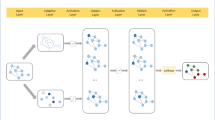
Abstract
The classification of complex networks allows us to compare sets of networks based on their topological characteristics. By being able to compare sets of known networks to unknown ones, we can analyze real-world complex systems such as neural pathways, traffic flow, and social relations. However, most network-classification methods rely on vertex-level measures or they characterize single fixed-structure networks. Also, these approaches can be computationally costly when analyzing a large number of networks, as they need to learn the network embeds. To address these issues, we propose a hand-crafted embedding method called Deep Topological Embedding (DTE) that builds multidimensional and deep embeddings from networks, based on the joint distribution of vertex centrality, that combined represents the global structure of the network. The DTE can be approached as a two or three-dimensional visual representation of complex networks. In this sense, we present a convolutional architecture to classify DTE representations of different topological models. Our method achieves improved classification accuracy compared to related methods when tested on three benchmarks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee, A., Jost, J.: Spectral plot properties: towards a qualitative classification of networks. Netw. Heterogen. Media 3(2), 395 (2008)
Barabási, A.L.: Network Science. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2016)
Barabási, A.L., Albert, R.: Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 286(5439), 509–512 (1999)
Bonacich, P.: Power and centrality: a family of measures. Am. J. Sociol. 92(5), 1170–1182 (1987)
Brandes, U., Fleischer, D.: Centrality measures based on current flow. In: Diekert, V., Durand, B. (eds.) STACS 2005. LNCS, vol. 3404, pp. 533–544. Springer, Heidelberg (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-31856-9_44
Bronstein, M.M., Bruna, J., LeCun, Y., Szlam, A., Vandergheynst, P.: Geometric deep learning: going beyond Euclidean data. IEEE Sig. Process. Mag. 34(4), 18–42 (2017)
Costa, L.F., Rodrigues, F.A., Travieso, G., Villas Boas, P.R.: Characterization of complex networks: a survey of measurements. Adv. Phys. 56(1), 167–242 (2007)
Dorogovtsev, S.N., Mendes, J.F.: Evolution of networks. Adv. Phys. 51(4), 1079–1187 (2002)
Estrada, E., Rodriguez-Velazquez, J.A.: Subgraph centrality in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 71(5), 056103 (2005)
Glorot, X., Bengio, Y.: Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp. 249–256 (2010)
Glorot, X., Bordes, A., Bengio, Y.: Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. In: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp. 315–323 (2011)
Hagberg, A., Swart, P., S Chult, D.: Exploring network structure, dynamics, and function using networkX. Technical report, Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States) (2008)
Kipf, T.N., Welling, M.: Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.02907 (2016)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Lin, M., Chen, Q., Yan, S.: Network in network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.4400 (2013)
Liu, C., Wu, X., Niu, R., Wu, X., Fan, R.: A new SAIR model on complex networks for analysing the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Nonlinear Dyn. 101(3), 1777–1787 (2020)
Machicao, J., Corrêa, E.A., Jr., Miranda, G.H., Amancio, D.R., Bruno, O.M.: Authorship attribution based on Life-Like Network Automata. PLoS ONE 13(3), e0193703 (2018)
Miranda, G.H.B., Machicao, J., Bruno, O.M.: Exploring spatio-temporal dynamics of cellular automata for pattern recognition in networks. Sci. Rep. 6, 37329 (2016)
Najafabadi, M.M., Villanustre, F., Khoshgoftaar, T.M., Seliya, N., Wald, R., Muharemagic, E.: Deep learning applications and challenges in big data analytics. J. Big Data 2(1), 1–21 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-014-0007-7
Oliveira, M., Ribeiro, E., Bastos-Filho, C., Menezes, R.: Spatio-temporal variations in the urban rhythm: the travelling waves of crime. EPJ Data Sci. 7(1), 29 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjds/s13688-018-0158-4
Perozzi, B., Al-Rfou, R., Skiena, S.: DeepWalk: online learning of social representations. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 701–710. ACM (2014)
Ribas, L.C., Machicao, J., Bruno, O.M.: Life-Like Network Automata descriptor based on binary patterns for network classification. Inf. Sci. 515, 156–168 (2020)
Rubinov, M., Sporns, O.: Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 52(3), 1059–1069 (2010)
Scabini, L.F., Condori, R.H., Gonçalves, W.N., Bruno, O.M.: Multilayer complex network descriptors for color-texture characterization. Inf. Sci. 491, 30–47 (2019)
Scabini, L.F., Ribas, L.C., Neiva, M.B., Junior, A.G., Farfán, A.J., Bruno, O.M.: Social interaction layers in complex networks for the dynamical epidemic modeling of COVID-19 in Brazil. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 564, 125498 (2020)
Scarselli, F., Gori, M., Tsoi, A.C., Hagenbuchner, M., Monfardini, G.: The graph neural network model. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 20(1), 61–80 (2008)
Sutskever, I., Martens, J., Dahl, G., Hinton, G.: On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1139–1147 (2013)
Watts, D.J., Strogatz, S.H.: Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 393(6684), 440–442 (1998)
Xin, R., Zhang, J., Shao, Y.: Complex network classification with convolutional neural network. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 25(4), 447–457 (2020)
Acknowledgments
L. Scabini and L. C. Ribas acknowledge support from FAPESP (grants #2019/07811-0, #2021/09163-6, and #2016/23763-8). O. M. Bruno acknowledges support from CNPq (Grant #307897/2018-4) and FAPESP (grants #2014/08026-1 and 2016/18809-9). The authors are also grateful to the NVIDIA GPU Grant Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Scabini, L., Ribas, L., Ribeiro, E., Bruno, O. (2022). Deep Topological Embedding with Convolutional Neural Networks for Complex Network Classification. In: Ribeiro, P., Silva, F., Mendes, J.F., Laureano, R. (eds) Network Science. NetSci-X 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13197. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97240-0_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97240-0_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-97239-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-97240-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)