Abstract
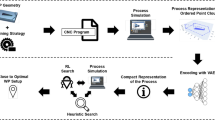
Fine-tuning and optimisation of production processes in manufacturing are often conducted with the help of algorithms from the field of Operations Research (OR) or directly by human experts. Machine Learning (ML) methods demonstrate outstanding results in tackling optimisation tasks within the research field referred to as Neural Combinatorial Optimisation (NCO). This opens multiple opportunities in manufacturing for learning-based optimisation solutions. In this work, we show a successful application of Reinforcement Learning (RL) to the task of workpiece (WP) clamping position and orientation optimisation for milling processes. A carefully selected clamping position and orientation of a WP are essential for minimising machine tool wear and energy consumption. With the example of 3- and 5-axis milling, we demonstrate that a trained RL agent can successfully find a near-optimal orientation and positioning for new, previously unseen WPs. The achieved solution quality is comparable to alternative optimisation solutions relying on Simulated Annealing (SA) and Genetic Algorithms (GA) while requiring orders of magnitude fewer optimisation iterations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhinge, R., et al.: An intelligent machine monitoring system for energy prediction using a Gaussian Process regression. In: Lin, J. (ed.) 2014 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data 2014), pp. 978–986. IEEE, Piscataway (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/BigData.2014.7004331
Brockman, G., et al.: OpenAI Gym (2016). https://arxiv.org/pdf/1606.01540
Campatelli, G., Scippa, A., Lorenzini, L., Sato, R.: Optimal workpiece orientation to reduce the energy consumption of a milling process. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2(1), 5–13 (2015)
Cioffi, R., Travaglioni, M., Piscitelli, G., Petrillo, A., de Felice, F.: Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications in smart production: progress, trends, and directions. Sustainability 12(2), 492 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020492
Du Preez, A., Oosthuizen, G.A.: Machine learning in cutting processes as enabler for smart sustainable manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 33, 810–817 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2019.04.102
Gandomi, A.H. (ed.): Metaheuristic Applications in Structures and Infrastructures, 1st edn. Elsevier Insights, Elsevier, London (2013)
Ke, G., et al.: LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree (2017, undefined)
Haarnoja, T., Zhou, A., Abbeel, P., Levine, S.: Soft Actor-Critic: Off-Policy Maximum Entropy Deep Reinforcement Learning with a Stochastic Actor (2018). http://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.01290v2
Hayes, G.: mlrose: Machine Learning, Randomized Optimization and SEarch package for Python (2019). https://github.com/gkhayes/mlrose
Hill, A., et al.: Stable Baselines (2018)
Kothuru, A., Nooka, S.P., Liu, R.: Application of audible sound signals for tool wear monitoring using machine learning techniques in end milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 95, 3797–3808 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1460-1
Merkel, D.: Docker: lightweight linux containers for consistent development and deployment. Linux J. 2014(239), 2 (2014)
Meyes, R., et al.: Interdisciplinary data driven production process analysis for the internet of production. Procedia Manufa. 26, 1065–1076 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2018.07.143
Mitchell, M.: An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms. Complex Adaptive Systems. MIT, Cambridge and London (1996)
Nti, I.K., Adekoya, A.F., Weyori, B.A., Nyarko-Boateng, O.: Applications of artificial intelligence in engineering and manufacturing: a systematic review. J. Intell. Manuf. 1–21 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-021-01771-6
Pol, S., Baer, S., Turner, D., Samsonov, V., Meisen, T.: Global reward design for cooperative agents to achieve flexible production control under real-time constraints. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems. SCITEPRESS - Science and Technology Publications (2021). https://doi.org/10.5220/0010455805150526
Rangarajan, A., Dornfeld, D.: Efficient tool paths and part orientation for face milling. CIRP Ann. 53(1), 73–76 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60648-9
Samsonov, V., Enslin, C., Köpken, H.G., Baer, S., Lütticke, D.: Using reinforcement learning for optimization of a workpiece clamping position in a machine tool. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pp. 506–514. SCITEPRESS - Science and Technology Publications (2020). https://doi.org/10.5220/0009354105060514
Serin, G., Sener, B., Ozbayoglu, A.M., Unver, H.O.: Review of tool condition monitoring in machining and opportunities for deep learning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 109(3–4), 953–974 (2020)
van Laarhoven, P.J.M., Aarts, E.H.L.: Simulated annealing. In: van Laarhoven, P.J.M., Aarts, E.H.L. (eds.) Simulated Annealing: Theory and Applications, pp. 7–15. Springer, Dordrecht (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-7744-1_2
Wang, J., Yan, J., Li, C., Gao, R.X., Zhao, R.: Deep heterogeneous GRU model for predictive analytics in smart manufacturing: application to tool wear prediction. Comput. Ind. 111, 1–14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2019.06.001
Wu, D., Jennings, C., Terpenny, J., Gao, R.X., Kumara, S.: A comparative study on machine learning algorithms for smart manufacturing: tool wear prediction using random forests. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 139(7) (2017). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4036350
Xanthopoulos, A.S., Kiatipis, A., Koulouriotis, D.E., Stieger, S.: Reinforcement learning-based and parametric production-maintenance control policies for a deteriorating manufacturing system. IEEE Access 6, 576–588 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2771827
Yuan, X., Li, L., Wang, Y., Yang, C., Gui, W.: Deep learning for quality prediction of nonlinear dynamic processes with variable attention-based long short-term memory network. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 98(6), 1377–1389 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.23665
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Enslin, C., Samsonov, V., Köpken, HG., Bär, S., Lütticke, D. (2022). Optimisation of a Workpiece Clamping Position with Reinforcement Learning for Complex Milling Applications. In: Nicosia, G., et al. Machine Learning, Optimization, and Data Science. LOD 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13164. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95470-3_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95470-3_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-95469-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-95470-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)