane. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 5(2), 206–221 (2013)
Arfin, T., Sonawane, K., Tarannum, A.: Review on detection of phenol in water. Adv. Mater. Lett. 10(111), 753–785 (2019)
Sadki, S., Schottland, P., Brodie, N., Sabouraud, G.: The mechanism of pyrrole electropolymerization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 29, 283–293 (2000)
Cheng, Y.-J., Luh, T.-Y.: Synthesizing optoelectronic heteroaromatic conjugated polymers by cross-coupling reactions. J. Organomet. Chem. 689(24), 4137–4148 (2004)
Bao, Z., Chan, W.K., Yu, L.: Exploration of the stille coupling reaction for the synthesis of functional polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117(50), 12426–12435 (1995)
Arfin, T., Rangari, S.N.: Graphene oxide-ZnO nanocomposite modified electrode for the detection of phenol. Anal. Methods 10(3), 347–358 (2018)
Arfin, T.: Functional graphene-based nanodevices: emerging diagnostic tool. In: Kanchi, S., Sharma, D. (eds.) Nanomaterials in Diagnostic Tools and Devices, pp. 85–112. Elsevier, Netherlands (2020)
Oyama, N., Sarukawa, T., Mochizuki, Y., Shimomura, T., Yamaguchi, S.: Significant effects of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) additive on redox responses of poly(2,5-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone-3,6-methylene) cathode for rechargeable Li batteries. J. Power Sources 189(1), 230–239 (2009)
Nigrey, P.J., MacInnes, D., Nairns, D.P., MacDiarmid, A.G., Heeger, A.J.: Lightweight rechargeable storage batteries using polyacetylene, (CH)x as the cathode-active material. J. Electrochem. Soc. 128(8), 1651 (1981)
Oyama, N., Tatsuma, T., Sato, T., Sotomura, T.: Dimercaptan-polyaniline composite electrodes for lithium batteries with high energy density. Nature 373, 598–600 (1995)
Sakaushi, K., Hosono, E., Nickerl, G., Gemming, T., Zhou, H., Kaskel, S., Eckert, J.: Aromatic porous-honeycomb electrodes for a sodium-organic energy storage device. Nat. Commun. 4, 1485 (2013)
Zhan, L., Song, Z., Zhang, J., Tang, J., Zhan, H., Zhou, Y., Zhan, C.: PEDOT: cathode active material with high specific capacity in novel electrolyte system. Electrochim. Acta 53(28), 8319–8323 (2008)
Poizot, P., Dolhem, F.: Clean energy new deal for a sustainable world: from non-CO2 generating energy sources to greener electrochemical storage devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 4(6), 2003–2019 (2011)
Gracia, R., Mecerreyes, D.: Polymers with redox properties: materials for batteries, biosensors and more. Polym. Chem. 4(7), 2206–2214 (2013)
Liang, Y., Yao, Y.: Positioning organic electrode materials in the battery landscape. Joule 2(9), 1690–1706 (2018)
Selvakumaran, D., Pan, A., Liang, S., Cai, G.: A review on recent developments and challenges of cathode materials for rechargeable aqueous Zn-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 18209–18236 (2019)
Li, H., Ma, L., Han, C., Wang, Z., Liu, Z., Tang, Z., Zhi, C.: Advanced rechargeable zinc-based batteries: recent progress and future perspectives. Nano Energy 62, 550–587 (2019)
Zhang, X., Xiao, Z., Liu, X., Mei, P., Yang, Y.: Redox-active polymers as organic electrode materials for sustainable supercapacitors. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 147, 111247 (2021)
Mo, D., Zhou, W., Ma, X., Xu, J.: Facile electrochemical polymerization of 2-(thiophen2-yl)furan and the enhanced capacitance properties of its polymer in acetonitrile electrolyte containing boron trifluoride diethyl etherate. Electrochim. Acta 155, 29–37 (2015)
Fusalba, F., El Mehdi, N., Breau, L., Bélanger, D.: Physicochemical and electrochemical characterization of polycyclopenta[2,1-b;3,4-b′]dithiophen-4-one as an active electrode for electrochemical supercapacitors. Chem. Mater. 11, 2743–2753 (1999)
Snook, G.A., Chen, G.Z.: Polythiophene-based supercapacitors. J. Electroanal. Chem. 612, 140–146 (2008)
Li, H., Wang, J., Chu, Q., Wang, Z., Zhang, F., Wang, S.: Theoretical and experimental specific capacitance of polyaniline in sulfuric acid. J. Power. Sources 190(2), 578–586 (2009)
Mo, D., Zhou, W., Ma, X., Xu, J., Jiang, F., Zhu, D.: Alkyl functionalized bithiophene endcapped with 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene units: synthesis, electropolymerization and the capacitive properties of their polymers. Electrochim. Acta 151, 477–488 (2015)
Arfin, T., Bhaisare, D.A., Waghmare, S.S.: Development of a PANI/Fe(NO3)2 nanomaterial for reactive orange 16 (RO16) dye removal. Anal. Methods 13(44), 5309–5327 (2021)
Bushra, R., Arfin, T., Oves, M., Raza, W., Mohammad, F., Khan, M.A., Ahmed, A., Azam, A., Muneer, M.: Development of PANI/MWCNTs decorated with cobalt oxide nanoparticles towards multiple electrochemical, photocatalytic and biomedical application sites. New J. Chem. 40, 9448–9459 (2016)
Diaz, A.F., Logan, J.A.: Electroactive polyaniline films. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 111(1), 111–114 (1980)
Shea, J.J., Luo, C.: Organic electrode materials for metal ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 12(5), 5361–5380 (2020)
Larcher, D., Tarascon, J.M.: Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage. Nat. Chem. 7, 19–29 (2015)
Otteny, F., Perner, V., Wassy, D., Kolek, M., Bieker, P., Winter, M., Esser, B.: Poly(vinylphenoxazine) as fast-charging cathode material for organic batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 8(1), 238–247 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges the Knowledge Resource Centre, CSIR-NEERI, (CSIR-NEERI/KRC/2021/DEC/HZC/2) for their support. We are thankful to the KIM-Division (CSIR-IICT) for providing a library. The Communication Number for this chapter is IICT/Pubs./2021/362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Arfin, T., Ranjan, P., Bansod, S., Singh, R., Ahmad, S., Neeti, K. (2022). Organic Electrodes: An Introduction. In: Gupta, R.K. (eds) Organic Electrodes. Engineering Materials. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98021-4_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98021-4_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-98020-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-98021-4
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)